Abstract
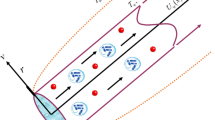
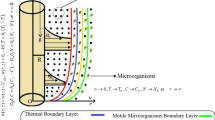
This study focusses on the heat and mass transfer and micro-organisms of the bioconvectional nanofluidic flow in the presence of activation energy. A mathematical model for the bioconvection has been incorporated with the existing nanofluid model past a stretching cylinder for which limited research works are present. The system of partial differential equations has been converted into ordinary differential equation by using suitable similarity transformation, and furthermore is solved by applying spectral quasilinearisation method, a newly developed numerical scheme. The obtained results are depicted graphically and analysed. Some observations regarding Brownian motion, thermal radiation, etc. are also seen in past research works, but explanation of these observations is provided in this study. Furthermore, we have reported some unprecedented behaviours of temperature and solute, microbe concentration as our conclusion, the explanation of which will be regarded as our future scope of research.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
S U Choi and J A Eastman, Argonne National Lab (1995)
K Kumar, Facta Universit. 20, 503 (2022)
J H He, N S Elgazery, K Elagamy and N Y Abd Elazem, J. Appl. Comput. Mech. 9, 848 (2023)
J H He and N Y Abd Elazem, Facta Universit. 20, 211 (2022)
H Zhang, A Nikolov and D Wasan, Langmuir 30, 9430 (2014)
S J Kou, C H He, X C Men and J H He, Fractals 30, 1 (2022)
R R Yang, J H He, J Y Yu and L Xu, Int. J. Nonlin. Sci. Numer. Simul. 11, 163 (2010)
Y Li and J H He, Adsorp. Sci. Technol. 37, 425 (2019)
P Sibanda, M Almakki, Z Mburu and H Mondal, Appl. Sci. 12, 108 (2022)
J Buongiorno, J. Heat Transfer 128, 240 (2006)
H Mondal and S Bharti, J. Appl. Comput. Mech. 6, 1058 (2020)
I Waini, A Ishak and I Pop, Mathematics 8, 612 (2020)
Q Nguyen, D Bahrami, R Kalbasi and Q V Bach, Math. Meth. Appl. Sci. (2020), https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.6705
F Haq, M Saleem and M Rahman, Phys. Scr. 95, 105 (2020)
J R Platt, Science 133, 1766 (1961)
A V Kuznetsov, Eur. J. Mech.-B\(/\)Fluids 30, 156 (2011)
S Ahmad, M Ashraf and K Ali, J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 13, 1539 (2020)
S Nadeem, A Alblawi, N Muhammad, IM Alarifi, A Issakhov and M T Mustafa, J. Mol. Liq. 298, 112033 (2020)
E Elanchezhian, R Nirmalkumar, M Balamurugan, K Mohana, K M Prabu and A Viloria, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 141, 2613 (2020)
M M Bhatti, M Marin, A Zeeshan, R Ellahi and S I Abdelsalam, Front. Phys. 8, 95 (2020)
A Shafiq, G Rasool, CM Khalique and S Aslam, Symmetry 12, 621 (2020)
Q H Shi, A Hamid, M I Khan, R N Kumar, R J P Gowda, B C Prasannakumara, N A Shah, S U Khan and J D Chung, Sci. Rep. 11, 1 (2021)
Y M Chu, M I Khan, N B Khan, S Kadry, S U Khan, I Tlili and M K Nayak, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 118, 104893 (2020)
A Abbasi, F Mabood, W Farooq and M Batool, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transfer 119, 104921 (2020)
U Farooq, S Munir, F Malik, B Ahmad and D Lu,AIP Adv. 10, 075110 (2020)
K Hosseinzadeh, S Roghani, A R Mogharrebi, A Asadi, M Waqas and D D Ganji, Alex. Eng. J. 59, 3297 (2020)
A A Khan, A Arshad, R Ellahi and S M Sait, Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 33, 135 (2023)
T Muhammad, S Z Alamri, H Waqas, D Habib and R Ellahi, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 143, 945 (2021)
A Majeed, A Zeeshan, S Z Alamri and R Ellahi, Neural Comput. Appl. 30, 1947 (2018)
M Dhlamini, H Mondal, P Sibanda, S S Mosta and S Shaw, Pramana – J. Phys. 96, 1 (2022)
C H He and Y O El-Dib, J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 41, 572 (2022)
N Anjum, J H He, Q T Ain and D Tian, Facta Universit. 19, 601 (2021)
Q P Ji, J Wang, L X Lu and C F Ge, J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control 40, 675 (2021)
C H He and C Liu, Fractals 30, 1 (2022)
A Samanta and H Mondal, Heat Transfer 51, 7773 (2022)
H Waqas, U Farooq, Z Shah, P Kumam and M Shutaywi, Sci. Rep. 11, 1 (2021)
L A Cameron, P A Giardini, F S Soo and J A Theriot, Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 1, 110 (2000)
P Rana and R Bhargava, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 17, 212 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samanta, A., Mondal, H. Numerical simulation of bioconvectional nanofluidic flow in the presence of activation energy past a stretching cylinder subject to swimming micro-organisms. Pramana - J Phys 97, 182 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-023-02644-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-023-02644-8
Keywords
- Bioconvection
- stretching cylinder
- spectral quasilinearisation method
- brownian motion
- curvature parameter
- thermal radiation