Abstract
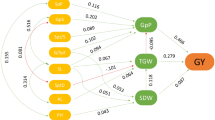
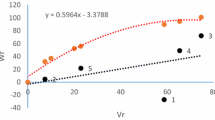
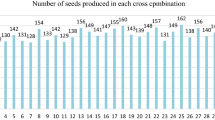
Grain yield is a complex polygenic trait representing a multiplicative end product of contributing yield attributes governed by simple to complex gene interactions. Deciphering the genetics and inheritance of traits/genes influencing yield is a prerequisite to harness the yield potential in any crop species. The objective of the present investigation was to estimate genetic variance components and type of gene action controlling yield and its component traits using six populations (P1, P2, F1, F2, BC1 and BC2) of the three bread wheat crosses. Cross I (25th HRWSN 2105 × WH 1080), cross II (22ndSAWYT323 × RSP 561) and cross III (22ndSAWYT333 × WH 1080) involving elite stripe rust resistant wheat genetic stocks in combination with commercial check varieties were used for analysis. A combination of morpho-physiological, biochemical and disease influencing traits were evaluated, thus exploring the possibility of multi-trait integration in future. Results revealed that the estimated mean effects (m) were highly significant for all the traits in all crosses, indicating that selected traits were quantitatively inherited. The estimate of dominant gene effect was highly significant for plant height, number of tillers per plant in all the three crosses. Grain yield per plant was highly significant in the cross II while total protein content was highly significant in both crosses II and III. Glycine betaine content showed significant additive genes effect. Duplicate epistasis was the most significant for traits like plant height, total protein content and grain yield per plant. Dominance gene effect was more important than additive gene effects in the inheritance of grain yield and most other traits studied. The magnitude of additive × additive gene effects was high and positively significant whereas dominance × dominance was negatively significant for most of the traits studied in the three crosses. Additive × dominance gene effects was of minor significance, thus indicating that selection for grain yield and its components should be delayed to later generations of breeding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cavalii L. L. 1952 An analysis of linkage in quantitative inheritance (ed. E. C. R. Reive and C. H. Waddington), pp. 135–144. HMSO, London.
Fethi B. and Mohamed E. 2010 Epistasis and genotype-by environment interaction of grain yield related traits in durum wheat. Plant Breed. Crop Sci. 2, 24–29.
Hasabnis S. N. and Kulkarni S. 2004 Genetics of leaf rust resistance in wheat. Indian J. Agric. Res. 38, 135–138.
Hayman B. I. 1958 The separation of epistatic from additive and dominance variation in generation mean. Heredity 12, 371–390.
Hussain F., Ashraf M., Hameed A. M., Hussain N. and Sial R. A. 2011 Genetic studies in wheat for leaf rust resistance (Puccinia recondite). Afr. J. Biol. 10, 3051–3054.
Jinkes J. L. and Jones R. M. 1958 Estimation of the components of heterosis. Genetics 43, 223–234.
Kaur N. and Singh P. 2004 Gene effect for grain yield and related attributes in Triticum durum. Indian J. Genet 64, 137–138.
Kearsey M. J., Pooni H. S. 1996 The genetical analysis of quantitative traits, 1st edition., pp. 46. Chapman and Hall, London.
Magda E. and El-Rahman A. 2013 Estimation of some genetic parameters through generation mean analysis in three bread wheat crosses. Alex. J. Agric. Res. 58, 183–195.
Mahpara S., Ali Z. and Ahsan M. 2008 Combining ability analysis for yield and yield related traits among wheat varieties and their F1 hybrids. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 10, 599–604.
Mahpara S., Ali Z., Rehmani M. I. A., Iqbal J. and Shafiq M. R. 2017 Studies of genetic and combining ability analysis for some physio-morphological traits in spring wheat using 7×7 diallel crosses. Int. J. Agric. Appl. Sci. 9, 33–40.
Mather K. V., Jinks J. L. 1982 Introduction to biometrical genetics. Chapman and Hall, London.
Memon J. 2010 Genetic basis of heat tolerance in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Ph.D. thesis, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad.
Menon U. and Sharma S. N. 1995 Inheritance studies for yield and yield component traits in bread wheat over environments. Indian J. Genet. 80, 1–5.
Miller P. A., Williams J. C., Robinson H. F. and Comstock R. E. 1958 Estimates of genotypic and environmental variances and covariances in upland cotton and their implications in selection. Agron. J. 50, 126–131.
Novoselovic D., Baric M., Drezner G., Gunjaca J. and Lalic A. 2004 Quantitative inheritance of some wheat plant traits. Genet. Mol. Biol. 27, 92–98.
Sharma S. N., Sain R. S. and Sharma R. K. 2002 Genetic control of quantitative traits in durum wheat under normal and late-sowing environments. SABRAO J. Bree. Genet. 34, 35–43.
Sharma S. N., Sain R. S. and Sharma R. K. 2003 Genetics of spike length in durum wheat. Euphytica 13, 155–161.
Snape J. W. 1987 Conventional methods of genetic analysis in wheat. In Wheat breeding, its scientific basis (ed. F. G. H. Lupton), pp. 109–128. Chapman and Hall, London, New York.
Acknowledgement
Authors wish to express their gratitude to the Sher-e-Kashmir University of Agricultural Sciences and Technology, Jammu for supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Durgadas Kasbekar
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Attri, H., Dey, T., Singh, B. et al. Genetic estimation of grain yield and its attributes in three wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) crosses using six parameter model. J Genet 100, 47 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-021-01298-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-021-01298-y