Abstract
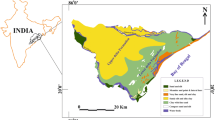
Seawater intrusion is one of the alarming processes that reduces the water quality and imperils the supply of freshwater in coastal aquifers. The region, north of the Chennai city, India is one such site affected by seawater intrusion. The objective of this study is to identify the extent of seawater intruded area by major geochemical and isotopic signatures. A total of 102 groundwater samples were collected and analysed for major and minor ions. Groundwater samples with electrical conductivity (EC) greater than 5000 μS/cm and a river mouth sample were analyzed for Oxygen-18 (δ 18O) and Deuterium (δ 2H) isotopes to study their importance in monitoring seawater intrusion. The molar ratio of geochemical indicators and isotopic signatures suggests an intrusion up to a distance of 13 km from the sea as on March 2012 and up to 14.7 km during May 2012.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcala F J and Custodio E 2008 Using the Cl/Br ratio as a tracer to identify the origin of salinity in aquifers in Spain and Portugal; J. Hydrol. 359 189–207.
Appelo C A J and Postma D 2005 Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution; 2nd edn, CRC Press, ISBN-10: 649.
Araguás L J 2003 Identification of the mechanisms and origin of salinisation of groundwater in coastal aquifers by isotope techniques; In: Proceedings of 18 th salt water intrusion meeting, IGME, pp. 365–371.
Chen K P and Jiao J J 2007 Seawater intrusion and aquifer freshening near reclaimed coastal area of Shenzhen; Water Science and Technology: Water Supply 7(2) 137–145.
Chidambaram S, Prasanna M, Ramanathan A L, Vasu K, Shahul H A, Warrier U K, Manivannan R, Srinivasamoorthy K and Ramesh R 2009 Stable isotopic signatures in precipitation of 2006 southwest monsoon of Tamil Nadu; Curr. Sci. 96(9) 1224–1229.
Custodio E and Bruggeman G A 1987 Groundwater problems in coastal areas; Studies and Reports in Hydrology 45 1–576.
Davis S N, Whittemore D O and Fabryka-Martin J 1998 Uses of chloride/bromide ratios in studies of potable water; Groundwater 36(2) 338–350.
Desai B I, Gupta S K, Shah M V and Sharma S C 1979 Hydrochemical evidence of sea water intrusion along the Mangrol–Chorwad coast of Saurashtra, Gujarat; Hydrol. Sci. 24(1) 71–82.
Elango L and Manickam S 1986 Groundwater quality of Madras aquifer: A study on Panjetti–Ponneri–Minjur area; Indian Geol. J. 61 41–49.
Elango L and Manickam S 1987 Hydrogeochemistry of the Madras aquifer, India – Spatial and temporal variation in chemical quality of groundwater; Geol. Soc. Hong Kong Bull. 3 525–534.
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization) 1997 Seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers: Guidelines for study, monitoring and control; FAO Water Reports 11. Rome, Italy: FAO 163.
Faye S, Maloszewski P, Stichler W, Trimborn P, Faye S C and Gaye C B 2005 Groundwater salinisation in the Saloum (Senegal) delta aquifer: Minor elements and isotopic indicators; Sci. Total Environ. 343 243–259.
Fritz P, Hennings C S, Suzolo O and Salati E 1979 Isotope hydrology in northern Chile; Int. J. Isotope Hydrol. 2 525–544.
Gaye C B 2001 Isotope techniques for monitoring groundwater salinisation; Proceeding of First International Conference on Seawater Intrusion and Coastal Aquifers – Modeling, Monitoring and Management, Morocco, pp. 23–25.
Gonfiantini R and Araguás L 1988 Los isótoposambientalesen el estudio de la intrusión marina; In: Tecnologíade la Intrusión Marina en acuíferoscosteros (ed.) Lopez-Camacho Camacho B, IGTE, Almuñecar, Spain, pp. 135–190.
Howard K W F and Lloyd J W 1983 Major ion characterization of coastal saline groundwaters; Groundwater 21(4) 429–437.
Indu S N, Parimala R S and Elango L 2013 Identification of seawater intrusion by Cl/Br ratio and mitigation through managed aquifer recharge in aquifers north of Chennai, India; J. Groundwater Res. 2 155–162.
Isotope hydrology investigations in Latin America 1994 IAEA-TECDOC 835.
Jones B F, Vengosh A, Rosenthal E and Yechieli Y 1999 Geochemical investigation of groundwater quality; In: Seawater intrusion in coastal aquifers – concepts, methods and practices, pp. 51–71.
Karahanoglu N 1997 Assessment of sea-water intrusion in a coastal aquifer by using correlation, principal component, and factor analyses; Water Environ. Res. 69(3) 331– 341.
Kim J H, Kim R H and Chang H W 2003a Hydrogeochemical characterization of major factors affecting the quality of shallow groundwater in the coastal area at Kimje in South Korea; Environ. Geol. 44 478–489.
Kim Y, Lee K S, Koh D C, Lee D H, Lee S G, Park W B, Koh G W and Woo N C 2003b Hydrogeochemical and isotopic evidence of groundwater salinization in a coastal aquifer: A case study in Jeju volcanic island, Korea ; J. Hydrol. 270 282–294.
Korfali F I and Jurdi M 2010 Deterioration of coastal water aquifers: Causes and impacts; European Water 29 3–10.
Kumar B, Rai S P, Kumar U S, Verma S K, Garg P, Kumar S V V, Jaiswal R, Purendra B K, Kumar S R and Pande N G 2010 Isotopic characteristics of Indian precipitation; Water Resour. Res., doi: 10.1029/2009WR008532.
McCaffrey M A, Lazar B and Holland H D 1987 The evaporation path of seawater and the co-precipitation of Br− and K+ with halite; J. Sedim. Petrol. 57 928–937.
Morris A W and Riley J P 1966 The bromide/chlorinity and sulphate/chlorinity ratio in seawater; Deep Sea Res. 13 669–705.
Moujabber E L M, Atallah T, Darwish T and Bou Samra B 2004 Monitoring of groundwater salination by seawater intrusion on the Lebanese Coast; Lebanese Sci. J. 5(2) 21–36.
Moujabber E L M, Bousamra B, Darwish T and Atallah T 2006 Comparison of different indicators for groundwater contamination by seawater intrusion on the Lebanese coast; J. Water Resour. Manag. 20 161–180.
Mustapha A, Aris A Z, Juahir H and Ramli M F 2012 Surface water quality contamination source apportionment and physicochemical characterization at the upper section of the Jakara Basin, Nigeria; Arab J. Geosci. doi: 10.1007/s12517-012-0731-2.
Nura U K, Mohammad F R, Wan N A S, Shaharin I, Ahmad Z A and Adamu M 2013 Evaluation of factors influencing the groundwater chemistry in a small tropical island of Malaysia; Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 10(5) 1861–1881.
Nwankwoala H O and Udom G J 2011 Hydrochemical facies and ionic ratios of groundwater in Port Harcourt, Southern Nigeria; Res. J. Chem. Sci. 1(3) 87–101.
Panteleit B, Kessels W, Kantor W and Schulz H D 2001 Geochemical characteristics of salinisation-zones in the coastal aquifer test field (CAT-Field) in North-Germany; In: Proceedings of 5th International Conference on saltwater intrusion and coastal aquifers – monitoring, modelling, and management, Essaouira, Morocco, pp. 1–11.
Revelle R 1941 Criteria for recognition of seawater in groundwater; Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 22 593–597.
Richter B C and Kreitler C W 1993 Geochemistry of saltwater beneath the Rolling Plains, North–Central Texas; Groundwater 24(6) 735–742.
Slama F, Bouhlila R and Tarhouni J 2010 Hydrochemical processes at the seawater–freshwater interface as indicators of seawater intrusion evolution: Case of Korba coastal plain (Tunisia); Proceedings of 21 st saltwater intrusion meeting SWIM-21, Portugal, pp. 11–1.
Subramanian S 1975 Report on the systemic geological mapping of quaternary formations in the coastal plains between Minjur and Madras, Tamil Nadu; Unpublished Report, Geol. Surv. India.
Sukhija B S, Varma V N, Nagabhushanam P and Reddy D V 1996 Differentiation of paleomarine and modern intruded salinities in coastal groundwaters (of Karaikal and Tanjavur, India) based on inorganic chemistry, organic biomarker fingerprints and radiocarbon dating ; J. Hydrol. 174 173–201.
Todd D K 1989 Sources of saline intrusion in the 400-foot aquifer, Castroville area, California; Report for Monterey country flood control and water conservation district, Salinas, California, p. 41.
UNDP 1987 Hydrogeological and artificial recharge studies; Madras Technical report, United Nations Department of technical co-operation for development, New York.
Vengosh A, Gill J, Davisson M L and Hudson B 2002 A multi-isotope (B, Sr, O, H and C) and age dating (3H–3He and 14C) study of groundwater from Salinas valley, California: Hydrochemistry, dynamics and contamination processes; Water Resour. Res. 38 9–1–9-7.
Vengosh A and Rosenthal A 1994 Saline groundwater in Israel: Its bearing on the water crisis in the country; J. Hydrol. 156 389–430.
Vengosh A, Spivack A J, Artzi Y and Ayalon A 1999 Geochemical and boron, strontium, and oxygen isotopic constraints on the origin of the salinity in groundwater from the Mediterranean coast of Israel; Water Resour. Res. 35 1877–1894.
Yi C H, Chou P Y, Yu C L, Ping K T and Wen M H 2010 Variation of groundwater quality in seawater intrusion area using cluster and multivariate factor analysis; Sixth International Conference on Natural Computation.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, India for providing fund to this research (Grant no.: DST/ WAR-WSI/05/2010). Co-funding for the collaborative project ‘Enhancement of natural water systems and treatment methods for safe and sustainable water supply in India – Saph Pani’ (www.saphpani.eu) from the European Commission within the Seventh Framework Programme (grant agreement no. 282 911) is also gratefully acknowledged. Stable isotope analysis at the Museum für Naturkunde in Berlin by Dr. Ulrich Struck is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nair, I.S., Rajaveni, S.P., Schneider, M. et al. Geochemical and isotopic signatures for the identification of seawater intrusion in an alluvial aquifer. J Earth Syst Sci 124, 1281–1291 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-015-0600-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-015-0600-y