Abstract
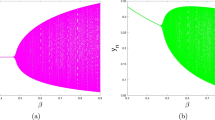
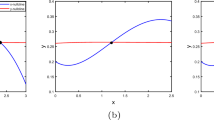
We consider the simplest model in the family of discrete predator–prey system and introduce for the first time an environmental factor in the evolution of the system by periodically modulating the natural death rate of the predator. We show that with the introduction of environmental modulation, the bifurcation structure becomes much more complex with bubble structure and inverse period doubling bifurcation. The model also displays the peculiar phenomenon of coexistence of multiple limit cycles in the domain of attraction for a given parameter value that combine and finally gets transformed into a single strange attractor as the control parameter is increased. To identify the chaotic regime in the parameter plane of the model, we apply the recently proposed scheme based on the correlation dimension analysis. We show that the environmental modulation is more favourable for the stable coexistence of the predator and the prey as the regions of fixed point and limit cycle in the parameter plane increase at the expense of chaotic domain.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
A J Lotka, Elements of physical biology (Williams and Wilkins, USA, 1925)
V Volterra, Mem. Acad. Lincei. 2, 31 (1926)
R M May, J. Theor. Biol. 51(2), 511 (1975)
R M May, Nature 261, 459 (1976)
Y A Kuznetzov, S Muratori and S Rinaldi, Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2, 117 (1992)
R R Dodd, J. Math. Biol. 35, 432 (1997)
S Krise and S R Choudhury, Chaos Solitons Fractals 16, 59 (2003)
X P Yan and Y D Chu, J. Comp. Appl. Math. 196, 198 (2006)
X Liu and L Chen, Chaos Solitons Fractals 16, 311 (2003)
H I Freedman, Deterministic mathematical models in population ecology (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1980)
J D Murray, Mathematical biology (Springer, New York, 1993)
F Brauer and C Chavez, Mathematical models in population biology and epidemology (Springer, New York, 2001)
D R Robertson, C W Peterson and J D Brawn, Ecol. Monograph 60, 311 (1990)
W M Schaffer, Amer. Nat. 124, 798 (1984)
E Gutierrez and H Almiral, Bull. Math. Biol. 51, 785 (1989)
A A Berryman, Ecology 73, 694 (1992)
A A Berryman, J. Animal Ecol. 64, 290 (1995)
H Tonnang, L V Nedorezov and J Owino, Agri. Forest Entomol. 12(3), 233 (2010)
H C J Godfray and P S Blythe, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. London B 330, 221 (1990)
N D Kazarinoff and P Driessche, Math. Biosci. 39, 125 (1978)
S Ruan and D Xiao, SIAM J. Appl. Math. 61, 1445 (2001)
G S K Walkowicz, SIAM J. Appl. Math. 48, 592 (1988)
P P Saratchandran, K C Ajithprasad and K P Harikrishnan, Ecol. Complexity 21, 112 (2015)
K P Harikrishnan, R Misra, G Ambika and A K Kembhavi, Physica D 215, 137 (2006)
K P Harikrishnan, G Ambika and R Misra, Mod. Phys. Lett. B 21, 129 (2007)
R Misra, K P Harikrishnan, G Ambika and A K Kembhavi, Astrophys. J. 643, 1114 (2006)
P Grassberger and I Proccacia, Phys. Rev. Lett. 50, 346 (1983)
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledges the hospitality and computing facilities in IUCAA, Pune.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harikrishnan, K.P. Complex bifurcation patterns in a discrete predator–prey model with periodic environmental modulation. Pramana - J Phys 90, 24 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-017-1516-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-017-1516-7