Abstract
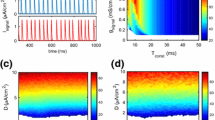
The effect of environmental temperature on neuronal spiking behaviors is investigated by numerically simulating the temperature dependence of spiking threshold of the Hodgkin-Huxley neuron subject to synaptic stimulus. We find that the spiking threshold exhibits a global minimum in a specific temperature range where spike initiation needs weakest synaptic strength, which form the engineering perspective indicates the occurrence of optimal use of synaptic transmission in the nervous system. We further explore the biophysical origin of this phenomenon associated with ion channel gating kinetics and also discuss its possible biological relevance in information processing in neuronal systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M I Rabinovich, P Varona, A I Selverston and H D I Abarbanel, Rev. Mod. Phys. 78, 1213 (2006)
J Feng and H C Tuckwell, Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 018101 (2003)
V A Makarov, V I Nekorkin and M G Velarde, Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 003431 (2001)
A L Hodgkin, A F Huxley and B Katz, J. Physiol. 116, 424 (1952)
J S Schweitzer, H Wang, Z Xiong and J L Stringer, J. Neurophysiol. 84, 927 (2000)
V Y Vasilenko, E M Belyavskii and V N Gurin, Neurophysiol. 21, 259 (1989)
J D Miller, V H Cao and H C Heller, Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 266, 1259 (1994)
H Xu and R M Robertson, J. Comp. Physiol. A175, 193 (1994)
M Radmilovich, A Fernández and O Trujillo-Cenóz, J. Exp. Biol. 206, 3085 (2003)
J W Moore, Fed. Proc. 17, 113 (1958)
X Cao and D Oertel, J. Neurophysiol. 94, 821 (2005)
A L Hodgkin and A F Huxley, J. Physiol. 117, 500 (1952)
F Bezanilla and R E Taylor, Biophys. J. 23, 479 (1978)
Y Zhao and J A Boulant, J. Physiol. 564, 245 (2005)
A L Hodgkin and B Katz, J. Physiol. 108, 37 (1949)
J J C Rosenthal and F Bezanilla, J. Exp. Biol. 205, 1819 (2002)
M Volgushev, T R Vidyasagar, M Chistiakova, T Yousef and U T Eysel, J. Physiol. 522, 59 (2000)
A F Huxley, Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 81, 221 (1959)
F Rieke, D Warland, R R Steveninck and W Bialek, Spikes: Exploring the neural code (MIT Press, 1997), p. 395
A V Holden, Nature (London) 428, 382 (2004)
M J Chacron, B Lindner and A Longtin, Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 080601 (2004)
R VanRullen, R Guyonneau and S J Thorpe, Trends Neurosci. 28, 1 (2005)
R A Sjodin and L J Mullins, J. Gen. Physiol. 42, 39 (1958)
R Guttman and B Sandler, J. Gen. Physiol. 46, 257 (1962)
Y Yu, W Wang, J Wang and F Liu, Phys. Rev. E63, 021907 (2001).
S Kuang, J Wang and T Zeng, Chin. Phys. Lett. 23, 3380 (2006)
R Guttman and R Barnhill, J. Gen. Physiol. 49, 1007 (1966)
R FitzHugh, Biophys. J. 2, 11 (1962)
R FitzHugh, J. Gen. Physiol. 49, 989 (1966)
C Koch, Biophysics of computation: Information processing in single neurons (Oxford University Press, 1999), p. 562
J S Rothman and P B Manis, J. Neurophysiol. 89, 3097 (2003)
T Zeng, J Wang and S Kuang, Influence of temperature on neuronal excitability in cochlear nucleus, submitted to Phys. Lett. A (also available on arXiv:q-bio/0702013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuang, S., Wang, J., Zeng, T. et al. Thermal impact on spiking properties in Hodgkin-Huxley neuron with synaptic stimulus. Pramana - J Phys 70, 183–190 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-008-0016-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-008-0016-1