Abstract
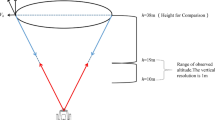
This research describes and interprets spatial variation in near-surface wind speed around a large scale wind generation operation in a desert steppe environment of Inner Mongolia. Wind speeds were measured at five different heights and distances in front of and behind turbines and compared to that measured simultaneously from reference points immediately outside of the wind farm. The results showed that wind turbines clearly influence the spatial distribution of near-surface wind speed. Relative to reference points, near-surface wind velocity profiles measured at various distances from wind turbines followed a logarithmic distribution. The correlation coefficients for all points were above 0.95 except for a coefficient of 0.8278 corresponding to wind speeds measured 20 m in front of turbines. The wind speed increment rate at 20, 100, and 300 m in front of and behind turbines demonstrated the varying influence of turbines at different points. The area 100 m behind the turbine experienced maximum wind speeds at all height levels observed in the measurement area. The overall wind speed at 300 m distance was relatively low and variation nearest to the turbine was the most complex.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi S A, Abbasi T and Abbasi T 2016 Impact of wind-energy generation on climate: A rising spectre; Renew. Sustain. Energ. Rev. 59 1591–1598, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.262.
Abbasi T, Premalatha M, Abbasi T and Abbasi S A 2014 Wind energy: Increasing deployment, rising environmental concerns; Renew. Sustain. Energ. Rev. 31 270–288, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.11.019.
Alona A, Ralph R B, Susan E L, Stephen M, Nicholas O, Victoria S, Susan W and Jeanette W 2016 Ground-level climate at a peatland wind farm in Scotland is affected by wind turbine operation; Environ. Res. Lett. 11(4) 044024, http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/11/4/044024.
An D M 2010 Studies on the impact of wind electricity exploitation on ecological environment of Bashang area; J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 38(14) 7479–7480.
Bijian T, Donghai W, Xiang Z, Tao Z, Wenqian Z and Hong W 2017 The observed impacts of wind farms on local vegetation growth in northern China; Remote Sens. 9 332, https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9040332.
Geng X, Liming Z, Jeffrey M F, Somnath B R, Ronald A H and Matthew C C 2016 A case study of effects of atmospheric boundary layer turbulence, wind speed, and stability on wind farm induced temperature changes using observations from a field campaign; Clim. Dyn. 46(7–8) 2179–2196, https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2696-9.
Geng X and Liming Z 2017 Detecting wind farm impacts on local vegetation growth in Texas and Illinois using MODIS vegetation greenness measurements; Remote Sens. 9 698, https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070698.
Gu C J 2010 Main environmental problems of the wind power generation projects and the possible solution counter measures; J. Environ. Prot. Sci. 36(2) 89–91.
Jenell M W T, Guido C, Peggy A and Germana M 2012 Further evidence of impacts of large-scale wind farms on land surface temperature; Renew. Sustain. Energ. Rev. 16 6432–6437.
Keith D W, Decarolis J F, Denkenberger D C, Lenschow D H, Malyshev S L, Pacala S and Rasch P J 2004 The influence of large-scale wind power on global climate; Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 101(46) 16,115–16,120, http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0406930101.
Leung D Y C and Yang Y 2012 Wind energy development and its environmental impact: A review; Renew. Sustain. Energ. Rev. 16(1) 1031–1039, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2011.09.024.
Li Z L 2015 Effect of wind power site construction on soil nutrients and vegetation of the surrounding disturbed region; Res. Soil Water Conserv. 22(4) 5–6.
Li G Q, Zhang C H, Zhang L and Zhang M 2016 Effects of wind farms on grassland vegetation: A case study of Huitengliang wind farm; Inner Mongolia Sci. Geogr. Sin. 36(6) 959–964.
Kaoshan D, Anthony B, Chao L, Wei-Ning X and Zhenhua H 2015 Environmental issues associated with wind energy – A review; Renew. Energ. 75 911–921, https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2014.10.074.
Roy S B, Pacala S W and Walko R L 2004 Can large wind farms affect local meteorology? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 109(D19) 1–6, http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2004JD004763.
Sa R L 2015 The analysis of the effect of grassland-style wind farm to the ecological environment – Setting the wind farm in Baingol of Inner Mongolia as example; Inner Mongolia Sci. Tech. Econ. 24 46–47.
Saidur R, Rahim N A, Islam M R and Solangi K H 2011 Environmental impact of wind energy; Renew. Sustain. Energ. Rev. 15(5) 2423–2430, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2011.02.024.
Shifeng W and Sicong W 2015 Impacts of wind energy on environment: A review; Renew. Sustain. Energ. Rev. 49 437–443, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.04.137.
Somnath B R 2011 Simulating impacts of wind farms on local hydrometeorology; J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 99 491–498, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2010.12.013.
Song W L 2011 The research on the accumulated ecological research of the wind farm project to Yancheng natural protection area; Master’s thesis, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing.
Stull R B 1988 An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology; Kluwer Academic Publisher, New York.
Sun J C 2011 The study of ecological environment impact on the Million KW Wind Power Base project in Jiuquan city of Gansu Province; Master’s thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou.
Tennekes H 1972 The logarithmic wind profile; J. Atmos. Sci. 30 234–238.
Wang C and Prinn R G 2010 Potential climatic impacts and reliability of very large-scale wind farms; Atmos. Chem. Phys. 10 2053–2061.
Wang F Y, Bai Z F, Li Q P, Zhang Z and Wu W B 2011 The eco-influence and countermeasures of wind power generation in Inner Mongolia grassland; Environ. Dev. 23(10) 90–91.
Wu W Y, Zhang D S and Tian L H 2013 Variable characteristics of wind profile of the artificial sand dune in sandy land around the Qinghai lake; Res. Soil Water Conserv. 20(6) 162–167.
Wu Z R, Liu W W and Wang S L 2014 Analysis of potential impacts of wind power generation to local climate; Electric Power 47(6) 101–105.
Xie Y H 2015 Effects of wind power station on vegetation and soil properties; Master’s thesis, Hohhot, Inner Mongolia Normal University.
Xu R H 2014 The impact of wind farm on local micro meteorological environment in arid region-taking Zhurihe wind farm as an example; Master’s thesis, Hohhot, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University.
Xue X D, Lin H Y, Zhou C F, Xiao M X and Lin F 2012 The impact of wind power generation on the ecological environment – Illustrated by the example of Dalian; Environ. Dev. 24(4) 161–162, 165.
Yang F 2014 The research on impact of Inner Mongolia wind farms in typical steppe; Master’s thesis, Hohhot, Inner Mongolia University.
Zhang S H, Zhang X Y and Ma Y F 2015 The research on the effect of the wind farm in the draught area in summer to the near-surface wind space; J. Hydraul. Inner Mongolia 155 14–15.
Zhang S S 2012 Research on ecological environment impacts because of the wind power plant construction-take Huitengliang wind power plant as example; Master’s thesis, Hohhot, Inner Mongolia University.
Zhao J J 2011 The ecological environment effect of the wind farm and the remedy measures; Sci. Tech. Innovation 26 43.
Zhao Z C, Luo Y and Jiang Y 2011 Advances in assessment on impacts of wind farms upon climate change; Adv. Climate Change Res. 7(6) 400–406.
Zhou D D and Hu S R 2018 General situations of wind energy resources in Inner Mongolia and its exploitation; J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 32(5) 177–182.
Zhou X J, Tao S C and Yao K 1991 Advanced Aerophysics; Meteorology Press, Beijing.
Zhou X, Tian L H and Zhan D S 2018 Study on wind-prevention and sand-fixing benefits of different vegetation on the east coast dune of Qinghai lake; J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 32(8) 180–185.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the organizations and scientists, who provided support to the present study. We are also thankful to Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Scientific Research Project (NJZY16044) and the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Natural Science Foundation Project (2019MS03044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by N V Chalapathi Rao
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, D., Hu, S., Dang, X. et al. Local effects of wind turbines on near-surface wind speed in a desert steppe wind farm. J Earth Syst Sci 129, 139 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-020-01404-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-020-01404-1