Abstract
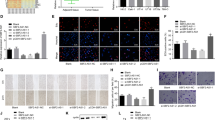
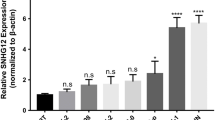
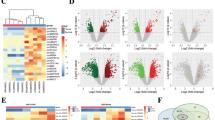
Wilms’ tumour (WT) is the most typical type of renal tumour in children, which has a poor prognosis and high recurrence rate. This study explored whether lncRNA EMX2 opposite strand / antisense RNA (EMX2OS) modulated the stemness, epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis of WT cells through the interaction with insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1). The expression levels of EMX2OS, IGF2BP1 and stem cell markers OCT4, Nanog, Sox2 and CD133 were detected by real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). The stemness, migration and invasion of WT cells were determined by sphere formation assay, scratch and transwell assay, respectively. The levels of EMT-related proteins were detected by Western blotting. RNA pull down and RIP assays were utilized to validate the interaction between EMX2OS and IGF2BP1. The tumourigenicity of WT cells in vivo was analysed using a xenograft tumour assay. EMX2OS was downregulated in WT patients, while IGF2BP1 was upregulated. EMX2OS overexpression or IGF2BP1 knockdown suppressed WT cell sphere formation, migration and invasion. Moreover, EMX2OS could directly interact with RNA-binding protein IGF2BP1, and IGF2BP1 overexpression counteracted the inhibitory effect of EMX2OS on WT cell stemness, migration, invasion and EMT. The in vivo tumour growth, stemness and EMT were repressed by EMX2OS through the interaction with IGF2BP1. In conclusion, EMX2OS acted as a tumour suppressor for WT by interacting with IGF2BP1, which might be a novel target for WT diagnosis and therapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brok J., Pritchard-Jones K., Geller J. I. and Spreafico F. 2017 Review of phase I and II trials for Wilms’ tumour - Can we optimise the search for novel agents? Eur. J. Cancer. 79, 205–213.
Chen Z. H., Cui M. Y. and Zhang H. M. 2022 EMX2OS Delays Wilms’tumour progression via targeting miR-654-3p. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 52, 12–20.
Cone E. B., Dalton S. S., Van Noord M., Tracy E. T., Rice H. E. and Routh J. C. 2016 Biomarkers for Wilms tumour: A systematic review. J. Urol. 196, 1530–1535.
Ding Y., Li Y., Duan Y., Wang W., Zheng W., Cheng W. et al. 2022 LncRNA MBNL1-AS1 represses proliferation and cancer stem-like properties of breast cancer through MBNL1-AS1/ZFP36/CENPA axis. J. Oncol. 2022, 9999343.
Ehrlich P. F. 2007 Wilms tumour: progress and considerations for the surgeon. Surg. Oncol. 16, 157–171.
Elcheva I. A., Wood T., Chiarolanzio K., Chim B., Wong M., Singh V. et al. 2020 RNA-binding protein IGF2BP1 maintains leukemia stem cell properties by regulating HOXB4, MYB, and ALDH1A1. Leukemia 34, 1354–1363.
Gao Y., Ruan B., Liu W., Wang J., Yang X., Zhang Z. et al. 2015 Knockdown of CD44 inhibits the invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma both in vitro and in vivo by reversing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 6, 7828–7837.
Groenendijk A., Spreafico F., de Krijger R. R., Drost J., Brok J., Perotti D. et al. 2021 Prognostic factors for Wilms tumour recurrence: a review of the literature. Cancers (basel) 13, 3142.
Guo K., Gong W., Wang Q., Gu G., Zheng T., Li Y. et al. 2020 LINC01106 drives colorectal cancer growth and stemness through a positive feedback loop to regulate the Gli family factors. Cell Death Dis. 11, 869.
Hentze M. W., Castello A., Schwarzl T. and Preiss T. 2018 A brave new world of RNA-binding proteins. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 19, 327–341.
Heydarnezhad Asl M., Pasban Khelejani F., Bahojb Mahdavi S. Z., Emrahi L., Jebelli A. and Mokhtarzadeh A. 2022 The various regulatory functions of long noncoding RNAs in apoptosis, cell cycle, and cellular senescence. J. Cell Biochem. 123, 995–1024.
Huang H., Wang D., Guo W., Zhuang X. and He Y. 2019 Correlated low IGF2BP1 and FOXM1 expression predicts a good prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 215, 152433.
Huang X., Zhang H., Guo X., Zhu Z., Cai H. and Kong X. 2018 Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 11, 88.
Li J., Mo M., Chen Z., Sheng Q., Mu H., Zhang F. et al. 2012 Adenoviral delivery of the EMX2 gene suppresses growth in human gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 7, e45970.
Li P., Zhang K., Tang S. and Tang W. 2022 Knockdown of lncRNA HAGLROS inhibits metastasis and promotes apoptosis in nephroblastoma cells by inhibition of autophagy. Bioengineered 13, 7552–7562.
Liu Y. C., Yeh C. T. and Lin K. H. 2020 Cancer stem cell functions in hepatocellular carcinoma and comprehensive therapeutic strategies. Cells 9, 1331.
Mahaira L. G., Katsara O., Pappou E., Iliopoulou E. G., Fortis S., Antsaklis A. et al. 2014 IGF2BP1 expression in human mesenchymal stem cells significantly affects their proliferation and is under the epigenetic control of TET1/2 demethylases. Stem Cells Dev. 23, 2501–2512.
Muller S., Glass M., Singh A. K., Haase J., Bley N., Fuchs T. et al. 2019 IGF2BP1 promotes SRF-dependent transcription in cancer in a m6A- and miRNA-dependent manner. Nucleic Acids Res. 47, 375–390.
Noonan F. C., Goodfellow P. J., Staloch L. J., Mutch D. G. and Simon T. C. 2003 Antisense transcripts at the EMX2 locus in human and mouse. Genomics 81, 58–66.
Pan L., Li Y., Jin L., Li J. and Xu A. 2020 TRPM2-AS promotes cancer cell proliferation through control of TAF15. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 120, 105683.
Pereira B., Billaud M. and Almeida R. 2017 RNA-binding proteins in cancer: old players and new actors. Trends Cancer 3, 506–528.
Qi C., Hu Y., Yang F., An H., Zhang J., Jin H. et al. 2016 Preliminary observations regarding the expression of collagen triple helix repeat-containing 1 is an independent prognostic factor for Wilms’ tumour. J. Pediatr. Surg. 51, 1501–1506.
Raggi C., Taddei M. L., Sacco E., Navari N., Correnti M., Piombanti B. et al. 2021 Mitochondrial oxidative metabolism contributes to a cancer stem cell phenotype in cholangiocarcinoma. J. Hepatol. 74, 1373–1385.
Spreafico F., Fernandez C. V., Brok J., Nakata K., Vujanic G., Geller J. I. et al. 2021 Wilms tumour. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 7, 75.
Wang Z., Zhang C., Chang J., Tian X., Zhu C. and Xu W. 2020 LncRNA EMX2OS, regulated by TCF12, interacts with FUS to regulate the proliferation, migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells through the cGMP-PKG signaling pathway. OncoTargets Ther. 13, 7045–7056.
Winkler L. and Dimitrova N. 2021 A mechanistic view of long noncoding RNAs in cancer. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 13, e1699.
Yang G., Lu X. and Yuan L. 2014 LncRNA: a link between RNA and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1839, 1097–1109.
Yang Y., Wu J., Liu F., He J., Wu F., Chen J. et al. 2021 IGF2BP1 promotes the liver cancer stem cell phenotype by regulating MGAT5 mRNA stability by m6A RNA methylation. Stem Cells Dev. 30, 1115–1125.
Zhao H., Wang P., Wang G., Zhang S. and Guo F. 2021 A long non-coding RNAs expression signature to improve prognostic prediction of Wilms tumour in children. Transl. Pediatr. 10, 525–540.
Zheng H., Li B. H., Liu C., Jia L. and Liu F. T. 2020 Comprehensive analysis of lncRNA-mediated ceRNA crosstalk and identification of prognostic biomarkers in Wilms’ tumour. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 4951692.
Zheng Q., Jia J., Zhou Z., Chu Q., Lian W. and Chen Z. 2021 The emerging role of thymopoietin-antisense RNA 1 as long noncoding RNA in the pathogenesis of human cancers. DNA Cell Biol. 40, 848–857.
Zhu P., He F., Hou Y., Tu G., Li Q., Jin T. et al. 2021 A novel hypoxic long noncoding RNA KB-1980E6.3 maintains breast cancer stem cell stemness via interacting with IGF2BP1 to facilitate c-Myc mRNA stability. Oncogene 40, 1609–1627.
Zou W., Zhang Y., Bai G., Zhuang J., Wei L., Wang Z. et al. 2022 siRNA-induced CD44 knockdown suppresses the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer stem cells through inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 26, 1969–1978.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Durgadas P. Kasbekar
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, HM., Cui, MY. & Chen, ZH. EMX2OS targeting IGF2BP1 represses Wilms’ tumour stemness, epithelial–mesenchymal transition and metastasis. J Genet 102, 12 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-022-01411-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-022-01411-9