Abstract
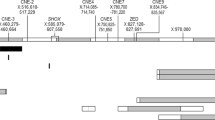
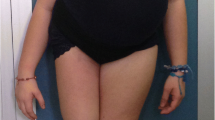
Haploinsufficiency of the short stature homeobox contaning SHOX gene has been shown to result in a spectrum of phenotypes ranging from Leri–Weill dyschondrosteosis (LWD) at the more severe end to SHOX-related short stature at the milder end of the spectrum. Most alterations are whole gene deletions, point mutations within the coding region, or microdeletions in its flanking sequences. Here, we present the clinical and molecular data as well as the potential molecular mechanism underlying a novel microdeletion, causing a variable SHOX-related haploinsufficiency disorder in a three-generation family. The phenotype resembles that of LWD in females, in males, however, the phenotypic expression is milder. The 15523-bp SHOX intragenic deletion, encompassing exons 3–6, was initially detected by array-CGH, followed by MLPA analysis. Sequencing of the breakpoints indicated an Alu recombination-mediated deletion (ARMD) as the potential causative mechanism.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belin V., Cusin V., Viot G., Girlich D., Toutain A., Moncla A. et al. 1998 SHOX mutations in dyschondrosteosis (Leri–Weill syndrome). Nat. Genet. 19, 67–69.
Benito-Sanz S., Gorbenko del Blanco D., Huber C., Thomas N. S., Aza-Carmona M., Bunyan D. et al. 2006 Characterization of SHOX deletions in Leri–Weill dyschondrosteosis (LWD) reveals genetic heterogeneity and no recombination hotspots. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 79, 409–414.
Binder G. 2011 Short stature due to SHOX deficiency: genotype, phenotype, and therapy. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 75, 81–89.
Binder G. and Rappold G. A. 2005 SHOX deficiency disorders. In Gene reviews (ed. R. A. Pagon, M. P. Adam, H. H. Ardinger et al.) University of Washington, Seattle, USA (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1215/.
Blaschke R. J. and Rappold G. 2006 The pseudoautosomal regions, SHOX and disease. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 16, 233–239.
Chen J., Wildhardt G., Zhong Z., Roth R., Weiss B., Steinberger D. et al. 2009 Enhancer deletions of the SHOX gene as a frequent cause of short stature: the essential role of a 250 kb downstream regulatory domain. J. Med. Genet. 46, 834–839.
Cordaux R. and Batzer M. A. 2009 The impact of retrotransposons on human genome evolution. Nat. Rev. Genet. 10, 691–703.
Cormier-Daire V., Huber C. and Munnich A. 2001 Allelic and nonallelic heterogeneity in dyschondrosteosis (Leri–Weill syndrome). Am. J. Med. Genet. 106, 272–274.
Ellison J. W., Wardak Z., Young M. F., Gehron Robey P., Laig-Webster M. and Chiong W. 1997 PHOG, a candidate gene for involvement in the short stature of Turner syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 6, 1341–1347.
Falcinelli C., Iughetti L., Percesepe A., Calabrese G., Chiarelli F., Cisternino M. et al. 2002 SHOX point mutations and deletions in Leri–Weill dyschondrosteosis. J. Med. Genet. 39, E33.
Flanagan S. F., Munns C. F., Hayes M., Williams B., Berry M., Vickers D. et al. 2002 Prevalence of mutations in the short stature homeobox containing gene (SHOX) in Madelung deformity of childhood. J. Med. Genet. 39, 758–763.
Fukami M., Dateki S., Kato F., Hasegawa Y., Mochizuki H., Horikawa R. et al. 2008 Identification and characterization of cryptic SHOX intragenic deletions in three Japanese patients with Leri–Weill dyschondrosteosis. J. Hum. Genet. 53, 454–459.
Fukami M., Naiki Y., Muroya K., Hamajima T., Soneda S., Horikawa R. et al. 2015 Rare pseudoautosomal copy-number variations involving SHOX and/or its flanking regions in individuals with and without short stature. J. Hum. Genet. 60, 553–556.
Funari M. F., Jorge A. A., Pinto E. M., Arnhold I. J., Mendonca B. B. and Nishi M. Y. 2008 Cryptic intragenic deletion of the SHOX gene in a family with Leri–Weill dyschondrosteosis detected by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA). Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metabol. 52, 1382–1387.
Gatta V., Antonucci I., Morizio E., Palka C., Fischetto R., Mokini V. et al. 2007 Identification and characterization of different SHOX gene deletions in patients with Leri–Weill dyschondrosteosis by MLPA assay. J. Hum. Genet. 52, 21–27.
Gatta V., Palka C., Chiavaroli V., Franchi S., Cannataro G., Savastano M. et al. 2014 Spectrum of phenotypic anomalies in four families with deletion of the SHOX enhancer region. BMC Med. Genet. 15, 87.
Karolchik D., Hinrichs A. S., Furey T. S., Roskin K. M., Sugnet C. W., Haussler D. et al. 2004 The UCSC table browser data retrieval tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, D493–D496.
Katoh K., Misawa K., Kuma K. and Miyata T. 2002 MAFFT: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, 3059–3066.
Kearse M., Moir R., Wilson A., Stones-Havas S., Cheung M., Sturrock S. et al. 2012 Geneious basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 28, 1647–1649.
Kent W. J. 2002 BLAT—the BLAST-like alignment tool. Genome Res. 12, 656–664.
Lien S., Szyda J., Schechinger B., Rappold G. and Arnheim N. 2000 Evidence for heterogeneity in recombination in the humanpseudoautosomal region: high resolution analysis by sperm typing and radiation-hybrid mapping. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 66, 557–566.
Marchini A., Marttila T., Winter A., Caldeira S., Malanchi I., Blaschke R. J. et al. 2004 The short stature homeodomain protein SHOX induces cellular growth arrest and apoptosis and is expressed in human growth plate chondrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 37103–37114.
Mills R. E., Bennett E. A., Iskow R. C. and Devine S. E. 2007 Which transposable elements are active in the human genome? Trends Genet. 23, 183–191.
Munns C. J., Haase H. R., Crowther L. M., Hayes M. T., Blaschke R., Rappold G. et al. 2004 Expression of SHOX in human fetal and childhood growth plate. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89, 4130–4135.
Rao E., Weiss B., Fukami M., Rump A., Niesler B., Mertz A. et al. 1997 Pseudoautosomal deletions encompassing a novel homeobox gene cause growth failure in idiopathic short stature and Turner syndrome. Nat. Genet. 16, 54–63.
Rappold G. A., Fukami M., Niesler B., Schiller S., Zumkeller W., Bettendorf M. et al. 2002 Deletions of the homeobox gene SHOX (short stature homeobox) are an important cause of growth failure in children with short stature. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 87, 1402–1406.
Ross J. L., Scott Jr C., Marttila P., Kowal K., Nass A., Papenhausen P. et al. 2001 Phenotypes associated with SHOX deficiency . J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 5674–5680.
Russell L. M., Strike P., Browne C. E. and Jacobs P. A. 2007 X chromosome loss and ageing. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 116, 181–185.
Schiller S., Spranger S., Schechinger B., Fukami M., Merker S., Drop S. L. et al. 2000 Phenotypic variation and genetic heterogeneity in Leri–Weill syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 8, 54–62.
Sen S. K., Han K., Wang J., Lee J., Wang H., Callinan P. A. et al. 2006 Human genomic deletions mediated by recombination between Alu elements. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 79, 41–53.
Shears D. J., Vassal H. J., Goodman F. R., Palmer R. W., Reardon W., Superti-Furga A. et al. 1998 Mutation and deletion of the pseudoautosomal gene SHOX cause Leri–Weill dyschondrosteosis. Nat. Genet. 19, 70–73.
Tanteles G. A., Alexandrou A., Evangelidou P., Gavatha M., Anastasiadou V. and Sismani C. 2015 Partial MEF2C deletion in a Cypriot patient with severe intellectual disability and a jugular fossa malformation: review of the literature. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 167, 664–669.
Tempel S. 2012 Using and understanding RepeatMasker. Methods Mol. Biol. 859, 29–51.
Acknowledgement
We thank the patient and her family for consenting to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Rajiva Raman
[Alexandrou A., Papaevripidou I., Tsangaras K., Alexandrou I., Tryfonidis M., Christophidou-Anastasiadou V., Zamba-Papanicolaou E., Koumbaris G., Neocleous V., Phylactou L. A., Skordis N., Tanteles G. A. and Sismani C. 2016 Identification of a novel 15.5 kb SHOX deletion associated with marked intrafamilial phenotypic variability and analysis of its molecular origin. J. Genet. 95, xx–xx]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ALEXANDROU, A., PAPAEVRIPIDOU, I., TSANGARAS, K. et al. Identification of a novel 15.5 kb SHOX deletion associated with marked intrafamilial phenotypic variability and analysis of its molecular origin. J Genet 95, 839–845 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-016-0698-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-016-0698-y