Abstract
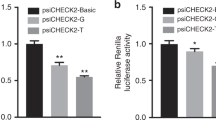
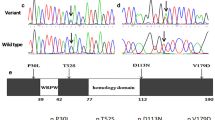
Hypoplastic right heart syndrome (HRHS) is characterized by hypoplastic right ventricle (RV); Numerous transcriptional cascades in the second heart field (SHF) regulate RV development. The relationship of SHF gene variants with human HRHS remains unknown. The whole lengths of 17 SHF genes were sequenced in 16 HRHS, and the selected single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) were then genotyped in HRHS, other congenital heart disease (CHD) and healthy control. Luciferase assay was performed to verify the effect of FOXC2: rs34221221 \(\hbox {A}{>}\hbox {G}\) and TBX20: rs59854940 \(\hbox {C}{>}\hbox {G}\) at the transcription level. There were 151 (12.86%) novel SNVs after sequence analysis, of which three were in exons (one was synonymous SNV and two were nonsynonymous SNVs), two in promoter, and most SNVs (89.95%) were in intronic regions. Genotype analyses revealed that the minor alleles of FOXC2: rs34221221 \(\hbox {A}{>}\hbox {G}\) and TBX20: rs59854940 \(\hbox {C}{>}\hbox {G}\) could increase HRHS risk (\(P{<}0.05\)), but not in other CHD or healthy control. Luciferase assay showed that the minor G allele in rs34221221 significantly increased FOXC2 transcription while in rs59854940 it decreased TBX20 transcription significantly. Novel variants of SHF gene associated with HRHS were identified. Minor alleles in two variants from FOXC2 and TBX20 could increase the risk of HRHS.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson K. R. and Lie J. T. 1979 The right ventricular myocardium in Ebstein’s anomaly: a morphometric histopathologic study. Mayo Clin. Proc. 54, 181–184.
Anderson K. R., Zuberbuhler J. R., Anderson R. H., Becker A. E. and Lie J. T. 1979 Morphologic spectrum of Ebstein’s anomaly of the heart: a review. Mayo Clin. Proc. 54, 174–180.
Buckingham M., Meilhac S. and Zaffran S. 2005. Building the mammalian heart from two sources of myocardial cells. Nat. Rev. Genet. 6, 826–837.
Cai C. L., Liang X., Shi Y., Chu P. H., Pfaff S. L., Chen J. et al. 2003 Isl1 identifies a cardiac progenitor population that proliferates prior to differentiation and contributes a majority of cells to the heart. Dev. Cell 5, 877–889.
Chessa M., Redaelli S., Masszi G., Iascone M. and Carminati M. 2000 Familial occurrence of isolated right ventricular hypoplasia. Am. J. Med. Genet. 90, 356–357.
Dai Y. S. 2002 The basic helix-loop-helix factor, HAND2, functions as a transcriptional activator by binding to E-boxes as a heterodimer. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 12604–12612.
Dodou E. 2004 Mef2c is a direct transcriptional target of ISL1 and GATA factors in the anterior heart field during mouse embryonic development. Development 131, 3931–3942.
Fahed A. C., Gelb B. D., Seidman J. G. and Seidman C. E. 2013 Genetics of congenital heart disease: the glass half empty. Circ. Res. 112, 707–720.
Gottlieb P. D., Pierce S. A., Sims R. J., Yamagishi H., Weihe E. K., Harriss J. V. et al. 2002 Bop encodes a muscle-restricted protein containing MYND and SET domains and is essential for cardiac differentiation and morphogenesis. Nat. Genet. 31, 25–32.
Grossfeld P. D., Lucas V. W., Sklansky M. S., Kashani I. A. and Rothman A. 1997 Familial occurrence of pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum. Am. J. Med. Genet. 72, 294–296.
Hanley F. L., Sade R. M., Freedom R. M., Blackstone E. H. and Kirklin J. W. 1993 Outcomes in critically ill neonates with pulmonary stenosis and intact ventricular septum: a multiinstitutional study. Congenital Heart Surgeons Society. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 22, 183–192.
Hoffman J. I. and Kaplan S. 2002 The incidence of congenital heart disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 39, 1890–1900.
Ilagan R., Abu-Issa R., Brown D., Yang Y. P., Jiao K., Schwartz R. J. et al. 2006 Fgf8 is required for anterior heart field development. Development 133, 2435–2445.
Inman K. E., Caiaffa C. D., Melton K. R., Sandell L. L., Achilleos A., Kume T. et al. 2018 Foxc2 is required for proper cardiac neural crest cell migration, outflow tract septation, and ventricle expansion. Dev. Dyn. 247, 1286–1296.
Kelly R. G., Brown N. A. and Buckingham M. E. 2001 The arterial pole of the mouse heart forms from Fgf10-expressing cells in pharyngeal mesoderm. Dev. Cell 1, 435–440.
Khoury G. H., Gilbert E. F., Chang C. H. and Schmidt R. 1969 The hypoplastic right heart complex. Clinical, hemodynamic, pathologic and surgical considerations. Am. J. Cardiol. 23, 792–800.
Lin L., Bu L., Cai C. L., Zhang X. and Evans S. 2006 Isl1 is upstream of sonic hedgehog in a pathway required for cardiac morphogenesis. Dev. Biol. 295, 756–763.
Marguerie A., Bajolle F., Zaffran S., Brown N. A., Dickson C., Buckingham M. E. et al. 2006 Congenital heart defects in Fgfr2-IIIb and Fgf10 mutant mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 71, 50–60.
McDaniell R., Lee B. K., Song L., Liu Z., Boyle A. P., Erdos M. R. et al. 2010 Heritable individual-specific and allele-specific chromatin signatures in humans. Science 328, 235–239.
Mjaatvedt C. H., Nakaoka T., Moreno-Rodriguez R., Norris R. A., Kern M. J., Eisenberg C. A. et al. 2001 The outflow tract of the heart is recruited from a novel heart-forming field. Dev. Biol. 238, 97–109.
Park E. J., Ogden L. A., Talbot A., Evans S., Cai C. L., Black B. L. et al. 2006 Required, tissue-specific roles for Fgf8 in outflow tract formation and remodeling. Development 133, 2419–2433.
Phan D., Rasmussen T. L., Nakagawa O., McAnally J., Gottlieb P. D., Tucker P. W. et al. 2005 BOP, a regulator of right ventricular heart development, is a direct transcriptional target of MEF2C in the developing heart. Development 132, 2669–2678.
Pierpont M. E., Basson C. T., Benson Jr D. W., Gelb B. D., Giglia T. M., Goldmuntz E. et al. 2007 Genetic basis for congenital heart defects: current knowledge: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Congenital Cardiac Defects Committee, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young: endorsed by the American Academy of Pediatrics. Circulation 115, 3015–3038.
Reamon-Buettner S. M., Ciribilli Y., Traverso I., Kuhls B., Inga A., Borlak J. 2009 A functional genetic study identifies HAND1 mutations in septation defects of the human heart. Hum. Mol. Genet. 18, 3567–3578.
Seo S. and Kume T. 2006 Forkhead transcription factors, Foxc1 and Foxc2, are required for the morphogenesis of the cardiac outflow tract. Dev. Biol. 296, 421–436.
Seo S., Fujita H., Nakano A., Kang M., Duarte A. and Kume T. 2006 The forkhead transcription factors, Foxc1 and Foxc2, are required for arterial specification and lymphatic sprouting during vascular development. Dev. Biol. 294, 458–470.
Srivastava D. 2006 Making or breaking the heart: from lineage determination to morphogenesis. Cell 126, 1037–1048.
Srivastava D., Cserjesi P. and Olson E. N. 1995 A subclass of bHLH proteins required for cardiac morphogenesis. Science 270, 1995–1999.
Srivastava D., Thomas T., Lin Q., Kirby M. L., Brown D. and Olson E. N. 1997 Regulation of cardiac mesodermal and neural crest development by the bHLH transcription factor, dHAND. Nat. Genet. 16, 154–160.
Stennard F. A. and Harvey R. P. 2005 T-box transcription factors and their roles in regulatory hierarchies in the developing heart. Development 132, 4897–4910.
Stennard F. A., Costa M. W., Elliott D. A., Rankin S., Haast S. J., Lai D. et al. 2003 Cardiac T-box factor Tbx20 directly interacts with Nkx2-5, GATA4, and GATA5 in regulation of gene expression in the developing heart. Dev. Biol. 262, 206–224.
Takeuchi J. K. 2005 Tbx20 dose-dependently regulates transcription factor networks required for mouse heart and motoneuron development. Development 132, 2463–2474.
Topf A., Griffin H. R., Glen E., Soemedi R., Brown D. L., Hall D. et al. 2014 Functionally significant, rare transcription factor variants in tetralogy of Fallot. PLoS One 9, e95453.
Tsuchihashi T., Maeda J., Shin C. H., Ivey K. N., Black B. L., Olson E. N. et al. 2011 Hand2 function in second heart field progenitors is essential for cardiogenesis. Dev. Biol. 351, 62–69.
van der Linde D., Konings E. E., Slager M. A., Witsenburg M., Helbing W. A., Takkenberg J. J. et al. 2011 Birth prevalence of congenital heart disease worldwide: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 58, 2241–2247.
Van Praagh R. D. I., Gordon D., Wright G. B. and Van Praagh S. 1982 Ventricular diagnosis and designation. In Paediatric cardiology (ed. M. J. Godman), pp. 153. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh.
Vong L., Bi W., O’Connor-Halligan K. E., Li C., Cserjesi P. and Schwarz J. J. 2006 MEF2C is required for the normal allocation of cells between the ventricular and sinoatrial precursors of the primary heart field. Dev. Dynam. 235, 1809–1821.
Waldo K. L., Kumiski D. H., Wallis K. T., Stadt H. A., Hutson M. R., Platt D. H. et al. 2001 Conotruncal myocardium arises from a secondary heart field. Development 128, 3179–3188.
Xiong F., Li Q., Zhang C., Chen Y., Li P., Wei X. et al. 2013 Analyses of GATA4, NKX2.5, and TFAP2B genes in subjects from southern China with sporadic congenital heart disease. Cardiovas. Pathol. 22, 141–145.
Xu H. and Baldini A. 2007 Genetic pathways to mammalian heart development: Recent progress from manipulation of the mouse genome. Sem. Cell Dev. Biol. 18, 77–83.
Yamagishi H., Maeda J., Hu T., McAnally J., Conway S. J., Kume T. et al. 2003 Tbx1 is regulated by tissue-specific forkhead proteins through a common sonic hedgehog-responsive enhancer. Genes Dev. 17, 269–281.
Yu S., Shao L., Kilbride H. and Zwick D. L. 2010 Haploinsufficiencies of FOXF1 and FOXC2 genes associated with lethal alveolar capillary dysplasia and congenital heart disease. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 152A, 1257–1262.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81400242, 81430006 and 81441010) and the National Basic Research Development Program in China (Program 973: 2010CB529505).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding Editor: H. A. Ranganath
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, E., Nie, Y., Fan, X. et al. Minor alleles of genetic variants in second heart field increase the risk of hypoplastic right heart syndrome. J Genet 98, 45 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-019-1092-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-019-1092-3