Abstract
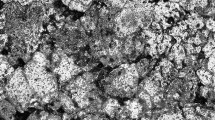
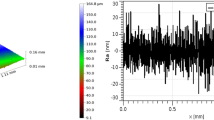
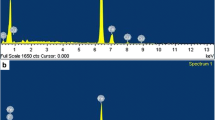
Iron-based alloys are materials of choice for engineering applications such as bearings and gears owing to their low cost, ease of manufacture, high strength, availability, and good wear resistance and low coefficient of friction. In this study, Fe–Cu–Sn composite containing varying percentage of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) is developed using simple single stage compaction and sintering. The friction and wear behaviors of these composites were studied ball-on-disc tribometer in which EN8 steel ball was used. It was found that with the increase in percentage of MoS2 from 0 to 3 wt% the coefficient of friction and wear rate substantially decreases from around 0.85 to 0.25. The wear mechanism in base composition (0% MoS2) is observed to be adhesive and abrasive, whereas mild abrasive wear was observed in the 3 wt% MoS2 composite. The hardness of composite was also found to improve with the increase in MoS2 weight fraction.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MoS2 :
-
molybdenum di sulfide
- PM:
-
powder metallurgy
- Wv :
-
wear volume
- Kw :
-
wear coefficient
- Sd :
-
sliding distance
- COF:
-
coefficient of friction
References
Teisanu G and Gheorghe S 2011 Development of new PM iron-based materials for self-lubricating bearings. Adv Tribol. 248037
de Mello J D B, Binder C, Hammes G and Klein A N 2013 Effect of the metallic matrix on the sliding wear of plasma assisted debinded and sintered MIM self-lubricating steel. Wear 301: 648–655
De H I M, Mello J D B, Binder R and Klein A N 2001 Effect of compaction pressure and powder grade on microstructure and hardness of steam oxidised sintered iron, Powder Metall. 441: 53–61
Lim S C and Brunton J H (1986) The unlubricated wear of iron. Wear 113: 371–382
Ahn H S, Kim J Y and Lim D S (1997) Tribological behavior of plasma-sprayed zirconia. Wear 203: 77–87
Sudhakar K V, Sampathkumaran P and Dwarakadasa E S 2000 Dry sliding wear in high-density Fe–2%Ni based P/M alloys. Wear 7: 202–242
Zuomin L and Childs T H 2004 The study of wear characteristics of sintered high-speed steels containing CaF2, MnS, TiC additives at elevated temperature. Wear 40: 257
Seraji H R, Khorsand H, Habibi S M, Yoozabashizadea H, Janghorban K and Reihani S M S 2002 The role of heat treatment on wear behavior of powder metallurgy low alloy steels. Mater Des. 23: 67–70
Candela N, Plaza R, Rosso M, Velasco F and Torralba J M 2001 Radial crushing strength and microstructure of molybdenum alloyed sintered steels. J Met Process Technol. 119: 7–13
Rapoport L, Feldman Y et al 1999 Inorganic fullerene-like material as additives to lubricants: structure-function relationship. Wear 972: 225–229
Velasco F, Gordo E, Isabel R, Ruiz Navas E M and Bautista A 2001 Mechanical and wear behavior of high-speed steels reinforced with TiCN particles. Int J Refract Meter Hard Mater 19: 319
Annamalai R, Upadhyaya A and Agrawal D 2013 An investigation on microwave sintering of Fe, Fe–Cu and Fe–Cu–C alloys. Bull Mater Sci. 36: 447–456
Shuhaib S and Wani M F 2017 Self-lubricating tribological characterization of lead-free Fe-Cu based plain bearing material. J Tribol. 12: 18–37
Miyoshi K 2001 Solid lubrication fundamentals and applications. Taylor & Francis, p. 9
Busch C, Dresel W and Mang T 2007 Solid lubricants and lubrication, 2nd ed. Wiley-Vch, pp. 231–235
Lansdown A 1999 MoS2 lubrication. Cambridge: Elsevier, p. 7.4
Sustarsic B, Kosec L, Jenko M and Leskovsek 2001 Vacuum sintering of water-atomized HSS powders with MoS2 additions. Vacuum. 61: 471–477
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mushtaq, S., Wani, M.F., Nadeem, M. et al. A study on friction and wear characteristics of Fe–Cu–Sn alloy with MoS2 as solid lubricant under dry conditions. Sādhanā 44, 240 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-019-1208-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-019-1208-8