Abstract
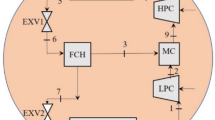
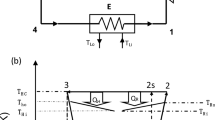
Finite-time exergoeconomic performance of a Newtonian heat transfer law system generalized irreversible combined refrigeration cycle model with finite-rate heat transfer, heat leakage and internal irreversibility is presented in this paper. The operation of the generalized irreversible combined refrigeration cycle is viewed as a production process with exergy as its output. The performance optimization of the cycle is performed by taking profit as the objective. The optimal profit rate, optimal COP (coefficient of performance), as well as the relation between the optimal profit rate and COP of the cycle are derived. The focus of this paper is to obtain the compromise optimization between economics (profit rate) and the energy utilization factor (COP) for the cycle, by searching the optimum COP at maximum profit rate, which is termed as the finite time exergoeconomic performance bound. Moreover, the effects of various factors, including heat leakage, internal irreversibility and the price ratio, on the profit rate performance of the cycle are analysed by detailed numerical examples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andresen B 1983 Finite-Time Thermodynamics, Physics Laboratory II, University of Copenhagen
Bejan A 1988 Theory of heat transfer-irreversible power plant. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 31(6): 1211–1219
Bejan A 1989 Theory of heat transfer-irreversible refrigeration plants. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 32(9): 1631–1639
Bejan A 1993 Power and refrigeration plants for minimum heat exchanger inventory. ASME Trans. J. Energ. Res. Tech. 115(2): 148–150
Bejan A 1996 Entropy generation minimization. The new thermodynamics of finite-size device and finite-time processes. J. Appl. Phys. 79(3): 1191–1218
Berry R S, Salamon P, Heal G 1978 On a relation between economic and thermodynamic optima. Resources and Energy 1(2): 125–137
Berry R S, Kazakov V A, Sieniutycz S, Szwast Z, Tsirlin A M 1999 Thermodynamic Optimization of Finite Time Processes. Chichester: Wiley
Chen J, Yan Z 1988 Optimal performance of an endoreversible-combined refrigeration cycle. J. Appl. Phys. 63(10): 4795–4799
Chen L, Sun F, Chen W 1991 Finite time exergoeconomic performance bound and optimization criteria for two-heat-reservoir refrigerators. Chinese Sci. Bull. 36(2): 156–157 (in Chinese)
Chen L, Sun F, Chen W 1995 Optimization of the specific rate of refrigeration in combined refrigeration cycles. Energy The Int. J. 20(10): 1049–1053
Chen L, Sun F, Wu C 1996 Maximum profit performance of an absorption refrigerator. Int. J. Energ. Environ. and Econom. 4(1): 1–7
Chen L, Wu C, Sun F 1997 Steady flow combined refrigeration cycle performance with heat leak. Appl. Thermal Eng. 17(7): 639–645
Chen L, Wu C, Sun F 1999a Finite time thermodynamic optimization or entropy generation minimization of energy systems. J. Non-Equilib. Thermodyn. 24(4): 327–359
Chen L, Bi Y, Sun F, Wu C 1999b A generalized model of combined refrigeration plant and its performance. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 38(8): 712–718
Chen L, Wu C, Sun F 2001 Effect of heat transfer law on finite time exergoeconomic performance of a Carnot refrigerator. Exergy An Int. J. 1(4): 295–302
Chen L, Sun F 2004 Advances in finite time thermodynamics analysis and optimization. New York: Nova. Science Publishers
Chen L, Sun F, Wu C 2004a Maximum profit performance for generalized irreversible Carnot engines. Appl. Energy 79(1): 15–25
Chen L, Sun F, Wu C 2004b Optimum allocation of heat exchanger area for refrigeration and air conditioning plants. Appl. Energy 77(3): 339–354
Chen L 2005 Finite-Time Thermodynamic Analysis of Irreversible Processes and Cycles. Higher Education Press, Beijing
Chen L, Sun F, Wu C 2005 Endoreversible thermoeconomics for heat engines. Appl. Energy 81(4): 388–396
De Vos A 1995 Endoreversible thermoeconomics. Energ. Convers. and Manage. 36(1): 1–5
De Vos A 1997 Endoreversible economics. Energ. Convers. and Manage. 38(4): 311–317
Durmayaz A, Sogut O S, Sahin B, Yavuz H 2004 Optimization of thermal systems based on finite-time thermodynamics and thermoeconomics. Progress on Energy & Combustion Science 30(2): 175–217
El-Sayed M 2003 The Thermoeconomics of Energy Conversion. London: Elsevier
Goktun S 1996 Coefficient of performance for an irreversible combined refrigeration cycle. Energy The Int. J. 21(7/8): 721–724
Ibrahim OM, Klein S A, Mitchell JW 1992 Effects of irreversibility and economics on the performance of a heat engine. ASME Trans. J. Sol. Energy Engng. 114(4): 267–271
Kodal A, Sahin B, Yilmaz T 2000a Effects of internal irreversibility and heat leakage on the finite time thermoeconomic performance of refrigerators and heat pumps. Energ. Convers. and Manage. 41(6): 607–619
Kodal A, Sahin B, Oktem A S 2000b Performance analysis of two stage combined heat pump system based on thermoeconomic optimization criterion. Energ. Convers. and Manage. 41(18): 1989–2008
Kodal A, Sahin B, Erdil A 2002 Performance analysis of a two-stage irreversible heat pump under maximum heating load per unit total cost conditions. Int. J. Exergy 2(3): 159–166
Kodal A, Sahin B, Ekmekci I, Yilmaz T 2003 Thermoeconomic optimization for irreversible absorption refrigerators and heat pumps. Energ. Convers. and Manage. 44(1): 109–123
Kodal A, Sahin B 2003 Finite time thermoeconomic optimization for irreversible heat engines. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 42(8): 777–782
Qin X, Chen L, Sun F, Wu C 2005 Thermoeconomic optimization of an endoreversible four-heat-reservoir absorption-refrigerator. Appl. Energy 81(4): 420–433
Sahin B, Kodal A 1999 Finite time thermoeconomic optimization for endoreversible refrigerators and heat pumps. Energ. Convers. and Manage. 40(9): 951–960
Sahin B, Kodal A, Koyun A 2001 Optimal performance characteristics of a two-stage irreversible combined refrigeration system under maximum cooling load per unit total cost conditions. Energ. Convers. and Manage. 42(4): 451–465
Sahin B, Kodal A 2001 Performance analysis of an endoreversible heat engine based on a new thermoeconomic optimization criterion. Energ. Convers. and Manage. 42(9): 1085–1093
Sahin B, Kodal A 2002 Thermoeconomic optimization a two-stage combined refrigeration system: A finite time approach. Int. J. Refrig. 25(7): 872–877
Salamon P, Nitzan A 1981 Finite time optimizations of a Newton’s law Carnot cycle. J. Chem. Phys. 74(6): 3546–3560
Sieniutycz S, Salamon P 1990 Advances in Thermodynamics, Volume 4: Finite Time Thermodynamics and Thermoeconomics. New York: Taylor & Francis
Tsatsaronts G 1993 Thermoeconomic analysis and optimization of energy systems. Progress on Energy and Combustion Science 19(3): 227–257
Wu C, Chen L, Sun F 1996 Effect of heat transfer law on finite time exergoeconomic performance of heat engines. Energy The Int. J. 21(12): 1127–1134
Wu C, Chen L, Sun F 1998 Effect of heat transfer law on finite time exergoeconomic performance of a Carnot heat pump. Energ. Convers. and Manage. 39(7): 579–588
Wu F, Chen L, Sun F, Wu C 2000 Finite-time exergoeconomic performance bound for a quantum Stirling engine. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 38(2): 239–247
Zheng Z, Chen L, Sun F, Wu C 2006 Maximum profit performance for a class of universal steady flow endoreversible heat engine cycles. Int. J. Ambient Energy 27(1): 29–36
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, K., Chen, L. & Sun, F. Profit rate performance optimization for a generalized irreversible combined refrigeration cycle. Sadhana 34, 851–864 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-009-0050-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-009-0050-9