Abstract
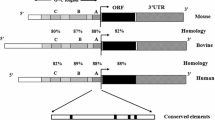
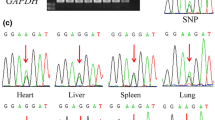
Genomic imprinting of the Cdkn1c/Kcnq1ot1 region shows lack of conservation between human and mouse. This region has been reported to be associated with Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome (BWS) and cancer. To increase our understanding of imprinted genes in bovine Cdkn1c/Kcnq1ot1 imprinting cluster, we assessed the imprinting status of four cattle genes (Tssc4, Nap1l4, Phlda2 and Osbpl5) in seven types of tissues: heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney, skeletal muscle and subcutaneous fat using polymorphism-based sequencing approach. It was found that all the four genes showed biallelic expression in tissues in which transcripts were detected. Nap1l4 and Tssc4 were detected in all examined tissues, while the expression of Phlda2 and Osbpl5 was tissue-specific. Phlda2 was not detected in heart and subcutaneous fat, and Osbpl5 was not detected in spleen and skeletal muscle. In addition, identification of species-specific imprinted genes is necessary to understand the evolution of genomic imprinting and to elucidate mechanisms leading to allele-specific expression.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bischoff S. R., Tsai S., Hardison N., Motsinger-Reif A. A., Freking B. A. and Piedrahita J. A. 2009 Functional genomic approaches for the study of fetal/placental development in swine with special emphasis on imprinted genes. Soc. Reprod. Fertil. Suppl. 66, 245–264.
Frank D., Mendelsohn C. L., Ciccone E., Svensson K., Ohlsson R. and Tycko B. 1999 A novel pleckstrin homology-related gene family defined by Ipl/Tssc3, TDAG51, and Tih1: tissue-specific expression, chromosomal location, and parental imprinting. Mamm. Genome 10, 1150–1159.
Frank D., Fortino W., Clark L., Musalo R., Wang W., Saxena A. et al. 2002 Placental overgrowth in mice lacking the imprinted gene Ipl. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 7490–7495.
Frost J. M., Udayashankar R., Moore H. D. and Moore G. E. 2010 Telomeric NAP1L4 and OSBPL5 of the KCNQ1 cluster, and the DECORIN gene are not imprinted in human trophoblast stem cells. PLoS One 5, e11595.
Higashimoto K., Soejima H., Saito T., Okumura K. and Mukai T. 2006 Imprinting disruption of the CDKN1C/KCNQ1OT1 domain: the molecular mechanisms causing Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome and cancer. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 113, 306–312.
Hu R. J., Lee M. P., Johnson L. A. and Feinberg A. P. 1996 A novel human homologue of yeast nucleosome assembly protein, 65 kb centromeric to the p57(KIP2) gene, is biallelically expressed in fetal and adult tissues. Hum. Mol. Genet. 5, 1743– 1748.
Kawahara M. and Kono T. 2012 Roles of genes regulated by two paternally methylated imprinted regions on chromosomes 7 and 12 in mouse ontogeny. J. Reprod. Dev. 58, 175–179.
Khatib H., Zaitoun I. and Kim E. S. 2007 Comparative analysis of sequence characteristics of imprinted genes in human, mouse and cattle. Mamm. Genome 18, 538–547.
Lee M. P., Hu R. J., Johnson L. A. and Feinberg A. P. 1997 Human KvLQT1 gene shows tissue specific imprinting and encompassesBeckwith–Wiedemann syndrome chromosomal rearrangements. Nat. Genet. 15, 181–185.
Lee M. P., Brandenburg S., Landes G. M., Adams M., Miller G. and Feinberg A. P. 1999 Two novel genes in the center of the 11p15 imprinted domain escape genomic imprinting. Hum. Mol. Genet. 8, 683–690.
Li S., Li J., Tian J., Dong R., Wei J., Qiu X. et al. 2012 Characterization, tissue expression, and imprinting analysis of the porcine CDKN1C and NAP1L4 genes. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 946527.
Mitsuya K., Meguro M., Lee M. P., Katoh M., Schulz T. C., Kugoh H. et al. 1999 LIT1, an imprinted antisense RNA in the human KvLQT1 locus identified by screening for differentially expressed transcripts using monochromosomal hybrids. Hum. Mol. Genet. 8, 1209–1217.
Monk D., Arnaud P., Apostolidou S., Hills F. A., Kelsey G., Stanier P. et al. 2006 Limited evolutionary conservation of imprinting in the human placenta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 6623–6628.
Morison I. M., Ramsay J. P. and Spencer H. G. 2005 A census of mammalian imprinting. Trends Genet. 21, 457–465.
Ohlsson R., Hedborg F., Holmgren L., Walsh C. and Ekström T. J. 1994 Overlapping patterns of IGF2 and H19 expression during human development: biallelic IGF2 expression correlates with a lack of H19 expression. Development 120, 361–368.
Okuwaki M., Kato K. and Nagata K. 2010 Functional characterization of human nucleosome assembly protein 1-like proteins as histone chaperones. Genes Cells 15, 13–27.
Paulsen M., El-Maarri O., Engemann S., Strödicke M., Franck O., Davies K. et al. 2000 Sequence conservation and variability of imprinting in the Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome gene cluster in human and mouse. Hum. Mol. Genet. 9, 1829–1841.
Qian N., Frank D., O’Keefe D., Dao D., Zhao L., Yuan L. et al. 1997 The IPL gene on chromosome 11p15.5 is imprinted in humans and mice and is similar to TDAG51, implicated in Fas expression and apoptosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 6, 2021–2029.
Reik W. and Walter J. 2001 Genomic imprinting: parental influence on the genome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2, 21–32.
Reik W., Santos F. and Dean W. 2003 Mammalian epigenomics: reprogramming the genome for development and therapy. Theriogenology 59, 21–32.
Rodriguez P., Munroe D., Prawitt D., Chu L. L., Bric E., Kim J. et al. 1997 Functional characterization of human nucleosome assembly protein-2 (NAP1L4) suggests a role as a histone chaperone. Genomics 44, 253–265.
Salas M., John R., Saxena A., Barton S., Frank D., Fitzpatrick G. et al. 2004 Placental growth retardation due to loss of imprinting of Phlda2. Mech. Dev. 121, 1199–1210.
Sikora K. M., Magee D. A., Berkowicz E. W., Lonergan P., Evans A. C., Carter F. et al. 2012 PHLDA2 is an imprinted gene in cattle. Anim. Genet. 43, 587–590.
Tunster S. J., Tycko B. and John R. M. 2010 The imprinted Phlda2 gene regulates extraembryonic energy stores. Mol. Cell. Biol. 30, 295–306.
Umlauf D., Goto Y., Cao R., Cerqueira F., Wagschal A., Zhang Y. et al. 2004 Imprinting along the Kcnq1 domain on mouse chromosome 7 involves repressive histone methylation and recruitment of polycomb group complexes. Nat. Genet 36, 1296–1300.
Zaitoun I. and Khatib H. 2008 Comparative genomic imprinting and expression analysis of six cattle genes. J. Anim. Sci. 86, 25–32.
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31372312).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
[Wang M., Li D., Zhang M., Yang W., Wu G., Cui Y. and Li S. 2015 Biallelic expression of Tssc4, Nap1l4, Phlda2 and Osbpl5 in adult cattle. J. Genet. 94, xx–xx]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WANG, M., LI, D., ZHANG, M. et al. Biallelic expression of Tssc4, Nap1l4, Phlda2 and Osbpl5 in adult cattle. J Genet 94, 391–395 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-015-0530-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-015-0530-0