Abstract
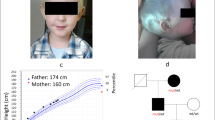
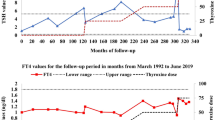
Five patients, four brothers and their paternal aunt, presented with a history of overt hyperthyroidism and goiter. Hyperthyroidism in this family was remarkable for its poor response to carbimazole (30–50 mg/d). The thyroid ultrasound showed a diffusely enlarged gland in all the affected members, and thyroid stimulating antibodies (TSAB) were negative. Screening for germline mutations in thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) receptor (TSHR) gene was performed by direct sequencing of genomic DNA extracted from peripheral blood leukocytes of all family members. The sequence analysis of all TSHR gene exons and intron borders revealed two genomic variants. The first was a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) within exon seven (Asn187Asn), whereas the other was located in intron seven (IVS7+68T>G). All affected members, two asymptomatic brothers with sub-clinical hyperthyroidism, and their father were heterozygous for those two genomic variants. Anti-thyroid drug treatment for several months successfully relieved symptoms in one subject, whereas the remaining patients required total thyroidectomy to control their disease. This is the first Jordanian family with familial non-autoimmune hyperthyroidism, with mutations affecting the TSHR gene.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akcurin S., Turkkahraman D., Tysoe C., Ellard S., De Leener A., Vassart G. and Costaqliola S. 2008 A family with a novel TSH receptor activating germline mutation (p.Ala485Val). Eur. J. Pediatr. 153, 122–126.
Alberti L., Proverbio M. C., Costagliola S., Weber G., Beck-Peccoz P., Chiumello G. and Persani L. 2001 A novel germline mutation in the TSH receptor gene causes non-autoimmune autosomal dominant hyperthyroidism. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 145, 249–254.
Arturi F., Chiefari E., Tumino S., Russo D., Squatrito S., Chazenbalk G. et al. 2002 Similarities and differences in the phenotype of members of an Italian family with hereditary non autoimmune hyperthyroidism associated with an activating germline mutation. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 25, 696–701.
Biebermann H., Schöneberg T., Krude H., Gudermann T. and Gruters A. 2000 Constitutively activating TSH-receptor mutations as a molecular cause of non-autoimmune hyperthyroidism in childhood. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 385, 390–392.
Biebermann H., Schöneberg T., Hess C., Germak J., Gudermann T. and Gruters A. 2001 the first activating TSH receptor mutation in transmembrane domain 1 identified in a family with non-autoimmune hyperthyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 4429–4433.
Claus M., Maier J., Paschke R., Kujat C., Stumvoll M. and Führer D. 2005 Novel thyrotropin receptor germline mutation (Ile568Val) in a Saxonian family with hereditary non-autoimmune hyperthyroidism. Thyroid 15, 1089–1094.
de Roux N., Misrahi M., Chatelain N., Gross B. and Milgrom E. 1996 Microsatellites and PCR primers for genetic studies and genomic sequencing of the human TSH receptor gene. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 117, 253–256.
Duprez L., Parma J., Van Sande J., Allgeier A., Leclere J., Schvartz C. et al. 1994 Germline mutations in the thyrotropin receptor gene cause non-autoimmune autosomal dominant hyperthyroidism. Nat. Genet. 7, 396–401.
Elgadi A., Arvidsson C. G., Janson A., Marcus C., Costagliola S. and Norgren S. 2005 Autosomal-dominant non-autoimmune hyperthyroidism presenting with neuromuscular symptoms. Acta Paediatr. 94, 1145–1148.
Ezquerra M., Campdelacreu J., Munoz E., Tolosa E. and Marti J. 2005 A novel intronic mutation in the DDP1 gene in a family with X-linked dystonia-deafness syndrome. Arch. Neurol. 62, 306–308.
Ferrara A., Capalbo D., Rossi G., Capuano S., Del Prete G., Esposito V. 2007 A new case of familial non-autoimmune hyperthyroidism caused by the M463V mutation in the TSH receptor with anticipation of the disease across generations: a possible role of iodine supplementation. Thyroid 17, 677–680.
Führer D., Wonerow P., Willgerodt H. and Paschke R. 1997 Identification of a new thyrotropin receptor germline mutation (Leu629Phe) in a famly with neonatal onset of autosomal dominant nonautoimmune hyperthyroidism. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 82, 4234–4238.
Füuhrer D., Warner J., Sequeira M., Paschke R., Gregory J. and Ludgate M. 2000 Novel TSHR germline mutation (Met463Val) masquerading as Graves’ disease in a large Welsh kindred with hyperthyroidism. Thyroid 10, 1035–1041.
Führer D., Lachmund P., Nebel I. and Paschke R. 2003 The thyrotropin receptor mutation database: Update 2003. Thyroid 13, 1123–1126.
Harland M., Mistry S., Bishop T. and Bishop J. 2001 A deep intronic mutation in CDKN2A is associated with disease in a subset of melanoma pedigrees. Hum. Mol. Genet. 10, 2679–2686.
Karges B., Krause G., Homoki J., Debtain K. M., de Roux N. and Karges W. 2005 TSH receptor mutation V509A causes familial hyperthyroidism by release of interhelical constraints between transmembrane helices TMH3 and TMH5. J. Endocrinol. 186, 377–385.
Khoo D. H., Parma J., Rajasoorya C., Ho S. C. and Vassart G. 1999 A germ line mutation of the thyrotropin receptor gene associated with thyrotoxicosis and mitral valve prolapse in a Chinese family. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 84, 1459–1462.
King K., Flinter F., Nihalani V. and Green P. 2002 Unusual deep intronic mutations in the COL4A5 gene cause X-linked Alport syndrome. Hum. Genet. 111, 548–554.
Kopp P. 2001 the TSH receptor and its role in thyroid disease. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 58, 1301–1322.
Kopp P., van Sande J., Parma J., Duprez L., Gerber H., Joss E. et al. 1995 Brief report: congenital hyperthyroidism caused by a mutation in the th yrotropin-receptor gene. N. Eng. J. Med. 332, 150–154.
Lee Y. S., Poh L. and Loke K. Y. 2002 An activating mutation of the thyrotropin receptor gene in hereditary non-autoimmune hyperthyroidism. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 15, 211–215.
LinksBrix T. H., Petersen H. C., Iachine I. and Hegedus L. 2003 Preliminary evidence of genetic anticipation in Graves’ disease. Thyroid 13, 447–451.
Liu Z., Sun Y., Dong Q., He M., Cheng C. H. and Fan F. 2008 A novel TSHR gene mutation (Ile691Phe) in a Chinese family causing autosomal dominant non-autoimmune hyperthyroidism. J. Hum. Genet. 53, 475–478.
Ludgate M. E. and Vassart G. 1995 The thyrotropin receptor as a model to illustrate receptor and receptor antibody diseases. Baillieres Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 9, 95–113.
Nishihara E., Nagayama Y., Amino N., Hishinuma A., Takano T., Yoshida H. et al. 2007 A novel thyrotropin receptor germline mutation (Asp617Tyr) causing hereditary hyperthyroidism. J. Endocrinol. 54, 927–934.
Nwosu B. U., Gourgiotis L., Gershengorn M. C. and Neumann S. 2006 A novel activating mutation in transmembrane helix 6 of the thyrotropin receptor as cause of hereditary non-autoimmune hyperthyroidism. Thyroid 16, 505–512.
Pagani F. and Baralle F. 2004 genomic variants in exons and introns: identifying the splicing spoilers. Nat. Rev. Genet. 5, 389–396.
Raponi M., Upadhyaya M. and Baralle D. 2006 Functional splicing assay shows a pathogenic intronic mutation in neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) due to intronic sequence exonization. Hum. Mut. 27, 294–295.
Ringkananont U., Van Durme J., Montanelli L., Ugrasbul F., Yu Y. M., Weiss R. E. et al. 2006 Repulsive separation of the cytoplasmic ends of transmembrane helices 3 and 6 is linked to receptor activation in a novel thyrotropin receptor mutant (M626I). Mol. Endocrinol. 20, 893–903.
Sakamoto O., Ohura T., Katsushima Y., Fujiwara I., Ogawa E., Miyabayashi S. and Iinuma K. 2001 A novel intronic mutation of the TAZ (G4.5) gene in a patient with Barth syndrome: creation of a 5′ splice site with variant GC consensus and elongation of the upstream exon. Hum. Genet. 109, 559–563.
Sanders J., Yasuo O., Roberts S., Maruyama M., Furmaniak J. and Smith B. 1997 understanding the thyrotropin receptor function-structure relationship. Baillieres Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 11, 451–479.
Schwab K. O., Sohlemann P., Gerlich M., Broecker M., Petrykowski W., Holzapfel H. P. et al. 1996 Mutations of the TSH receptor as cause of congenital hyperthyroidism. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 104, 124–128.
Tonacchera M., Van Sande J., Cetani F., Swillens S., Schvartz C., Winiszewski P. et al. 1996 Functional characteristics of three new germline mutations of the thyrotropin receptor gene causing autosomal dominant toxic thyroid hyperplasia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 81, 547–554.
Vaidya B., Campbell V., Tripp J. H., Spyer G., Hattersley A. T. and Ellard S. 2004 Premature birth and low birth weight associated with non autoimmune hyperthyroidism due to an activating thyrotropin receptor gene mutation. Clin. Endocrinol. 60, 711–718.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ismail, S.I., Mahmoud, I.S., Al-Ardah, M. et al. Detection of combined genomic variants in a Jordanian family with familial non-autoimmune hyperthyroidism. J Genet 88, 233–238 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-009-0032-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-009-0032-z