Abstract
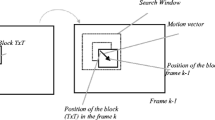
This paper presents a fast block matching motion esti mation algorithm and its architecture. The proposed architecture is based on Global Elimination (GE) Algorithm, which uses pixel averaging to reduce complexity of motion search while keeping performance close to that of full search. GE uses a preprocessing stage which can skip unnecessary Sum Absolute Difference (SAD) calculations by comparing minimum SAD with sub-sampled SAD (SSAD). In the second stage SAD is computed at roughly matched candidate positions. GE algorithm uses fixed sub-block sizes and shapes to compute SSAD values in preprocessing stage. Complexity of this GE algorithm is further reduced by adaptively changing the sub-block sizes depending on the macro-block features. In this paper adaptive Global Elimination algorithm has been implemented which reduces the computational complexity of motion estimation algorithm and thus resulted in low power dissipation. Proposed architecture achieved 60% less number of computations compared to existing full search architecture and 50% high throughput compared to existing fixed Global Elimination Architecture.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jong-Nam Kim and Tae-Sun Choi 1998 A fast three-step search algorithm with minimum checking points using unimodal error surface assumption. IEEE Trans. Consumer Electron. 44(3): 638–648
Lai-Man Po and Wing-Chung Ma 1996 A novel four-step search algorithm for fast block motion estimation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 6(3): 313–317
Zhu C, Xiao Lin and Lap-Pui Chau 2002 Hexagon-based search pattern for fast block motion estimation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 12(5): 349–355
Chan Y L and Siu W C 1996 New adaptive pixel decimation for block motion vector estimation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 6(1): 113–118
Li W and Salari E 1995 Successive elimination algorithm for motion estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 4(1): 105–107
Gao X Q, Duanmu C J and Zou C R 2000 A multilevel successive elimination algorithm for block matching motion estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 9(3): 501–504
Yu-Wen Huang, Shao-Yi Chien, Bing-Yu Hsieh and Liang-Gee Chen 2004a Global elimination algorithm and architecture design for fast block matching motion estimation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 14(6): 898–907
Fan C -P and Lin S -W 2007 fast global elimination algorithm and lowcost VLSI design for motion estimation. TENCON 2007–2007 IEEE Region 10 Conference, November, pp 1–4
Huang Y -W, Tsai C -H and Chen L -G 2004b Parallel global elimination algorithm and architecture design for fast block matching motion estimation. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 2004. Proceedings. (ICASSP ’04) vol 5, pp. V -153–156
Griselda Saldaha and Miguel Arias-Estrada 2007 Compact fpga based systolic array architecture for architecture motion estimation using full search block matching algorithm. Programmable logic, 2007. SPL’07.2007 3 rd Southern conference
Li Man Ho 2006 Variable block size motion estimation hardware for video encoders. (Master of Philosophy thesis) the Chinese University of Hong Kong
Sinan Yalcin, Hasan F Ates and Ilker HAmzoglu 2005 A high performance hardware architecture for a sad reuse based heirarchial motion estimation algorithm for H.264 video coding. Field programmable logic and applications 2005
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MURALIDHAR, P., RAMARAO, C.B. Efficient architecture for global elimination algorithm for H.264 motion estimation. Sadhana 41, 47–54 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-015-0455-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-015-0455-6