Abstract
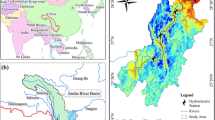
The present paper attempts to quantify the amount of soil loss occurring in the Mayurakshi River basin of eastern India with the help of the empirical Revised Universal Soil Equation (RUSLE) Model. The areas of high erosion were identified and their spatial and temporal patterns and trends were monitored for the years 2008 and 2018. It was observed that the average soil loss increased by about 6% from 2008 to 2018. Among a variety of causal factors, the Shannon’s Entropy Index used in this study has identified the slope length and steepness factor (LS factor) as the most significant causal factor of erosion in the studied river basin. One of the novel approaches used in this study is the application of landscape ecological metrics in the domain of temporal erosion monitoring. An important conclusion drawn from the analysis is that the patches of high and moderate erosion are increasing significantly in terms of areal extent, whereas the extent of the patches of low erosion is decreasing with time. Therefore, appropriate management strategies prioritised on the high and moderate erosion patches are the need of the hour.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera F, Valenzuela L M and Botequilha-Leitao A 2011 Landscape metrics in the analysis of urban landuse patterns: A case study in a Spanish metropolitan area; Landscape Urban Plan 99(3–4) 226–238, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2010.10.004.
Aneseyee A B, Elias E, Soromessa T and Feyisa G L 2020 Land use/land cover change effect on soil erosion and sediment delivery in the Winike watershed, Omo Gibe Basin, Ethiopia; Sci. Total Environ. 728 138776, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138776.
Arnoldus H M J 1980 An Approximation of the rainfall factor in the universal soil loss equation; In: Assessment of erosion (eds) De Boodt M and Gabriels D, John Wiley & Sons Limited, Chichester, UK, pp. 127–132.
Atoma H, Suryabhagavan K V and Balakrishan M 2020 Soil erosion assessment using RUSLE model and GIS in Huluka watershed, Central Ethiopia; Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 6(12), https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-020-00365-z.
Balasubramani K, Veena M, Kumaraswamy K and Saravanabavan V 2015 Estimation of soil erosion in a semi-arid watershed of Tamil Nadu (India) using revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) model through GIS; Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 1(10), https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-015-0015-4.
Blanco-Canqui H and Lal R 2008 Principles of soil conservation and management; Springer-Dordrecht, Netherlands, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-8709-7.
Butt M J, Waqas A and Mahmood R 2010 The combined effect of vegetation and soil erosion in the water resource management; Water Resour. Manag. 24 3701–3714, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9627-7.
Chen Y, Wang F, Liu G, Yu X, Jia G and Gan P 2011 Modified vegetation-erosion dynamics model and its application in typical watersheds in the Loess Plateau; Int. J. Sedim. Res. 26 78–86, https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6279(11)60077-2.
Das A, Agrawal R and Mohan S 2015 Topographic correction of ALOS-PALSAR images using InSAR-derived DEM; Geocarto Int. 30(2) 145–153, https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2014.883436.
Das B, Paul A, Bordoloi R, Tripathi O P and Pandey P K 2018 Soil erosion risk assessment of hilly terrain through integrated approach of RUSLE and geospatial technology: A case study of Tirap District, Arunachal Pradesh; Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 4(1) 373–381, https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-018-0435-z.
David W P 1988 Soil and water conservation planning: Policy issues and recommendations; J. Phillip. Dev. 15 47–84.
Diaz-Varela E R, Marey-Perez M F, Rigueiro-Rodriguez A and Alvarez-Alvarez P 2009 Landscape metrics for characterisation of forest landscapes in a sustainable management framework: Potential application and prevention of misuse; Ann. for. Sci. 66 301, https://doi.org/10.1051/forest/2009004.
Dutta M, Saikia J, Taffarel S R, Waanders F B, Medeiros D, Cutruneo C M, Silva L F O and Saikia B K 2017 Environmental assessment and nano-mineralogical characterisation of coal, overburden, and sediment from Indian coal mining acid drainage; Geosci. Front. 8(6) 1285–1297, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2016.11.014.
Ebabu K, Tsunekawa A, Haregeweyn N, Tsubo M, Adgo E, Fenta A A, Meshesha D T, Berihun M L, Sultan D, Vanmaercke M, Panagos P, Borrelli P, Langendoen E J and Poesen J 2022 Global analysis of cover management and support practice factors that control soil erosion and conservation; Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 10(2) 161–176, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2021.12.002.
Eekhout J P C and de Vente J 2022 Global impact of climate change on soil erosion and potential for adaptation through soil conservation; Earth-Sci. Rev. 226 103921, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2022.103921.
Erencin Z 2000 C-factor mapping using remote sensing and GIS: A case study of Lom Sak/Lom Kao, Thailand; Unpublished thesis submitted for the degree of Professional Masters in Geoinformation Science and Earth Observation to the Department of Geoinformatics and Remote Sensing of the Institute of Geography at the Justus-Liebig-Universität Giessen, Germany.
Eniyew S, Teshome M, Sisay E and Bezabih T 2021 Integrating RUSLE model with remote sensing and GIS for evaluation soil erosion in Telkwonz Watershed, Northwestern Ethiopia; Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 24 1000623, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2021.100623.
FAO 2019 Soil erosion: The greatest challenge to sustainable soil management. Rome; 100p, Licence: CC BYNC-SA 3.0 IGO.
Gebremicael T G, Mohamed Y A, Betrie G D, van der Zaag P and Teferi E 2013 Trend analysis of runoff and sediment fluxes in the Upper Blue Nile basin: A combined analysis of statistical tests, physically-based models and landuse maps; J. Hydrol. 482 57–68, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.12.023.
Graham E H 1942 Soil erosion as an ecological process; Sci. Mon. 55(1) 42–51, http://www.jstor.org/stable/17699.
Griffin M L, Beasley D B, Fletcher J J and Foster G R 1988 Estimating soil loss on the topographically non-uniform field and farm units; J. Soil Water Conserv. 43(4) 326–331.
Guerra A J T, Fullen M A, Jorge M, Bezerra J F R and Shokr M S 2017 Slope processes, mass movement and soil erosion: A review; Pedosphere 27(1) 27–41, https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(17)60294-7.
Gupta S, Roy M and Sarkar A 2013 Identification of urban sprawl dynamics in a rapid growing city using GIS; Int. J. Geomat. Geosci. 3(3) 486–499.
Haile G W and Fetene M 2012 Assessment of soil erosion hazard in Kilie catchment, East Shoa, Ethiopia; Land Degrad. Dev. 23(3) 293–306, https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.1082.
Hoyos N 2005 Spatial modeling of soil erosion potential in a tropical watershed of the Colombian Andes; Catena 63(1) 85–108, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2005.05.012.
Islam A and Deb Barman S 2020 Drainage basin morphometry and evaluating its role on flood-inducing capacity of tributary basins of Mayurakshi River, India; SN Appl. Sci. 2 1087, https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2839-4.
Islam A and Ghosh S 2021 Economic transformation in the wake of flood: A case of the lower stretch of Mayurakshi River Basin, India; Environ. Dev. Sustain. 23 15,550–15,590, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01310-6.
Islam A and Sarkar B 2020 Analysing flood history and simulating the nature of future floods using Gumbel method and Log-Pearson Type III: The case of the Mayurakshi River Basin, India; Bull. Geogr. Phys. Geog. Ser. 19 43–69, https://doi.org/10.2478/bgeo-2020-0009.
Janse R J, Hoekstra T, Jager K J, Zoccali C, Tripepi G, Dekker F W and van Diepen M 2021 Conducting correlation analysis: Important limitations and pitfalls; Clin. Kidney J. 14(10) 2332–2337, https://doi.org/10.1093/ckj/sfab085.
Jenks G F 1967 The data model concept in statistical mapping; Int. Yearb. Cartogr. 7 186–190.
Jug D, Durdevic B, Birkas M, Brozovic B, Lipiec J, Vukandinovic V and Jug I 2019 Effect of conservation tillage on crop productivity and nitrogen use efficiency; Soil Till. Res. 194 104327, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.104327.
Kolli M K, Opp C and Groll M 2021 Estimation of soil erosion and sediment yield concentration across the Kolleru Lake catchment using GIS; Environ. Earth Sci. 80 161, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09443-7.
Kumar S and Gupta S 2016 Geospatial approach in mapping soil erodibility using CartoDEM – A case study in hilly watershed of Lower Himalayan Range; J. Earth Syst. Sci. 125 1463–1472, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-016-0738-2.
Lal R 2003 Soil erosion and the global carbon budget; Environ. Int. 29(4) 437–450, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(02)00192-7.
Lee S 2004 Soil erosion assessment and its verification using the universal soil loss equation and geographic information system: A case study at Boun, Korea; Environ. Geol. 45 457–465, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-003-0897-8.
Lee J H and Heo J H 2011 Evaluation of estimation methods for rainfall erosivity based on annual precipitation in Korea; J. Hydrol. 409 30–48, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.07.031.
Lorup J K and Styczen M 1990 Soil erosion modelling; In: Distributed hydrological modelling (eds) Abbott M B and Refsgaard J C, Water Science and Technology Library, Springer, Dordrecht, 22 93–120, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-0257-2_6.
McCool D K, Foster G R, Mutchler C K and Meyer L D 1989 Revised slope length factor for the universal soil loss equation; T. Am. Soc. Agr. Biol. Eng. 32 1571–1576, https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.31192.
Milliman J D and Syvitski J P M 1992 Geomorphic/tectonic control of sediment discharge to the ocean: The importance of small mountainous rivers; J. Geol. 100(5) 525–544, https://doi.org/10.1086/629606.
Mitchell T D, Hulme M and New M 2003 Climate data for political areas; Area 34 109–112.
Moore I D and Burch G J 1986a Modelling erosion and deposition: Topographic effects; T. Am. Soc. Agr. Biol. Eng. 29(6) 1624–1630, https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.30363.
Moore I D and Burch G J 1986b Physical basis of the length-slope factor in the universal soil loss equation; Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 50(5) 1294–1298, https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1986.03615995005000050042x.
Mulumba L N and Lal R 2008 Mulching effects on selected soil physical properties; Soil Till. Res. 98(1) 106–111, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2007.10.011.
Mutua B M, Klik A and Loiskandl W 2006 Modelling soil erosion and sediment yield at a catchment scale: the case of Masinga catchment, Kenya; Land Degrad. Dev. 17(5) 557–570, https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.753.
Negese A, Fekadu E and Getnet H 2021 Potential soil loss estimation and erosion-prone area prioritisation using RUSLE, GIS, and remote sensing in Chereti Watershed, northeastern Ethiopia; Air Soil Water Res., https://doi.org/10.1177/1178622120985814.
Niipele J N and Chen J 2019 The usefulness of ALOS-PALSAR DEM data for drainage extraction in semi-arid environments in the Iishana sub-basin; J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 21 57–67, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2018.11.003.
Oliveira M L S, Saikia B K, Da Boit K, Pinto D, Tutikian B F and Silva L F O 2019 River dynamics and nanoparticles formation: A comprehensive study on the nanoparticle geochemistry of suspended sediments in the Magdalena River, Caribbean Industrial Area; J. Clean. Prod. 213 819–824, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.230.
Pandey A, Mathur A, Mishra S K and Mal B C 2009 Soil erosion modelling of a Himalayan Watershed using RS and GIS; Environ. Earth Sci. 59 399–410, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0038-0.
Pavlis N K, Holmes S A, Kenyon S C and Factor J K 2012 The development and evaluation of the Earth Gravitational Model 2008 (EGM 2008); J. Geophys. Res. 117 B04406, https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JB008916.
Pimentel D and Kounang N 1998 Ecology of soil erosion in ecosystems; Ecosystems 1 416–426, https://doi.org/10.1007/s100219900035.
Renard K G and Foster G R 1983 Soil conservation: Principles of erosion by water; In: Dryland agriculture (eds) Dregne H E and Willis W O, Agri. Monog. No. 23.
Renard K G and Freimund J R 1994 Using monthly precipitation data to estimate the R factor in the revised USLE; J. Hydrol. 157 287–306, https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(94)90110-4.
Renard K G, Foster G R, Weesies G A, McCool D K and Yoder D C 1997 Predicting soil erosion by water: A guide to conservation planning with the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE). Agriculture Handbook No. 703, USDA, Washington DC.
Rogers A S and Kearney M S 2004 Reducing signature variability in unmixing coastal marsh Thematic Mapper scenes using spectral indices; Int. J. Remote Sens. 25(12) 2317–2335, https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160310001618103.
Roy S, Das S and Sengupta S 2022 Predicting terrain erosion susceptibility from drainage basin morphometry using ALOS-PALSAR DEM: Analysis from PCA-weighted AHP approach in a river system of Eastern India; Environ. Dev. Sustain., https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02450-z.
Sarkar A, Roy L, Das S and Sengupta S 2021 Fluvial response to active tectonics: Analysis of DEM-derived longitudinal profiles in the Rangit River Basin, Eastern Himalayas, India; Environ. Earth Sci. 80 258, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09561-2.
Setegn S G, Dargahi B, Srinivasan R and Melesse A M 2010 Modeling of sediment yield from Anjeni-gauged watershed, Ethiopia using SWAT model; J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 46 514–526, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.2010.00431.x.
Sharda V N, Mandal D and Ojasvi P R 2013 Identification of soil erosion risk areas for conservation planning in different states of India; J. Environ. Biol. 34 219–226.
Shannon C E 1948 A mathematical theory of communication; Bell Syst. Tech. J. 27 379–423.
Steinhoff-Knopp B, Kuhn T K and Burkhard B 2021 The impact of soil erosion on soil-related ecosystem services: Development and testing a scenario-based assessment approach; Environ. Monit. Assess. 193 274, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08814-0.
Sudhira H S, Ramachandra T V and Jagadish K S 2003 Urban sprawl pattern recognition and modelling using GIS; Proceedings of Map India 2003, New Delhi.
Thomas J, Joseph S and Thrivikramji K P 2018 Assessment of soil erosion in a tropical mountain river basin of the southern western ghat, India using RUSLE and GIS; Geosci. Front. 9 893–906, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2017.05.011.
Turner M G 2005 Landscape ecology in North America: Past, present, and future; Ecology 86(8) 1967–1974, https://doi.org/10.1890/04-0890.
Van Remortel R D, Hamilton M E and Hickey R J 2001 Estimating the LS factor for RUSLE through iterative slope length processing of digital elevation data within Arc lnfo grid; Cartography 30 27–35, https://doi.org/10.1080/00690805.2001.9714133.
Walling D E and Webb B W 1996 Erosion and sediment yield: A global overview; In: Erosion and sediment yield: Global and Regional Perspectives (eds) Walling D E and Webb B W, Proceedings of the Exeter Symposium, July 1996, IAHS Publ. No. 236.
Wartmann F M, Stride C B, Keinast F and Hunziker M 2021 Relating landscape ecological metrics with public survey data on perceived landscape quality and place attachment; Landscape Ecol. 36 2367–2393, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-021-01290-y.
Wischmeier W H and Smith D D 1978 Predicting rainfall erosion losses: A guide to conservation planning; Agriculture Handbook No. 537, USDA, Washington, DC.
Xiao Y, Xiao Q, Xiong Q and Yang Z 2020 Effects of ecological restoration measures on soil erosion risk in the Three Gorges Reservoir area since the 1980s; GeoHealth 4(12) e2020GH000274, https://doi.org/10.1029/2020GH000274.
Wei C, Dong X, Yu D, Zhang T, Zhao W, Ma Y and Su B 2022 Spatio-temporal variations of rainfall erosivity, correlation of climatic indices and influence on human activities in the Huaihe River Basin, China; Catena 217 106486, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2022.106486.
Zhang H, Yang Q, Li R, Liu Q, Moore D, He P, Ritesma C J and Geissen V 2013 Extension of a GIS procedure for calculating the RUSLE equation LS factor; Comput. Geosci. 52 177–188, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2012.09.027.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude for the fellowship received by the first author from The University of Burdwan, West Bengal (Ref. No. FC(Sc.) RS/SF/GEO./2021-22/WFH-60). Acknowledgements are also due to Dr George Mathew, Associate Editor, Journal of Earth System Science, and two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments, which helped in improving the clarity of an earlier version of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Subha Roy initiated this research, designed the methodology, made field investigations and laboratory analysis and analysed the data. Souvik Das accompanied in the fieldwork and carried out the analysis of satellite imageries. Somasis Sengupta supervised the entire research work, was involved in designing the methodology of this work and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Sukhendu Mistry accompanied in the field and was involved in the manuscript editing. Jaya Chatterjee was involved in the preparation of maps and GIS analysis.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by George Mathew
Supplementary material pertaining to this article is available on the Journal of Earth System Science website (http://www.ias.ac.in/Journals/Journal_of_Earth_System_Science).
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, S., Das, S., Sengupta, S. et al. Monitoring the temporal dimension of soil erosion in Mayurakshi Basin, India: A novel approach integrating RUSLE, Shannon’s entropy and landscape ecological metrics. J Earth Syst Sci 131, 249 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-022-02006-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-022-02006-9