Abstract
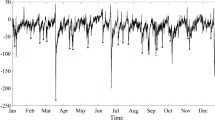
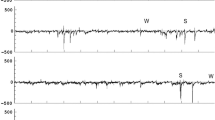
Potential analysis (PA) method is used to investigate the randomness or stochastic noise in 1-minute Dst and SYM-H data during highly disturbed as well as solar minimum quiet periods. This method is helpful in understanding the behaviour of a system whose internal parameters are unknown. The effect of random noise is exhibited in the number of wells in the potential function and in the bifurcation of states. Higher the number of state, higher the effect of random noise in the system. Our study focuses on PA of 12 intense geomagnetic storms of solar cycle (SC) 23 with peak Dst ≤ –200 nT and 12 quiet events with Dst ≥ –50 nT during solar minimum periods, using 1-minute Dst and SYM-H data for a period of 10 days each. Storm phases were least affected by random noise, while undisturbed periods were episodes of higher noisy states. Random noise in the indices can be attributed to different factors, including the effect of solar wind dynamic pressure on Dst estimation, contribution of different ion species to ring current, storm time super substorms, etc. Role of other factors is subjected to further analysis.
Research highlights
-
Different noisy states of Dst and SYM-H indices during disturbed and noisy periods are studied using the method of potential analysis.
-
Storm phases are found to be least affected by noise
-
Pre-storm and post storm periods transit to higher noisy states from noiseless storm phases.
-
Solar minimum quiet periods are episodes of higher random noise compared to other disturbed periods.
-
Random noise in the indices can be attributed to different factors like SW dynamic pressure, geomagnetic energy, ion contributions to ring currents, storm time substorms etc.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberti T, Consolini G, De Michelis P, Laurenza M and Marcucci M F 2018 On fast and slow Earth’s magnetospheric dynamics during geomagnetic storms: A stochastic Langevin approach; J. Space Weather Space Clim. 8(A56) 1–14, https://doi.org/10.1051/swsc/2018039.
Bayanjargal G 2015 The total energy of geomagnetic field; Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 1 29–33, https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-015-0006-y.
Bhaskar A and Vichare G 2019 Forecasting of SYMH and ASYH indices for geomagnetic storms of solar cycle 24 including St. Patrick’s day, 2015 storm using NARX neural network; J. Space Weather Space Clim. 9(A12), https://doi.org/10.1051/swsc/2019007.
Burton R K, McPherron R L and Russell C T 1975 An empirical relationship between interplanetary conditions and Dst; J. Geophys. Res. 80(31) 4204–4214, https://doi.org/10.1029/ja080i031p04204.
Campbell W H 1989 An introduction to quiet daily geomagnetic fields; PAGEOPH 131(3) 315–331, https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00876831.
Daglis I A 2006 Geospace storm dynamics; Eff. Space Wea. Technol. Infrastruct. 176 27–42, https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-2754-0_2.
Dasso S, Gómez D and Mandrini C H 2002 Ring current decay rates of magnetic storms: A statistical study from 1957 to 1998; J. Geophys. Res. 107(A5) 1–8, https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JA000430.
Dessler A J and Parker E N 1959 Hydromagnetic theory of geomagnetic storms; J. Geophys. Res. 64(12) 2239–2252, https://doi.org/10.1029/jz064i012p02239.
Fu S, Jiang Y and Zhang X 2020 Effects of solar activity on ionospheric ion upflow during geomagnetic quiet periods: DMSP observations; Open Astron. 29 158–167, https://doi.org/10.1515/astro-2020-0018.
Gannon J L and Love J J 2011 USGS 1-min Dst index; J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 73 323–334, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jastp.2010.02.013.
Gonzalez W D, Joselyn J A, Kamide Y, Kroehl H W, Rostoker G, Tsurutani B T and Vasyliunas V M 1994 What is a geomagnetic storm?; J. Geophys. Res. 99(A4) 5771–5792.
Gopalswamy N, Yashiro S, Michalek G, Xie H, Lepping R and Howard R A 2005 Solar source of the largest geomagnetic storm of cycle 23; Geophys. Res. Lett. 32(12) 1–5, https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL021639.
Gopinath S, Suji K J and Prince P R 2015 Information measures based analysis of complex solar wind-magnetosphere interaction dynamics during geomagnetic storms; Indian J. Phys. 89(8) 759–772, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-015-0655-2.
Greenspan M E and Hamilton D C 2000 A test of the Dessler–Parker–Sckopke relation during magnetic storms; J. Geophys. Res. 105(A3) 5419–5430, https://doi.org/10.1029/1999ja000284.
Ioannis A Daglis, Richard M Thorne, Wolfgang Baumjohann and Stefano Orsini 1999 The terrestrial ring current: Origin, formation, and decay; Rev. Geophys. 37(4) 407–438, https://doi.org/10.1029/1999RG900009.
Jayalekshmi G L, Prince P R and Satheesh Kumar K 2018 Potential analysis of sunspot parameters and behaviour of random noise; Indian J. Radio Space Phys. 46(2) 55–65.
Kakad B, Kakad A, Ramesh D S and Lakhina G S 2019 Diminishing activity of recent solar cycles (22–24) and their impact on geospace; J. Space Weather Space Clim. 9 1–15, https://doi.org/10.1051/swsc/2018048.
Kwasniok F and Lohmann G 2009 Deriving dynamical models from paleoclimatic records: Application to glacial millennial-scale climate variability; Phys. Rev. E 80(6) 1–9, https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.80.066104.
Livina V N, Kwasniok F and Lenton T M 2009 Potential analysis reveals changing number of climate states during the last 60 kyr; Clim. past. 6 77–82, https://doi.org/10.5194/cpd-5-2223-2009.
Livina V N, Kwasniok F, Lohmann G, Kantelhardt J W and Lenton T M 2011 Changing climate states and stability: From Pliocene to present; Clim. Dyn. 37 2437–2453, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-010-0980-2.
Loewe C A and Prolss G W 1997 Classification and mean behavior of magnetic storms; J. Geophys. Res. 102(A7) 14,209–14,213, https://doi.org/10.1029/96JA04020.
Hirota Marina, Holmgren Milena, Van Nes Egbert H and Scheffer Marten 2011 Global resilience of tropical forest; Science 334 232–235, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1210657.
Mayaud P N 1973 A hundred year series of geomagnetic data 1868–1967; IAGA Bull. (33) Paris IUGG Publications Office, pp. 3–8.
Oprea C, Mierla M, Beşliu-Ionescu D, Stere O and Mariş Muntean G 2013 A study of solar and interplanetary parameters of CMEs causing major geomagnetic storms during SC 23; Ann. Geophys. 31(8) 1285–1295, https://doi.org/10.5194/angeo-31-1285-2013.
Pandey S K and Dubey S C 2009 Characteristic features of large geomagnetic storms observed during solar cycle 23; Indian J. Radio Space Phys. 38(6) 305–312.
Paper O, Rathore B S, Kaushik S C, Bhadoria R S, Parashar K K and Gupta D C 2012 Sunspots and geomagnetic storms during solar cycle-23; Indian J. Phys. 86(7) 563–567, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-012-0106-2.
Parker E N 1962 Dynamics of geomagnetic storm; Space Sci. Rev. 1 62–99, https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00174636.
Rathore B S, Kaushik S C, Bhadoria R S, Parashar K K and Gupta D C 2012 Sunspots and geomagnetic storms during solar cycle-23; Indian J. Phys. 86 563–567, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-012-0106-2.
Sandhu J K, Rae I J, Freeman M P, Forsyth C, Gkioulidou M, Reeves G D, Spence H E, Jackman C M and Lam M M 2018 Energization of the ring current by substorms; J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys. 123(10) 8131–8148, https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JA025766.
Sckopke N 1966 A general relation between the energy of trapped particles and the disturbance field near the Earth; J. Geophys. Res. 71(13) 3125–3130, https://doi.org/10.1029/JZ071i013p03125.
Singh S, Panday A C, Singh K and Mishra A P 2017 Effect of geomagnetic storms and their association with solar wind velocity and IMF during solar cycle 23 and 24; Int. J. Pure Appl. Phys. 13(1) 35–43.
Smith A W, Forsyth C, Rae J, Rodger C J and Freeman M P 2021 The impact of sudden commencements on ground magnetic field variability: Immediate and delayed consequences; Space Weather 19(7) 1–17, https://doi.org/10.1029/2021SW002764.
Sokol-Kutylovskii O L 2019 Amplitude–frequency characteristics of geomagnetic noise at low frequencies; Izv.- Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 55(8) 905–912, https://doi.org/10.1134/S0001433819080103.
Sugiura M 1964 Hourly values of equatorial Dst for the IGY; Ann. Int. Geophys. Yr. 35 9–45.
Sun W and Akasofu S I 2000 On the formation of the storm-time ring current belt; J. Geophys. Res. 105(A3) 5411–5418, https://doi.org/10.1029/1999ja000339.
Tsurutani B T, Hajra R, Echer E and Gjerloev J W 2015 Extremely intense (SML ≤2500 nT) substorms: Isolated events that are externally triggered?; Ann. Geo-Phys. 33(5) 519–524, https://doi.org/10.5194/angeo-33-519-2015.
Wanliss J and Showalter K 2006 High-resolution global storm index: Dst versus SYM-H; J. Geophys. Res. 111(2) 1–10, https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JA011034.
Wanliss J A 2004 Nonlinear variability of SYM-H over two solar cycles; Earth Planet. Space 56(5) 13–16, https://doi.org/10.1186/bf03352507.
Yao X, Zhang S, Teng Y and Yang D 2018 Background noise estimation of the geomagnetic signal; Geosci. Instrum. Method. Data Syst. 7(3) 189–193, https://doi.org/10.5194/gi-7-189-2018.
Zerbo J, Amory-Mazaudier C and Ouattara Frederic 2013 Geomagnetism during solar cycle 23: Characteristics; J. Adv. Res. 4(3) 265–274, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2012.08.010.
Acknowledgement
We thank NASA SPDF OMNIWEB data explorer, USGS Geomagnetism Program: (https://doi.org/10.5066/P9V6WO7G.), CDAWeb-Space Physics Data Facility, NASA for providing the data for carrying out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The first author has carried out all data collection and analysis part, and the second author has performed all interpretations of the results obtained.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T Narayana Rao
Correesponding editor: T Narayana Rao
Appendix
Appendix
Correlation of SW pressure with storm indices.
Event | Correlation of SW pressure with | |
|---|---|---|
SYM-H | Dst | |
1 | –0.308 | –0.407 |
2 | Data gap | |
3 | –0.564 | –0.593 |
4 | –0.062 | –0.157 |
5 | –0.190 | –0.193 |
6 | –0.724 | –0.736 |
7 | 0.240 | 0.200 |
8 | –0.361 | –0.420 |
9 | –0.331 | –0.354 |
10 | 0.305 | 0.345 |
11 | –0.278 | –0.233 |
12 | –0.036 | 0.007 |
Average correlation | –0.210 | –0.231 |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nair, D.R., Prince, P.R. Investigation of random noise in SYM-H and Dst during intense geomagnetic storms and solar quiet days of SC 23 using the method of potential analysis. J Earth Syst Sci 132, 172 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-023-02168-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-023-02168-0