Abstract
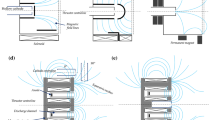
A hollow cathode source is designed to generate multiple double layer (MDL) structures by the trapping of charged particles in the absence of any auxiliary plasma source or magnetic field, while the glow discharge switches between two distinctly different stable regimes. The generation and dynamics of localised and intensely luminous MDL formations are experimentally investigated in low-frequency sheath oscillation inhibited glow discharge by modified Langmuir probes in a linear vacuum vessel. The localised complex structures grow axially into visibly glowing coaxial formations along with structural changes in MDL formations, on increasing the applied voltage in nitrogen plasma at 0.1 mbar pressure. The discharge gradually expands to fill up the entire vessel through redistribution of energetic charged particles and formation of multiple sheaths on increasing the applied voltage across the electrodes. The present experimental study reveals interesting information about the formation of the sheath, stability of the plasma sheath and charged particle dynamics during the discharge transformations. The paper relates the plasma parameter variations with the nonlinear time series analysis of the discharge current and floating potential fluctuations through the reconstructed phase space in different discharge domains to analyse the dynamics of MDL formations and harmonic generation through sheath oscillations during the hollow cathode discharge regimes. The radial motion of the charged particles during the glow discharge between the semi-transparent gridded cylindrical cathode and the central anode might be useful for a better understanding of the underlying basic sheath physics related to particle acceleration in plasma as well as application in plasma sputtering.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
R L Stenzel, C Ionita and R Schrittwieser, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 17, 035006 (2008)
N Hershkowitz, Space Sci Rev. 41(3), 351(1985)
S Chakraborty, M K Paul, J N Roy and A Nath, Phys. Plasmas 25, 033518 (2018)
T Gyergyek, M Čerček, R Schrittwieser and C Ionita, Contrib. Plasma Phys. 42(5), 508 (2002)
R L Stenzel and J M Urrutia, Phys. Plasmas 19, 082105 (2012)
R L Stenzel and J M Urrutia, Phys. Plasmas 19, 082107 (2012)
C Ionita, D G Dimitriu and R W Schrittwieser, Int. J. Mass Spectrometry 233, 343 (2004)
J C Johnson, N D’Angelo and R L Merlino, J. Phys. D 23, 682 (1990)
R Armstrong and R Schrittwieser, Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 33(12), 1407 (1991)
M C Griskey and R L Stenzel, Phys. Rev. Lett. 82, 556 (1999)
I B Bernstein, J M Greene and M D Kruska, Phys. Rev. 108, 546 (1957)
Y Choueiri, Sci. Am. 300, 58 (2009)
E V Sysoeva, F da Silva, E Z Gusakov, S Heuraux and A Yu Popov, Nucl. Fusion 55, 033016 (2015)
D A Uzdensky and S Rightley, Rep. Prog. Phys. 77, 036902 (2014)
R L Stenzel, J M Urrutia, C T Teodorescu-Soare, C Ionita and R Schrittwieser, Phys. Plasmas 20, 083503 (2013)
T Furukawa, K Takizawa, D Kuwahara and S Shinohara, AIP Adv. 7, 115204 (2017)
J Musil, S Kadlec and W D Münz, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 9(3), 1171 (1991)
C H K Chen, J. Plasma Phys. 82(6), 535820602 (2016)
R L Stenzel and J M Urrutia, Phys. Plasmas 19, 082108 (2012)
R L Stenzel, J Gruenwald, B Fonda, C Ionita and R Schrittwieser, Phys. Plasmas 18, 012105 (2011)
R L Stenzel, J Gruenwald, C Ionita and R Schrittwieser, Phys. Plasmas 18, 062112 (2011)
R L Stenzel, J Gruenwald, C Ionita and R Schrittwieser, Plasma Source. Sci. Technol. 20, 045017 (2011)
C T Teodorescu-Soare, D G Dimitriu, C Ionita and R W Schrittwieser, Phys. Scr. 91, 034002 (2016)
S Chauhan, M Ranjan, M Bandyopadhyay and S Mukherjee, Phys. Plasmas 23, 123524 (2016)
S Chauhan, M Ranjan, M Bandyopadhyay and S Mukherjee, Phys. Plasmas 23, 013502 (2016)
E Ahedo, Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 53(12), 124037 (2011)
M K Paul, S Chakraborty and Subhojit Bose, Phys. Plasmas 26, 023516 (2019)
I D Sudit and F F Chen, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 3, 162 (1998)
M K Paul and D Bora, Pramana – J. Phys. 71, 117 (2008)
R Schrittwieser, C Ionită, P C Balan, C A F Varandas, H F C Figueiredo, J Stöckel, J Adámek, M Hron, J Ryszawy, M Tichý, E Martines, G Van Oost, T Klinger and R Madani, Rom. J. Phys. 50(7–8), 723 (2005)
V A Godyak and B M Alexandrovich, J. Appl. Phys. 118, 233302 (2015)
L Conde, C F Fontan and J Lambas, Phys. Plasmas 13, 113504 (2006)
M K Paul, P K Sharma, A Thakur, S V Kulkarni and D Bora, Phys. Plasmas 21, 062112 (2014)
M K Paul, A Lyssoivan, R Koch, G Van Wassenhove, M Vervier, G Bertschinger, R Laengner, B Unterberg, G Sergienko, V Philipps, T Wauters and The TEXTOR Team, Pramana – J. Phys. 80(1): 121 (2013)
M K Paul and S Chakraborty, Phys. Plasmas 27, 014704 (2020)
V A Godyak, R B Piejak and M Alexandrovich, Plasma Source Sci. Technol. 1, 36 (1992)
M J Druyvesteyn, Z. Phys. 64, 781 (1930)
M Megalingam, B Sarma, V Mitra, N Hari Prakash and Arun Sarma, Phys. Plasmas 23, 072102 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the SERB-DST, Government of India (Sanction No. SERB/F/3963/2015-16) under the Extra Mural Research (EMR) scheme and (Sanction No. SR/FST/PSI-196/2014) under the FIST programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bose, S., Chakraborty, S., Nath, A. et al. On multiple complex structure formations in expanding hollow cathode discharge. Pramana - J Phys 95, 186 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-021-02223-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-021-02223-9