Abstract
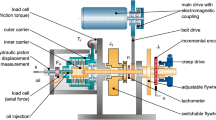
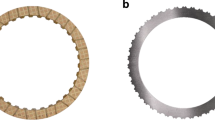
A commercially available sintered friction pad is coupled with a standard gray cast iron pressure plate (FG 250 grade) and tested in a clutch dynamometer for understanding the engagement characteristics and thereby predicting the useful life in number of engagements. Results show that sintered friction pad has a very stable range of friction coefficient (0.43–0.61) even after 5000 engagement cycles. The torque transmitted ranges from 350 to 400N during one engagement cycle. The energy dissipation and mass loss of friction materials linearly increases with increasing sliding distance. A correlation is derived based on energy dissipation and mass loss in terms of total number of useful or available engagements before replacement or repair of friction pad or clutch pressure plate. Both the pressure plate and clutch disc with the sintered friction pad was tested in a 49 tons load capacity vehicle on a test track. Both sintered friction pad and pressure plate showed scoring marks along the sliding direction. Friction pad showed dense cracks along the top edge. Microscopic features of worn sintered friction pads show silica particle providing the required wear resistance for the pads. Pressure plate showed transfer layer of oxides and carbon with less scoring marks due to short duration vehicle level trials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleksandrova A B, Kryachek V M, Levit G B, Rozenshtein D G, Fedorchenko I M, Prikhod″ko L P, Izvekov G V 1972 Effect of sintering conditions on the structure and frictional and wear properties of powder metallurgy friction disks. Powder Metallurgy and Metal Ceramics 11(10): 831–834
Ghorbani M, Mazaheri M and Afshar A 2005 Wear and friction characteristics of electrodeposited graphite-bronze composite coatings. Surface and Coatings Technology 190(1): 32–38
Jorge Alberto, Lewis Esswein Jr, Fabiano Edovirges Arrieche, Lírio Schaeffer 2008 Analysis of Wear in Organic and Sintered Friction Materials Used in SmallWind Energy Converters. Materials Research 11(3): 269–273
Kato Hirotaka 2003 Severe-mild wear transition by supply of oxide particles on sliding surface. International Conference on Wear of Materials 255: 426–429
Khamlichi A, Bezzazi M, Jabbouri A, Reis P, Davim J P 2008 Optimizing friction behaviour of clutch facings using pin-on-disk test. Inter. J. Physical Sci. 3(2): 65–70
Mustafa Boz, Adem Kurt 2007 The effect of Al2O3 on the friction performance of automotive brake friction materials. Tribology International 40(7): 1161–1169
Ost W, De Baets P, Degrieck J 2001 The tribological behaviour of paper friction plates for wet clutch application investigated on SAE II and pin-on-disk test rigs. Wear 249(5–6): 361–371
Peter W Lee 1998 Friction Powder Metallurgy Materials, Powder Metal Technologies and Applications. ASM Handbook, 7: 823–850
Roberto C Dante, Francesco Vannucci, Pietro Durando, Enzo Galetto, Czeslaw K Kajdas 2009 Relationship between wear of friction materials and dissipated power density. Tribology International 42(6): 958–963
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vadiraj, A. Engagement characteristics of a friction pad for commercial vehicle clutch system. Sadhana 35, 585–595 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-010-0042-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-010-0042-9