Abstract
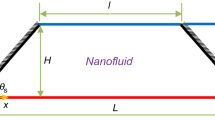
Second law analysis of copper–water nanofluid flow in an inclined channel filled with a porous medium having variable permeability is presented in the literature. Hydrodynamic slip and convective boundary conditions are assumed for the flow. Nanoparticles of different shapes are considered, namely, platelet, blade, cylinder and brick. The permeability of the porous medium is assumed to decrease exponentially across the width of the channel. The highly non-linear governing equations are solved using the homotopy analysis method and verified with a closed form solution for a reduced equation. Moreover, comparisons with the existing literature are presented, the results of which were found to be in excellent agreement. Impact of pertinent flow parameters influencing the flow on entropy generation, Bejan number, Nusselt number, skin friction and volume flow rate are discussed and supplemented with graphs. Platelet-shaped nanoparticles have generated the least amount of entropy in the study. The impact of channel inclination angle on skin friction was observed to be highly significant in the analysis.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
S Choi and J Eastman, ASME Int. Mech. Eng. Congr. Expo. 66, 99 (1995)
S K Das, S U S Choi and H E Patel, Heat Transf. Eng. 27(10), 3 (2006)
X Q Wang and A S Mujumdar, Int. J. Therm. Sci. 46(1), 1 (2007)
D Wen, G Lin, S Vafaei and K Zhang, Particuology 7(2), 141 (2009)
R Saidur, K Y Leong and H A Mohammad, Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 15(3), 1646 (2011)
R L Hamilton and O K Crosser, Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1, 187 (1962)
E V Timofeeva, J L Routbort and D Singh, J. Appl. Phys. 106(1), (2009)
E H Ooi and V Popov, Int. J. Therm. Sci. 65, 178 (2013)
F Selimefendigil and H F Öztop, J. Mol. Liq. 212, 509 (2015)
Y Lin, B Li, L Zheng and G Chen, Powder Technol. 301, 379 (2016)
I Khan, J. Mol. Liq. 233, 442 (2017)
M Sheikholeslami and S A Shehzad, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 115, 180 (2017)
M Sheikholeslami and M Shamlooei, Phys. Lett. Sect. A Gen. At. Solid State Phys. 381(36), 3071 (2017)
U Khan, Adnan, N Ahmed and S T Mohyud-Din, Eur. Phys. J. Plus 132(4), 166 (2017)
M Hamid, M Usman, T Zubair, R U Haq and W Wang, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 124, 706 (2018)
M Sheikholeslami, M Shamlooei and R Moradi, Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 124, 71 (2018)
A Shakiba and A B Rahimi, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 138, 501 (2019)
M S Mahmoud and H Deresiewicz, Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 4(1), 57 (1980)
I A Hassanien, Appl. Math. Comput. 138(1), 41 (2003)
R C Chaudhary and P K Sharma, J. Zhejiang Univ. A 4, 181 (2003)
I A Hassanien, A A Salama and A M Elaiw, Appl. Math. Comput. 154(2), 313 (2004)
M A Mansour and N A El-Shaer, Transp. Porous Media 57(3), 333 (2004)
A M Elaiw, F S Ibrahim and A A Bakr, ZAMM 87, 528 (2007)
P K Gaur, A K Jha and R Sharma, Int. J. Appl. Mech. Eng. 21(2), 323 (2016)
I Siddique and I A Mirza, Results Phys. 7, 3928 (2017)
A Bejan, J. Heat Transfer 101(4), 718 (1979)
J Li and C Kleinstreuer, J. Heat Transfer 132(12), 122401 (2010)
C K Chen, B S Chen and C C Liu, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 79, 750 (2014)
G Ibáñez, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 80, 274 (2015)
R Ellahi, M Hassan and A Zeeshan, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 81, 449 (2015)
A Zeeshan, M Hassan, R Ellahi and M Nawaz, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part E J. Process Mech. Eng. 231, 871 (2017)
A A A A Al-Rashed, R Ranjbarzadeh, S Aghakhani, M Soltanimehr, M Afrand and T K Nguyen, Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 521, 724 (2019)
D S Bondarenko, M A Sheremet, H F Öztop and M E Ali, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 136(2), 673 (2019)
X Shi, P Jaryani, A Amiri, A Rahimi and E H Malekshah, Powder Technol. 346, 160 (2019)
S Liao, Beyond Perturbation: Introduction to the homotopy analysis method (Chapman and Hall\(/\)CRC, 2003)
R K Tiwari and M K Das, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 50, 2002 (2007)
W Aung and G Worku, J. Heat Transfer 108, 485 (1986)
S Liao, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 15(8), 2003 (2010)
A Barletta, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 41(22), 3501 (1998)
E Zanchini, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 41(23), 3949 (1998)
Acknowledgements
The researchers thank TEQIP-III, NIT Mizoram, for the financial support provided to Mr Lalrinpuia Tlau for his PhD work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tlau, L., Ontela, S. Effect of shape of nanoparticles on mixed convection nanofluid flow in a porous medium with variable permeability: Analysis of the second law of thermodynamics. Pramana - J Phys 95, 188 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-021-02221-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-021-02221-x