Abstract
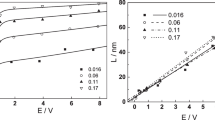
Anodization and subsequent cathodic reactions on a thin-film sample of Zr were studied with in-situ neutron reflectometry (NR) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The NR results during anodization showed the originally 485 Å thick Zr film generally behaved similar to a bulk electrode in neutral solution. The anodization ratio measured at applied potentials increased in steps of 0.5 V was somewhat higher than the value determined by coulometry, while the Pilling Bedworth ratio is in good agreement with published data. Thickening of the oxide layer, accelerated immediately after each potential increase, gradually decreased over several hours, but remained nonzero even after ∼12 h. The thickened oxide eventually cracked when its thickness reached ∼120 Å, causing loss of passivation. Surprisingly, neither the anodization ratio nor the Pilling Bedworth ratio showed any discontinuity at the time of oxide cracking, and the EIS behaviour remained qualitatively as before. This observation is taken as the evidence that the cracked and intact regions of the electrode behave more or less independently as parallel electrodes. When the potential was eventually switched to cathodic polarity, NR shows, as expected, that the effects of oxide cracking were irreversible. However, the electrode resistance recovered partially suggesting the cracks were rapidly plugged with newly formed oxide.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D G Wiesler and C F Majkrzak, Physica B198, 181 (1994)
Z Tun, J J Noël and D W Shoesmith, J. Electrochem. Soc. 146, 988 (1999)
J F Ankner and C F Majkrzak, in Proc. Soc. Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE, Bellingham, WA, 1988) Vol. 1738, p. 260
P Meisterhahn, H W Hoppe and J W Schultze, J. Electroanal. Chem. 217, 159 (1987)
CRC handbook of chemistry and physics, 60th edition, edited by R C Weast (CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton, FL, 1979). Specific gravity for Zr, ZrO2 (zirconia), and ZrO2 (baddeleyite) are 6.49, 5.6, and 5.8 respectively, giving R PB = 1.56 for zirconia and 1.50 for baddeleyite.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tun, Z., Noël, J.J. & Shoesmith, D.W. Anodic oxide growth on Zr in neutral aqueous solution. Pramana - J Phys 71, 769–776 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-008-0192-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-008-0192-z