Abstract
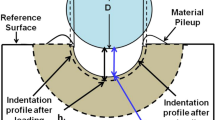
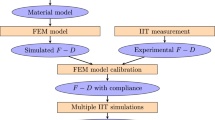
A combined mechanical property evaluation methodology with ABI (Automated Ball Indentation) simulation and Artificial Neural Network (ANN) analysis is evolved to evaluate the mechanical properties for Carbon Manganese Steel (SA-333 Grade-6) and Stainless Steel (SS-304LN). The experimental load deflection data is converted into meaningful mechanical properties for these materials and their evaluated property is verified with experimental tensile specimen results. An ANN database is generated with the help of contact type finite element analysis by numerically simulating the ABI process for various magnitudes of yield strength (σ yp ) (200 MPa–400 MPa) with a range of strain hardening exponent (n) (0.05–0.5) and strength coefficient (K) (600 MPa–1600 MPa). For the present problem, a ball indenter of 1.57 mm diameter having Young’s modulus higher than test piece is used to minimize the error due to indenter deformation. Test piece dimension is kept large enough in comparison to the indenter configuration in the simulation to minimize the deflection at the outer edge of the test piece. Further, this database after the neural network training; is used to analyse measured material properties of different test pieces. The ANN predictions are reconfirmed with contact type finite element analysis for an arbitrary selected test sample. The methodology evolved in this work can be extended to predict material properties for any irradiated nuclear material in the service. Extensions of the ABI tests and the associated database analysis could lead to evaluation of the indentation energy to fracture needed for the structural integrity assessment of aged components.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Byan T S, Kim J W, Hong J H 1998 A theoretical model for determination of fracture toughness of reactor pressure vessel steels in the transition region from automated ball Indentation test. J. Nuclear Materials, 252: 187–194
Haggag F M 1993 In-situ measurements of mechanical properties using novel automated ball indentation system. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia 27–44
Haggag F M, Nanstad R K 1989 Estimation fracture toughness using tension or ball indentation tests and a modified critical strain model. ASME Pressure Vessel and Piping Conference, 170: 41–46.
Lee Y H, Ji W J, Kwon D 2004 Stress measurement of SS400 steel beam using the continuous indentation technique. Experimental Mechanics, 44: 55–61.
Mathew M D, Murthy K L, Lietzan L M, Shah V N 1999 Low temperature aging embitterment of CF-8 stainless steel. Material Science and Engineering A269: 186–196
Meyer E 1908 VDI Zeitschrift, 645: 740–835.
Murthy K L, Mirgania P Q, Mathew M D 1999 Characterization of gradients in mechanical properties of SA-533B steel welds using ball indentation. Int. J. Pressure Vessel and Piping, 76: 361–369
Tabor D 1951 The Hardness of Metals. Oxford Univ. Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SHARMA, K., BHASIN, V., VAZE, K.K. et al. Numerical simulation with finite element and artificial neural network of ball indentation for mechanical property estimation. Sadhana 36, 181–192 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-011-0019-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-011-0019-3