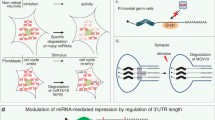
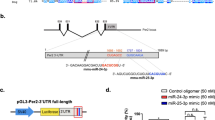
Abstract
MicroRNA (miRNA) is a recently discovered new class of small RNA molecules that have a significant role in regulating gene and protein expression. These small RNAs (∼22 nt) bind to 3′ untranslated regions (3′ UTRs) and induce degradation or repression of translation of their mRNA targets. Hundreds of miRNAs have been identified in various organisms and have been shown to play a significant role in development and normal cell functioning. Recently, a few studies have suggested that miRNAs may be an important regulators of circadian rhythmicity, providing a new dimension (posttranscriptional) of our understanding of biological clocks. Here, we describe the mechanisms of miRNA regulation, and recent studies attempting to identify clock miRNAs and their function in the circadian system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar R. A., Reddy A. B., Maywood E. S., Clayton J. D., King V. M., Smith A. G. et al. 2002 Circadian cycling of the mouse liver transcriptome, as revealed by cDNA microarray, is driven by the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Curr. Biol. 12, 540–550.
Alabadi D., Oyama T., Yanovsky M. J., Harmon F. G., Mas P. and Kay S. A. 2001 Reciprocal regulation between TOC1 and LHY/CCA1 within the Arabidopsis circadian clock. Science 293, 880–883.
Ambros V. 2004 The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431, 350–355.
Ambros V., Bartel B., Bartel D. P., Burge C. B., Carrington J. C., Chen X. et al. 2003 A uniform system for microRNA annotation. RNA 9, 277–279.
Behm-Ansmant I., Rehwinkel J., Doerks T., Stark A., Bork P. and Izaurralde E. 2006 mRNA degradation by miRNAs and GW182 requires both CCR4:NOT deadenylase and DCP1:DCP2 decapping complexes. Genes Dev. 20, 1885–1898.
Bernstein E., Caudy A. A., Hammond S. M. and Hannon G. J. 2001 Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 409, 363–366.
Bohnsack M. T., Czaplinski K. and Gorlich D. 2004 Exportin 5 is a RanGTP-dependent dsRNA-binding protein that mediates nuclear export of pre-miRNAs. RNA 10, 185–191.
Brennecke J., Stark A., Russell R. B. and Cohen S. M. 2005 Principles of microRNA-target recognition. PLoS Biol. 3, e85.
Bushati N. and Cohen S. M. 2007 microRNA functions. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 23, 175–205.
Ceriani M. F., Hogenesch J. B., Yanovsky M., Panda S., Straume M. and Kay S. A. 2002 Genome-wide expression analysis in Drosophila reveals genes controlling circadian behavior. J. Neurosci. 22, 9305–9319.
Cheng H. Y., Papp J. W., Varlamova O., Dziema H., Russell B., Curfman J. P. et al. 2007 microRNA modulation of circadianclock period and entrainment. Neuron 54, 813–829.
Claridge-Chang A., Wijnen H., Naef F., Boothroyd C., Rajewsky N. and Young M. W. 2001 Circadian regulation of gene expression systems in the Drosophila head. Neuron 32, 657–671.
Crosthwaite S. K. 2004 Circadian clocks and natural antisense RNA. FEBS Lett. 567, 49–54.
Darlington T. K., Wager-Smith K., Ceriani M. F., Staknis D., Gekakis N., Steeves T. D. et al. 1998 Closing the circadian loop: CLOCK-induced transcription of its own inhibitors per and tim. Science 280, 1599–1603.
Davis C. J., Bohnet S. G., Meyerson J. M. and Krueger J. M. 2007 Sleep loss changes microRNA levels in the brain: a possible mechanism for state-dependent translational regulation. Neurosci. Lett. 422, 68–73.
Denli A. M., Tops B. B., Plasterk R. H., Ketting R. F. and Hannon G. J. 2004 Processing of primary microRNAs by the microprocessor complex. Nature 432, 231–235.
Didiano D. and Hobert O. 2006 Perfect seed pairing is not a generally reliable predictor for miRNA-target interactions. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13, 849–851.
Duffield G. E. 2003 DNA microarray analyses of circadian timing: the genomic basis of biological time. J. Neuroendocrinol. 15, 991–1002.
Dunlap J. C. 1999 Molecular bases for circadian clocks. Cell 96, 271–290.
Esau C., Davis S., Murray S. F., Yu X. X., Pandey S.K., Pear M. et al. 2006 miR-122 regulation of lipid metabolism revealed by in vivo antisense targeting. Cell Metab. 3, 87–98.
Farh K. K., Grimson A., Jan C., Lewis B. P., Johnston W. K., Lim L. P. et al. 2005 The widespread impact of mammalian MicroRNAs on mRNA repression and evolution. Science 310, 1817–1821.
Gallego M. and Virshup D. M. 2007 Post-translational modifications regulate the ticking of the circadian clock. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 139–148.
Giraldez A. J., Mishima Y., Rihel J., Grocock R. J., Van Dongen S., Inoue K. et al. 2006 Zebrafish MiR-430 promotes deadenylation and clearance of maternal mRNAs. Science 312, 75–79.
Green C. B., Nicholas D., Shihoko K., Carl A. S., Joseph F., David L. et al. 2007 Loss of nocturnin, a circadian deadenylase, confers resistance to hepatic steatosis and diet-induced obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 9888–9893.
Griffiths-Jones S., Saini H. K., van Dongen S. and Enright A. J. 2008 miRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, 154–158.
Grimson A., Farh K. K., Johnston W. K., Garrett-Engele P., Lim L. P. and Bartel D. P. 2007 MicroRNA targeting specificity in mammals: determinants beyond seed pairing. Mol. Cell 27, 91–105.
Grun D., Wang Y. L., Langenberger D., Gunsalus K. C. and Rajewsky N. 2005 microRNA target predictions across seven Drosophila species and comparison to mammalian targets. PLoS Comput. Biol. 1, e13.
Han S., Kim T., Ha D. and Kim K. 2005 Rhythmic expression of adenylyl cyclase VI contributes to the differential regulation of serotonin N-acetyltransferase by bradykinin in rat pineal glands. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 38228–38234.
Hardin P. E., Hall J. C. and Rosbash M. 1990 Feedback of the Drosophila period gene product on circadian cycling of its messenger RNA levels. Nature 343, 536–540.
Hayama R. and Coupland G. 2003 Shedding light on the circadian clock and the photoperiodic control of flowering. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 6, 13–19.
Hsu P. W. C., Huang H., Hsu S., Lin L., Tsou A., Tseng C. et al. 2006 miRNAMap: genomic maps of microRNA genes and their target genes in mammalian genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, D135–139.
Humphreys D. T., Westman B. J., Martin D. I. and Preiss T. 2005 MicroRNAs control translation initiation by inhibiting eukaryotic initiation factor 4E/cap and poly(A) tail function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 102, 16961–16966.
Impey S., McCorkle S. R., Cha-Molstad H., Dwyer J. M., Yochum G. S., Boss J. M. et al. 2004 Defining the CREB regulon: a genome-wide analysis of transcription factor regulatory regions. Cell 119, 1041–1054.
Jung J. H., Seo Y. H., Seo P. J., Reyes J. L., Yun J., Chua N. H. et al. 2007 The GIGANTEA-regulated microRNA172 mediates photoperiodic flowering independent of CONSTANS in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19, 2736–2748.
Karaganis S., Kumar V., Beremand P., Bailey M., Thomas T. and Cassone V. 2008 Circadian genomics of the chick pineal gland in vitro. BMC Genomics 9, 206.
Keegan K. P., Pradhan S., Wang J. P. and Allada R. 2007 Metaanalysis of Drosophila circadian microarray studies identifies a novel set of rhythmically expressed genes. PLoS Comput. Biol. 3, e208.
Kojima S., Gatfield D. and Green C. 2008 Nocturnin expression is regulated post-transcriptionally by miR-122. 20th meeting, Society for research on biological rhythms, Destin, Florida.
Kramer C., Loros J. J., Dunlap J. C. and Crosthwaite S. K. 2003 Role for antisense RNA in regulating circadian clock function in Neurospora crassa. Nature 421, 948–952.
Krek A., Grun D., Poy M. N., Wolf R., Rosenberg L., Epstein E. J. et al. 2005 Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat. Genet. 37, 495–500.
Kume K., Zylka M. J., Sriram S., Shearman L. P., Weaver D. R., Jin X. et al. 1999 mCRY1 and mCRY2 are essential components of the negative limb of the circadian clock feedback loop. Cell 98, 193–205.
Landthaler M., Yalcin A. and Tuschl T. 2004 The human DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 8 and its D. melanogaster homolog are required for miRNA biogenesis. Curr. Biol. 14, 2162–2167.
Lee K., Loros J. J. and Dunlap J. C. 2000 Interconnected feedback loops in the Neurospora circadian system. Science 289, 107–110.
Lee R. C., Feinbaum R. L. and Ambros V. 1993 The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75, 843–854.
Lee Y. S., Nakahara K., Pham J. W., Kim K., He Z., Sontheimer E. J. et al. 2004 Distinct roles for Drosophila Dicer-1 and Dicer-2 in the siRNA/miRNA silencing pathways. Cell 117, 69–81.
Lewis B. P., Shih I. H., Jones-Rhoades M. W., Bartel D. P. and Burge C. B. 2003 Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 115, 787–798.
Lin Y., Han M., Shimada B., Wang L., Gibler T. M., Amarakone A. et al. 2002 Influence of the period-dependent circadian clock on diurnal, circadian, and aperiodic gene expression in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 9562–9567.
Long D., Lee R., Williams P., Chan C. Y., Ambros V. and Ding Y. 2007 Potent effect of target structure on microRNA function. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 14, 287–294.
Matranga C., Tomari Y., Shin C., Bartel D. P. and Zamore P. D., 2005 Passenger-strand cleavage facilitates assembly of siRNA into Ago2-containing RNAi enzyme complexes. Cell 123, 607–620.
McDonald M. J. and Rosbash M. 2001 Microarray analysis and organization of circadian gene expression in Drosophila. Cell 107, 567–578.
Mishima Y., Giraldez A. J., Takeda Y., Fujiwara T., Sakamoto H., Schier A. F. et al. 2006 Differential regulation of germline mRNAs in soma and germ cells by zebrafish miR-430. Curr. Biol. 16, 2135–2142.
Miyoshi K., Tsukumo H., Nagami T., Siomi H. and Siomi M. C. 2005 Slicer function of Drosophila argonautes and its involvement in RISC formation. Genes Dev. 19, 2837–2848.
Mizoguchi T., Wright L., Fujiwara S., Cremer F., Lee K., Onouchi H. et al. 2005 Distinct roles of GIGANTEA in promoting flowering and regulating circadian rhythms in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17, 2255–2270.
Nottrott S., Simard M. J. and Richter J. D. 2006 Human let-7a miRNA blocks protein production on actively translating polyribosomes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13, 1108–1114.
Panda S., Antoch M. P., Miller B. H., Su A. I., Schook A. B., Straume M. et al. 2002 Coordinated transcription of key pathways in the mouse by the circadian clock. Cell 109, 307–320.
Petersen C. P., Bordeleau M. E., Pelletier J. and Sharp P. A. 2006 Short RNAs repress translation after initiation in mammalian cells. Mol. Cell 21, 533–542.
Pillai R. S., Bhattacharyya S. N., Artus C. G., Zoller T., Cougot N., Basyuk E. et al. 2005 Inhibition of translational initiation by Let-7 MicroRNA in human cells. Science 309, 1573–1576.
Rajewsky N. 2006 microRNA target predictions in animals. Nat. Genet. 38, 8–13.
Rana T. M. 2007 Illuminating the silence: understanding the structure and function of small RNAs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 23–36.
Reddy A. B., Karp N. A., Maywood E. S., Sage E. A., Deery M., O’Neill J. S. et al. 2006 Circadian orchestration of the hepatic proteome. Curr. Biol. 16, 1107–1115.
Samach A. and Coupland G. 2000 Time measurement and the control of flowering in plants. Bioessays 22, 38–47.
Schmid M., Uhlenhaut N. H., Godard F., Demar M., Bressan R., Weigel D. et al. 2003 Dissection of floral induction pathways using global expression analysis. Development 130, 6001–6012.
Shende V. R., Beremand P. D. and Cassone V. M. 2008 MicroRNA rhythms in the chick pineal gland. 20th meeting, Society for research on biological rhythms, Destin, Florida.
Stark A., Brennecke J., Bushati N., Russell R. B. and Cohen S. M. 2005 Animal microRNAs confer robustness to gene expression and have a significant impact on 3′UTR evolution. Cell 123, 1133–1146.
Storch K., Lipan O., Leykin I., Viswanathan N., Davis F. C., Wong W. H. et al. 2002 Extensive and divergent circadian gene expression in liver and heart. Nature 417, 78–83.
Ueda H. R., Matsumoto A., Kawamura M., Iino M., Tanimura T. and Hashimoto S. 2002 Genome-wide transcriptional orchestration of circadian rhythms in Drosophila. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 14048–14052.
Vasudevan S., Tong Y. and Steitz J. A. 2007 Switching from repression to activation: microRNAs can up-regulate translation. Science 318, 1931–1934.
Vella M. C., Choi E. Y., Lin S. Y., Reinert K. and Slack F. J. 2004a The C. elegans microRNA let-7 binds to imperfect let-7 complementary sites from the lin-41 3′UTR. Genes Dev. 18, 132–137.
Vella M. C., Reinert K. and Slack F. J. 2004b Architecture of a validated microRNA::target interaction. Chem. Biol. 11, 1619–1623.
Wightman B., Ha I. and Ruvkun G. 1993 Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell 75, 855–862.
Wu L., Fan J. and Belasco J. G. 2006 MicroRNAs direct rapid deadenylation of mRNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 4034–4039.
Xu S., Witmer P. D., Lumayag S., Kovacs B. and Valle D. 2007 MicroRNA (miRNA) transcriptome of mouse retina and identification of a sensory organ-specific miRNA cluster. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 25053–25066.
Yang M., Lee J. E., Padgett R. W. and Edery I. 2008 Circadian regulation of a limited set of conserved microRNAs in Drosophila. BMC Genomics 9, 83.
Yanovsky M. J. and Kay S. A. 2003 Living by the calendar: how plants know when to flower. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 4, 265–275.
Zheng X. and Sehgal A. 2008 Probing the relative importance of molecular oscillations in the circadian clock. Genetics 178, 1147–1155.
Zuker M. 2003 Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 3406–3415.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pegoraro, M., Tauber, E. The role of microRNAs (miRNA) in circadian rhythmicity. J Genet 87, 505–511 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-008-0073-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-008-0073-8