Abstract
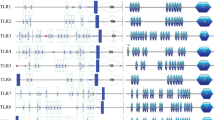
Domain shuffling, which is an important mechanism in the evolution of multi-domain proteins, has shaped the evolutionary development of the immune system in animals. Toll and Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate and adaptive immune systems. Draft genome sequences provide the opportunity to compare the Toll/TLR gene repertoire among representative metazoans. In this study, we investigated the combination of Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) and leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domains of metazoan Toll/TLRs. Before Toll with both domains occurred in Cnidaria (sea anemone, Nematostella vectensis), through domain combinations, TIR-only and LRR-only proteins had already appeared in sponges (Amphimedon queenslandica). Although vertebrate-like TIR (V-TIR) domain already appeared in Cnidaria, the vertebrate-like TLR (V-TLR) with both domains appeared much later. The first combination between V-TIR domain and vertebrate-like LRR (V-LRR) domain for V-TLR may have occurred after the divergence of Cnidaria and bilateria. Then, another combination for V-TLR, a recombination of both domains, possibly occurred before or during the evolution of primitive vertebrates. Taken together, two rounds of domain combinations may thus have co-shaped the vertebrate TLRs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abascal F., Zardoya R. and Posada D. 2005 ProtTest: selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics 21, 2104–2105.
Chang M. M., Zhang J. and Miao D. 2006 A lamprey from the Cretaceous Jehol biota of China. Nature 441, 972–974.
Davidson C. R., Best N. M., Francis J. W., Cooper E. L. and Wood T. C. 2008 Toll-like receptor genes (TLRs) from Capitella capitata and Helobdella robusta (Annelida). Dev. Comp. Immunol. 32, 608–612.
Gess R. W., Coates M. I. and Rubidge B. S. 2006 A lamprey from the Devonian period of South Africa. Nature 443, 981–984.
Guindon S., Lethiec F., Duroux P. and Gascuel O. 2005 PHYML Online-a web server for fast maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic inference. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, W557–W559.
Guo P., Hirano M., Herrin B. R., Li J., Yu C., Sadlonova A. et al. 2009 Dual nature of the adaptive immune system in lampreys. Nature 459, 796–801.
Hemmrich G., Miller D. J. and Bosch T. C. 2007 The evolution of immunity: a low-life perspective. Trends Immunol. 28, 449–454.
Hibino T., Loza-Coll M., Messier C., Majeske A. J., Cohen A. H., Terwilliger D. P. et al. 2006 The immune gene repertoire encoded in the purple sea urchin genome. Dev. Biol. 300, 349–365.
Huang S., Yuan S., Guo L., Yu Y., Li J., Wu T. et al. 2008 Genomic analysis of the immune gene repertoire of amphioxus reveals extraordinary innate complexity and diversity. Genome Res. 18, 1112–1126.
Ishii A., Kawasaki M., Matsumoto M., Tochinai S. and Seya T. 2007a Phylogenetic and expression analysis of amphibian Xenopus Toll-like receptors. Immunogenetics 59, 281–293.
Ishii A., Matsuo A., Sawa H., Tsujita T., Shida K., Matsumoto M. et al. 2007b Lamprey TLRs with properties distinct from those of the variable lymphocyte receptors. J. Immunol. 178, 397–406.
Kasamatsu J., Oshiumi H., Matsumoto M., Kasahara M. and Seya T. 2010 Phylogenetic and expression analysis of Lamprey Toll-like receptors. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 34, 855–865.
Larkin M. A., Blackshields G., Brown N. P., Chenna R., McGettigan P. A., McWilliam H. et al. 2007 Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23, 2947–2948.
LeBouder E., Rey-Nores J. E., Rushmere N. K., Grigorov M., Lawn S. D., Affolter M. et al. 2003 Soluble forms of Toll-like receptor (TLR)2 capable of modulating TLR2 signaling are present in human plasma and breast milk. J. Immunol. 171, 6680–6689.
Lemaitre B., Nicolas E., Michaut L., Reichhart J. M. and Hoffmann J. A. 1996 The dorsoventral regulatory gene cassette spatzle/Toll/cactus controls the potent antifungal response in Drosophila adults. Cell 86, 973–983.
Medzhitov R., Preston-Hurlburt P. and Janeway Jr C. A. 1997 A human homologue of the Drosophila Toll protein signals activation of adaptive immunity. Nature 388, 394–397.
Miller D. J., Hemmrich G., Ball E. E., Hayward D. C., Khalturin K., Funayama N. et al. 2007 The innate immune repertoire in cnidaria–ancestral complexity and stochastic gene loss. Genome Biol. 8, R59.
Oshiumi H., Tsujita T., Shida K., Matsumoto M., Ikeo K. and Seya T. 2003 Prediction of the prototype of the human Toll-like receptor gene family from the pufferfish, Fugu rubripes, genome. Immunogenetics 54, 791–800.
Pasare C. and Medzhitov R. 2004 Toll-like receptors and acquired immunity. Semin. Immunol. 16, 23–26.
Roach J. C., Glusman G., Rowen L., Kaur A., Purcell M. K., Smith K. D. et al. 2005 The evolution of vertebrate Toll-like receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 9577–9582.
Sasaki N., Ogasawara M., Sekiguchi T., Kusumoto S. and Satake H. 2009 Toll-like receptors of the ascidian Ciona intestinalis: prototypes with hybrid functionalities of vertebrate Toll-like receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 27336–27343.
Takeda K. and Akira S. 2005 Toll-like receptors in innate immunity. Int. Immunol. 17, 1–14.
Tamura K., Dudley J., Nei M. and Kumar S. 2007 MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24, 1596–1599.
Tsujita T., Tsukada H., Nakao M., Oshiumi H., Matsumoto M. and Seya T. 2004 Sensing bacterial flagellin by membrane and soluble orthologs of Toll-like receptor 5 in rainbow trout (Onchorhynchus mikiss). J. Biol. Chem. 279, 48588–48597.
Tsukada H., Fukui A., Tsujita T., Matsumoto M., Iida T. and Seya T. 2005 Fish soluble Toll-like receptor 5 (TLR5S) is an acute-phase protein with integral flagellin-recognition activity. Int. J. Mol. Med. 15, 519–525.
Wiens M., Korzhev M., Perovic-Ottstadt S., Luthringer B., Brandt D., Klein S. et al. 2007 Toll-like receptors are part of the innate immune defense system of sponges (demospongiae: Porifera). Mol. Biol. Evol. 24, 792–804.
Yilmaz A., Shen S., Adelson D. L., Xavier S. and Zhu J. J. 2005 Identification and sequence analysis of chicken Toll-like receptors. Immunogenetics 56, 743–753.
Yuan S., Huang S., Zhang W., Wu T., Dong M., Yu Y. et al. 2009 An amphioxus TLR with dynamic embryonic expression pattern responses to pathogens and activates NF-kappaB pathway via MyD88. Mol. Immunol. 46, 2348–2356.
Zhang Q., Zmasek C. M., Dishaw L. J., Mueller M. G., Ye Y., Litman G. W. et al. 2008 Novel genes dramatically alter regulatory network topology in amphioxus. Genome Biol. 9, R123.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Wu B., Huan T., Gong J., Zhou P. and Bai Z. 2011 Domain combination of the vertebrate-like TLR gene family: implications for their origin and evolution. J. Genet. 90, xx-xx
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WU, B., HUAN, T., GONG, J. et al. Domain combination of the vertebrate-like TLR gene family: implications for their origin and evolution. J Genet 90, 401–408 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-011-0097-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-011-0097-3