Abstract
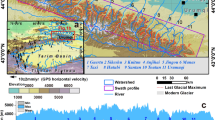
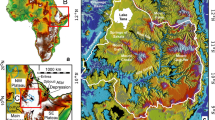
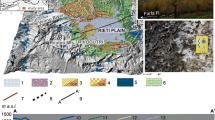
The present study is undertaken in the Kulsi River valley, a tributary of the Brahmaputra River that drains through the tectonically active Shillong Plateau in northeast India. Based on the fluvial geomorphic parameters and Landsat satellite images, it has been observed that the Kulsi River migrated 0.7–2 km westward in its middle course in the past 30 years. Geomorphic parameters such as longitudinal profile analysis, stream length gradient index (SL), ratio of valley floor width to valley height (Vf), steepness index (\(k_{s})\) indicate that the upstream segment of the Kulsi River is tectonically more active than the downstream segment which is ascribed to the tectonic activities along the Guwahati Fault. \(^{14}\hbox {C}\) ages obtained from the submerged tree trunks of the Chandubi Lake, which is located in the central part of the Kulsi River catchment suggests inundation (high lake levels) during 160 ± 50 AD, 970 ± 50 AD, 1190 ± 80 AD and 1520 ± 30 AD, respectively. These periods broadly coincide with the late Holocene strengthened Indian Summer Monsoon (ISM), Medieval Warm Period (MWP) and the early part of the Little Ice Age (LIA). The debris which clogged the course of the river in the vicinity of the Chandubi Lake is attributed to tectonically induced increase in sediment supply during high magnitude flooding events.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen J R L 1965 A review of the origin and characteristics of recent alluvial sediments; Sedimentology 5 89–191.
An Yin, Dubey C S, Webb A A G, Kelty T K, Grove M, Gehrels G E and Burgess W P 2010a Geologic correlation of the Himalayan orogen and Indian craton: Part 1. Structural geology, U–Pb zircon geochronology and tectonic evolution of the Shillong Plateau and its neighboring regions in NE India; Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 122 336–359.
Assine M L 2005 River avulsions on the Taquari mega fan, Pantanal wetland, Brazil; Geomorphology 70(3–4) 357–371.
Banerjee P, Bürgmann R, Nagarajan B and Apel E 2008 Intraplate deformation of the Indian subcontinent; Geophys. Res. Lett. 35 L18301, https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GL035468.
Benn D I and Owen L A 1998 The role of the Indian Summer Monsoon and the mid-latitude westerlies in Himalayan glaciation: Review and speculative discussion; J. Geol. Soc. 155(2) 353–363.
Bilham R and England P 2001 Plateau pop-up during the great 1897 Assam earthquake; Nature 410 806–809.
Biswas S and Grasemann B 2005 Quantitative morphotect-onics of the southern Shillong Plateau (Bangladesh/India); Austr. Earth Sci. 97 82–93.
Björklund P P 2015 Morphdynamics of rivers strongly affected by monsoon precipitation: Review of depositional style and forcing factors; Sedim. Geol. 323 110–147.
Bookhagen B, Thiede R C and Strecker M R 2005 Abnormal monsoon years and their control on erosion and sediment flux in the high, arid northwest Himalaya; Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 231(1) 131–146.
Bowman S 1990 Radiocarbon dating; Univ. of California Press.
Bradely R S and Jones P D 1993 ‘Little Ice Age’ summer temperature variations: Their nature and relevance to recent global warming trend; Holocene 3(4) 367–376.
Bristow C S 1987 Brahmaputra River: Channel migration and deposition; In: Recent Developments in Fluvial Sedimentology (eds) Ethridge F G, Flores R M and Harvey M D, Soc. Econ. Palaeontol. Mineral. Spec. Publ. 39 63–74.
Brookfield M E 1998 The evolution of the great river systems of southern Asia during the Cenozoic India–Asia collision: Rivers draining southwards; Geomorphology 22(3–4) 285–312.
Bull W B 1977 Tectonic geomorphology of the Mojave Desert, California: U.S. Geological Survey contract report, 14-08-001-G-394; Office of Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Engineering, Menlo Park, California, 188p.
Bull W B and McFadden L D 1977 Tectonic geomorphology north and south of the Garlock fault, California; In: Geomorphology in arid regions (ed.) Doehring D O, State University of New York at Binghamton, pp. 115–138.
Burbank D W 1992 Causes of recent Himalayan uplift deduced from deposited patterns in the Ganges basin; Nature 357 680–683.
Burbank D W and Anderson R S 2001 Tectonic Geomorphology; 1st edn, Blackwell Science Ltd.
Chauhan M S, Mazari R K and Rajagopala G 2000 Vegetation and climate in upper Spiti region, Himachal Pradesh during late Holocene; Curr. Sci. 79(3) 373–377.
Chauhan O S, Vogelsang E, Basavaiah N and Abdul K U S 2010 Reconstruction of the variability of SW monsoon during the past 3 Ka from the continental margin of the south-eastern Arabian Sea; J. Quat. Sci. 25(6) 798–807.
Chen W P and Molnar P 1990 Source parameters of earthquakes and intraplate deformation beneath the Shillong Plateau and the northern Indo-Burman Ranges; J. Geophys. Res. 95(B8) 12527–12552.
Chen Y C, Sung Q and Cheng K Yu 2003 Along-strike variations of morphotectonic features in the western foothills of Taiwan: Tectonic implications based on stream-gradient and hypsometric analysis; Geomorphology 56 109–137.
Coleman J M 1969 Brahmaputra River: Channel processes and sedimentation; Sedim. Geol. 3(2–3) 129–239.
Cox T 1994 Analysis of drainage-basin symmetry as a rapid technique to identify areas of possible Quaternary tilt-block tectonics: An example from the Mississippi Embayment; Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 106 571–581.
Dasgupta S 2011 Earthquake geology, geomorphology and hazard scenario in northeast India: Appraisal; National workshop on Earthquake risk mitigation strategy in northeast, February 24–25, Guwahati Assam, pp. 24–39.
Davis M 1899 The geographical cycle; Geograph. J. 14(5) 481–504.
Duarah B P and Phukan S 2011 Understanding the tectonic behaviour of Shillong Plateau, India using remote sensing data; Geol. Soc. India 77 105–112.
Duvall A, Kirby E and Burbank D 2004 Tectonic and lithologic controls on bedrock channel profiles and process in coastal California; J. Geophys. Res. 109 F03002.
England P and Bilham R 2015 The Shillong Plateau and the great 1897 Assam earthquake; Tectonics 34(9) 1792–1812.
Evans P 1964 The tectonic framework of Assam; Geol. Soc. India 5 80–96.
Font M, Amorese D and Lagrade J L 2010 DEM and GIS analysis of the stream gradient index to evaluate effects of tectonics: The Normandy intraplate area (NW France); Geomorphology 119 172–180.
Geological Survey of India (GSI) 2000 Seismotectonic Atlas.
Goudie A, Anderson M, Burt T, Lewin J, Richards K, Whalley B and Worsely P 2005 Geomorphological Techniques; 2nd edn, Routledge, Taylor and Francis, pp. 49–107.
Grujic D, Coutand I, Bookhagen B, Bonnet S, Blythe A and Duncan C 2006 Climatic forcing of erosion, landscape, and tectonics in the Bhutan Himalayas; Geology 34(10) 801–804.
Gupta A K, Anderson D M and Overpeck J T 2003 Abrupt changes in the Asian southwest monsoon during the Holocene and their links to the North Atlantic Ocean; Nature 421 354–357.
Gupta R P and Sen A K 1988 Imprints of the Ninety-East ridge in the Shillong Plateau, Indian Shield; Tectonophys. 154 335–341.
Hack J T 1957 Studies of longitudinal stream profiles in Virginia and Maryland; Geol. Surv. Prof. Paper 294-B 45–97.
Hack J T 1960 Interpretation of erosional topography in humid temperate regions; Am. J. Sci. 258 80–97.
Hack J T 1973 Stream profile analysis and stream gradient Index; J. Res. US Geol. Survey 1(4) 421–429.
Imsong W, Choudhury S and Phukan S 2016 Ascertaining the neotectonic activities in the southern part of Shillong Plateau through geomorphic parameters and remote sensing data; Curr. Sci. 110 91–98.
Islam M S, Ryuichi S and Kayal J R 2011 Pop-up tectonics of the Shillong Plateau in northeastern India: Insight from numerical simulations; Gondwana Res., https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2010.11.007.
Jones L S and Schumm S A 1999 Causes of avulsion: An overview; Spec. Publ. Int. Assoc. Sedimentol. 28 171–178.
Jones P D and Mann M E 2004 Climate over past Millennia; Rev. Geophys. 42 RG2002.
Juyal N, Pant R K, Basavaiah N, Bhushan R, Jain M, Saini N K, Yadava M G and Singhvi A K 2009 Reconstruction of last Glacial to early Holocene monsoon variability from relict lake sediments of the Higher Central Himalaya, Uttarakhand, India; J. Asian Earth Sci. 34 437–449.
Kayal J R 1987 Microseismicity and source mechanism study: Shillong Plateau, northeast India; Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 77 184–194.
Kayal J R and De R 1991 Microseismicty and tectonic in northeast India; Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 81(1) 131–138.
Kayal J R, Arefiev S S, Barua S, Hazarika D, Gogoi N, Gautam J L, Barauah S, Dorbath C and Tatevossia R 2012 Large and great earthquakes in the Shillong Plateau–Assam valley area of northeast India region: Pop-up and transverse tectonics; Tectonophys. 532 186–192.
Kayal J R, Arefiev S S, Barua S, Hazarika D, Gogoi N, Kumar A, Chowdhury S N and Kalita S 2006 Shillong Plateau earthquakes in the northeast India region: Complex tectonic model; Curr. Sci. 91(1) 109–114.
Keller E A and Pinter N 2002 Active Tectonics: Earthquake, Uplift, and Landscape; 2nd edn, Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, pp. 121–147.
Kirby E and Whipple K X 2001 Quantifying differential rock uplift rates via stream profile analysis; Geol. Soc. Am. 29(5) 415–418.
Kirby E, Whipple K X, Tang W and Chen Z 2003 Distribution of active rock uplift along the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau: Inferences from bedrock channel longitudinal profiles; J. Geophys. Res. 108(B4) 2217.
Kotlia B S, Ahmad S M, Zhao J X, Raza W, Collerson K D, Joshi L M and Sanwal J 2012 Climatic fluctuations during the LIA and post-LIA in the Kumaun Lesser Himalaya, India: Evidence from a 400 yr old stalagmite record; Quat. Int., https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2012.01.025.
Leopold L B and Maddock T Jr 1953 The hydraulic geometry of stream channels and some physiographic implications; Geol. Surv. Prof. Paper 252.
Libby W F, Anderson E C and Arnold J R 1949 Age determination by radiocarbon content: World-wide assay of natural radiocarbon; Science 109(2827) 227–228.
Luirei K, Bhakuni S S, Srivastava P and Suresh N 2012 Late Pleistocene–Holocene tectonic activities in the frontal part of NE Himalaya between Siang and Dibang river valleys, Arunachal Pradesh, India; Zeitschrift für Geomorphologie 56(4) 477–493.
Mackin H J 1948 Concept of the graded river; Geol. Soc. Am. 55 463–512.
Mann M E, Bradely R S and Hughes M K 1998 Global-scale temperature patterns and climate forcing over the past six centuries; Nature 392 779–787.
Mazumder S K 1976 A summary of the Precambrian geology of the Khasi Hills, Meghalaya; Geol. Surv. India, Misc. Publ. 23.
Meetei L I, Pattanayak S K, Bhaskar A, Pandit M K and Tandon S K 2007 Climatic imprints in Quaternary valley fill deposits of the middle Teesta valley, Sikkim Himalaya; Quat. Int. 159 32–46.
Metcalfe S E, Jones M D, Davies S J, Noren A and MacKenzie A 2010 Climate variability over the last two millennia in the North American monsoon region, record in laminated lake sediments from Laguna de Juanacatlan, Mexico; Holocene 20(8) 1195–1206.
Miall A D 1996 The Geology of fluvial deposits; Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Moberg A, Sonechkin D M, Holmgren K, Datsenko N M and Karlen W 2005 Highly variable Northern Hemisphere temperatures reconstructed from low- and high- resolution proxy data; Nature 433 613–617.
Morrill C, Overpeck J T, Cole J E, Liu K, Shen C and Tang L 2006 Holocene variations in the Asian monsoon inferred from the geochemistry of lake sediments in central Tibet; Quat. Res. 65 232–243.
Murata F, Hayashi T, Matsumoto J and Asada H 2007 Rainfall on the Meghalaya Plateau in the northeastern India – one of the rainiest places in the world; Nat. Hazards 42 391–399.
Nandy D R 2001 Geodynamics of northeastern India and the adjoining region; ACB Publications.
Nandy D R and Dasgupta S 1991 Seismotectonic domains of northeastern India and adjacent areas; Phys. Chem. Earth 18 371–384.
Oberlander T M 1985 Origin of drainage transverse to structures in orogeny; Tectonic Geomorph., pp. 155–182.
Oldham R D 1898 General Report – The earthquake of \(12^{{\rm th}}\) June 1897; Asiat. Misc. 2 16–18.
Peckham S D 2015 Longitudinal elevation profiles of rivers: Curve fitting with functions predicted by theory; In: Geomorphometry for Geosciences (eds) Jasiewicz J, Zwolinski Zb, Mitasova H and Hengl T, Int. Soc. Geomorphometry, Poland, pp. 137–140.
Prabhu C N, Shankar R, Anupama K, Taieb M, Bonnefille R, Vidal L and Prasad S 2004 A 200-Ka pollen and oxygen – isotopic record from two sediment cores from the eastern Arabian Sea; Paleogeogr. Paleoclimatol. Paleoecol. 214 309–321.
Rühland K, Phadtare N R, Pant R K, Sangode S J and Smol J P 2006 Accelerated melting of Himalayan snow and ice triggers pronounced changes in a valley peatland from northern India; Geophys. Res. Lett. 33 L15709.
Rajendran C P, Rajendran K, Duarah B P, Baruah S and Earnest A 2004 Interpreting the style of faulting and paleoseismicity associated with the 1897 Shillong, northeast India, earthquake: Implications for regional tectonism; Tectonics 23 TC4009.
Rao N P and Kumar M R 1997 Uplift and tectonics of the Shillong Plateau, northeast India; J. Phys. Earth 45 167–176.
Reimer P J, Baillie M G L, Bard E, Bayliss A, Beck J W, Blackwell P G, Bronk R C, Buck C E, Burr G S, Edwards R L, Friedrich M, Grootes P M, Guilderson T P, Hajdas I, Heaton T J, Hogg A G, Hughen K A, Kaiser K F, Kromer B, McCormac F G, Manning S W, Reimer R W, Richards D A, Southon J R, Talamo S, Turney C S M, van der Plicht J and Weyhenmeyer C E 2009 IntCal09 and Marine09 radiocarbon age calibration curves, 0–50,000 years cal BP; Radiocarbon 51(4) 1111–1150.
Reimer P J, Bard E, Bayliss A and Beck J W 2013 IntCal13 and Marine13 radiocarbon age calibration curves 0–50,000 years cal BP; Radiocarbon 55(4) 1869–1887.
Roe G H, Montgomery D R and Hallet B 2002 Effects of orographic precipitation variations on the concavity of steady-state river profiles; Geology 30(2) 143–146.
Sarma J N 2005 Fluvial process and morphology of the Brahmaputra River in Assam, India; Geomorphology 70 226–256.
Sarma J N, Acharjee S, Murgante B 2015 Morphotectonic study of the Brahmaputra basin using geoinformatics; J. Geol. Soc. of India 86 324–330.
Sato T 2013 Mechanism of orographic precipitation around the Meghalaya Plateau associated with intra-seasonal oscillation and the diurnal cycle; Mon. Wea. Rev. 141(7) 2451–2466.
Schumm S A 1977 The Fluvial System; John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Seeber L and Gornitz V 1983 River profiles along the Himalayan arc as indicators of active tectonics; Tectonophys. 92 335–367.
Sharma R, Gouda H C, Singh R K and Nagaraju B V 2012 Structural study of Meghalaya Plateau through aeromagnetic data; J. Geol. Soc. India 79 11–29.
Sinha A, Cannariato K G, Stott L D, Cheng H, Edwards R L, Yadav M G, Ramesh R and Singh I B 2007 A 900-year (600 to 1500 AD) record of the Indian summer monsoon precipitation from the core monsoon zone of India; Geophys. Res. Lett. 34 L16707.
Slingerland R and Smith N D 1998 Necessary conditions for a meandering-river avulsion; Geology 26(5) 435–438.
Slingerland R and Smith N D 2004 River avulsions and their deposits; Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 32 257–285.
Snyder N P, Whipple K X, Tucker G E and Merritts D J 2000 Landscape response to tectonic forcing: Digital elevation model analysis of stream profiles in the Medocino triple junction region, northern California: Geol. Geol. Surv. Am. Bull. 112(8) 1250–1263.
Soja R and Starkel L 2007 Extreme rainfalls in eastern Himalaya and southern slope of Meghalaya Plateau and their geomorphologic impacts; Geomorphology 84 170–180.
Srivastava P and Misra D K 2008 Morpho-sedimentary records of active tectonics at the Kameng River exit, NE Himalaya; Geomorphology 97 187–198.
Stewart R J, Hallet B, Zeitler P K, Malloy M A, Allen C M and Trippett C 2008 Brahmaputra sediment flux dominated by highly localized rapid erosion from the easternmost Himalaya; Geol. Soc. Am. 36(9) 711–714.
Street F A and Grove A T 1979 Global maps of lake-level fluctuations since 30,000 yr B.P; Quat. Res. 12 83–118.
Troiani F and Seta D M 2008 The use of the stream length-gradient index in morphotectonic analysis of small catchments: A case study from central Italy; Geomorphology 102 159–168.
Tyagi A K, Chaudhary S, Rana N, Sati S P and Juyal N 2009 Identifying areas of differential uplift using steepness index in the Alaknanda basin, Garhwal Himalaya, Uttarakhand; Curr. Sci. 97(10) 1473–1477.
Vance R E, Mathews R W and Clague J J 1992 7000-year record of lake-level change on the northern Great Plains: A high-resolution proxy of past climate; Geology 20 879–882.
Vernant P, Bilham R, Szeliga W, Drupka D, Kalita S, Bhattacharyya A K, Gaur V K, Pelgay P, Cattin R and Berthet T 2014 Clockwise rotation of the Brahmaputra Valley relative to India: Tectonic convergence in the eastern Himalaya, Naga Hills, and Shillong Plateau; J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 119(8) 6558–6571.
Whipple K and Tucker G 2002 Implications of sediment–flux dependent river incision models for landscape evolution; J. Geophys. Res. 107, https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JB000044.
Whittaker A C, Cowie P A, Attal M, Tucker G E and Roberts G P 2007 Bedrock channel adjustment to tectonic forcing: Implications for predicting river incision rates; Geol. Soc. Am. 35(2) 103–106.
Wobus WC, Hodges K V and Whipple K X 2003 Has focused denudation sustained active thrusting at the Himalayan topography front?; Geol. Soc. Am. 31(10) 861–864.
Yadav R R 2010 Long-term hydro climatic variability in monsoon shadow zone of western Himalaya, India; Clim. Dyn., https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-010-0800-8.
Zhisheng A, Clemens S C, Shen J, Qiang X, Zhangdong J, Sun Y, Prell W L, Luo J, Wang S, Xu H, Cai Y, Zhou W, Liu X, Liu W, Shi Z, Yan L, Xiao X, Chang H, Wu F, AI Li and Lu F 2011 Glacial–interglacial Indian summer monsoon dynamics; Science 333 719–723.
Zhisheng An, Kutzbach J E, Prell W L and Porter S C 2001 Evolution of Asian monsoon and phased uplift of the Himalayan–Tibetan Plateau since late Miocene times; Nature 411 62–66.
Zhu L, Zhen X, Wang J, Lü H, Kitagawa H and Possnert G 2008 A \(\sim \)30,000-year record of environmental changes inferred from Lake Chen Co, southern Tibet; J. Paleolimnol. 42 343–358.
Acknowledgements
This study is part of WI’s Ph.D thesis. WI acknowledges Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, HRDG New Delhi for SRF-NET fellowship (file no: 09/420/(0002)/2012-EMR-I). The authors are thankful to Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology, Dehardun and Gauhati University, Assam for research facilities. WI is also thankful to Mr. Atul Sarma, Executive Engineer, Brahmaputra Board, Guwahati for providing river discharge data on Kulsi River and Mr. K K Deka, Forest Range Officer, Loharghat Forest Reserve for providing official reports on Chandubi Lake. The authors are also thankful to the two anonymous reviewers who helped to improve the manuscript substantially.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Navin Juyal
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imsong, W., Choudhury, S., Phukan, S. et al. Morphodynamics of the Kulsi River Basin in the northern front of Shillong Plateau: Exhibiting episodic inundation and channel migration. J Earth Syst Sci 127, 5 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-017-0904-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-017-0904-1