Abstract
The performance of a dynamical seasonal forecast system is evaluated for the prediction of summer monsoon rainfall over the Indian region during June–September (JJAS) by using hindcast of the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) seasonal ensemble prediction system (EPS) model, based on five ensembles of March, April and May initial states for a period of 32 years (1979–2010).
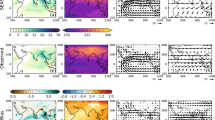
The hindcast climatology during JJAS simulates the mean monsoon circulation at lower and upper tropospheres very well in JMA model using March, April and May ensembles with a more realistic simulation of Webster and Yang’s broad scale monsoon circulation index. The JMA hindcast climatology during JJAS simulates the rainfall maxima over the west-coast of India and the head Bay of Bengal reasonably well, although, the latter is slightly shifted southwestward. Associated with better forecast skills of El Nino in the JMA model, the interannual variability of All India Summer Monsoon Rainfall (AISMR) during the 32-year period has also been very well simulated with a high significant (99% level) correlation in April ensemble followed by that of March and May ensembles. Thus, the present analysis indicates that the JMA seasonal forecast model can prove to be a useful tool for the dynamical seasonal forecast of AISMR.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanford H F 1884 On the connection of the Himalayan snowfalls with dry winds and seasons of draughts in India; Proc. Roy. Soc. London 37 3–22.
Brankovic C and Palmer T N 1997 Atmospheric seasonal predictability and estimates of ensemble size; Mon. Wea. Rev. 125 859–874.
Brankovic C, Palmer T N, Molenti F, Tibaldi S and Cubasch U 1990 Extended range predictions with ECMWF models: Time lagged ensemble forecasting; Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 116 867–912.
Charney J G and Shukla J 1981 Predictability of monsoons; In: Monsoon dynamics (eds) Lighthill J and Pearce R P (Cambridge: University Press), pp. 99–109.
Chen T C and Yen M C 1994 Interannual variation of the Indian monsoon simulated by the NCAR Community Climate Model: Effect of the tropical Pacific SST; J. Climate 7 1403–1415.
Findlater J 1966a Cross-equatorial jet stream at low level over Kenya; Meteorol. Mag. 95 353–364.
Findlater J 1966b Mean monthly airflow at low levels over the western Indian Ocean; Geophys. Memoir 16 1–53.
Gowariker V, Thapliyal V, Kulshrestha S M, Mandal G S, Sen Roy N and Sikka D R 1991 A power regression model for long-range forecast of southwest monsoon rainfall over India; Mausam 42 125–130.
Huffman G J, Adler R F, Morrissey M, Bolvin D, Curtis S, Joyce R, McGavock B and Susskind J 2001 Global precipitation at one-degree daily resolution from multi-satellite observations; J. Hydrometeor. 2 36–50.
Ishikawa I, Tsujino H, Hirabara M, Nakano H, Yasuda T and Ishizaki H 2005 Meteorological Research Institute Community Ocean Model (MRI.COM) manual; Technical Reports of the Meteorological Research Institute, 47 189p (in Japanese).
Kalnay E M and Coauthors 1996 The NCEP/NCAR 40-year Reanalysis Project; Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 77 437–471. doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1996)077<0437:TNYRP>2.0.CO;2.
Kang I S, Jin K, Wang B, Lau K M, Shukla J, Krishnamurthy V, Schubert S D, Waliser D E, Stern W F, Kitoh A, Meehl G., Kanamitsu M, Galin V Y, Satyan V, Park C K and Liu Y 2002 Intercomparison of the climatological variations of Asian summer monsoon precipitation simulated by 10 GCMs; Clim. Dyn. 19 383–395.
Koteswaram P 1958a The easterly jet stream in the tropics; Tellus. 10 43–57.
Koteswaram P 1958b The Asian summer monsoon and the general circulation over the tropics; Monsoons of the World, pp. 105–110.
Pai D S and Rajeevan M 2006 Empirical prediction of Indian summer monsoon rainfall with different lead periods based on global SST anomalies; Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 92 33–43, doi: 10.1007/s00703-005-0136-9.
Palmer T N and Anderson D L T 1994 The prospects for seasonal forecasting – a review paper; Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 126 2013–2033.
Palmer T N, Brankowic C, Viterbo P and Miller M J 1992 Modelling interannual variations of summer monsoons ; J. Climate 5 399–417.
Pant G B and Parthasarathy B 1981 Some aspects of an association between the southern oscillation and Indian summer monsoon; Arch. Meteorol. Geophys. Biokl. Ser. B 29 245–5.
Pattanaik D R and Kumar A 2010 Prediction of summer monsoon rainfall over India using the NCEP climate forecast system; Clim. Dyn. 34 557–572.
Pattanaik D R and Kumar A 2014a A hybrid model based on latest version of NCEP CFS coupled model for Indian monsoon rainfall forecast; Atmos. Sci. Lett., doi: 10.1002/asl2.513.
Pattanaik D R and Kumar A 2014b Prediction of summer monsoon rainfall over India using the NCEP climate forecast system; Clim. Dyn., doi: 10.1007/s00382-009-0648-y.
Pattanaik D R, Kalsi S R and Hatwar H R 2005 Evolution of convection anomalies over the Indo-Pacific region in relation to Indian monsoon rainfall; Mausam 56 811–824.
Pattanaik D R, Tyagi Ajit, Mohanty U C and Brookshaw Anca 2011 An evaluation of the simulation of summer monthly to seasonal rainfall over India with a coupled Ocean Atmosphere GCM (GloSea); In: Challenges and Opportunities in Agrometeorology (eds) Attri S D, Rathore L S, Sivakumar M V K and Dash S K, Springer Publication, pp. 101–122.
Rajeevan M and Ravi S Nanjundiah 2009 Coupled model simulations of twentieth century climate of the Indian summer monsoon; Curr. Trends in Sci., pp. 537–567.
Rajeevan M, Pai D S, Dikshit S K and Kelkar R R 2003 IMD’s new operational models for long-range forecast of southwest monsoon rainfall over India and their verification for 2003; Curr. Sci. 86 422–430.
Rasmusson E M and Carpenter T H 1983 The relationship between the eastern Pacific sea surface temperature and rainfall over India and Sri Lanka; Mon. Wea. Rev. 111 354–384.
Saha S, Nadiga S, Thiaw C, Wang J, Wang W, Zhang Q, Van den Dool H M, Pan H L, Moorthi S, Behringer D, Stokes D, Pena M, Lord S, White G, Ebisuzki W, Peng P and Xie P 2006 The NCEP climate forecast system ; J. Climate 19 3483–3517.
Saha Suranjana, Shrinivas Moorthi, Xingren Wu, Jiande Wang, Sudhir Nadiga, Patrick Tripp, Hua-Lu Pan, David Behringer, Yu-Tai Hou, Hui-ya Chuang, Mark Iredell, Michael Ek, Jesse Meng, Rongqian Yang, Huug van den Dool, Qin Zhang, Wanqiu Wang and Mingyue Chen 2014 The NCEP Climate Forecast System Version 2; J. Clim. 27 2185–2208. doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00823.1.
Sahai A K, Pattanaik D R, Satyan V, Grimm A M and Alice M 2003a Teleconnections in recent time and prediction of Indian summer monsoon rainfall; Meteor. Atmos. Phys. 83 217–227.
Sahai A K, Grimm A M, Satyan V and Pant G B 2003b Long-lead prediction of Indian summer monsoon rainfall from global SST evolution; Clim. Dyn. 20 855–863.
Shukla J and Mooley D A 1987 Empirical prediction of the summer monsoon rainfall over India; Mon. Wea. Rev. 115 695–703.
Shukla J, Anderson J, Baumhefner D, Brankovic C, Chang Y, Kalnay E, Marx L, Palmer T N, Paolino D A, Ploshay J, Schubert S, Straus D M, Suarez M and Tribbia J 2000 Dynamical seasonal prediction; Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 81 2593–2606.
Sikka D R and Gadgil S 1980 On the maximum cloud zone and the ITCZ over Indian longitudes during the southwest monsoon; Mon. Wea. Rev. 108 1840–1853.
Slingo J M and Annamalai H 2000 1997 The El Nino of the century and the response of the Indian summer monsoon; Mon. Wea. Rev. 128 178–179.
Smith T M, Reynolds R W, Thomas C Peterson and Jay Lawrimore 2008 Improvements to NOAA’s historical merged land–ocean surface temperature analysis 1880–2006; J. Climate 21 2283–2296.
Soman M K and Slingo J 1997 Sensitivity of Asian summer monsoon aspects of sea surface temperature anomalies in the tropical Pacific Ocean; Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 123 309–339.
Sperber K R and Palmer T 1996 Interannual tropical rainfall variability in general circulation model simulations associated with the Atmospheric Model Intercomparison Project; J. Climate 9 2727–2750.
Usui N, Ishizaki S, Fujii Y, Tsujino H, Yasuda T and Kamachi M 2006 Meteorological Research Institute multivariate ocean variational estimation (MOVE) system: Some early results; Adv. Space Res. 37 806–822.
Webster P J and Yang S 1992 Monsoon and ENSO: Selectively interactive systems; Quart. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 118 877–926.
Xue Y, Smith T M and Reynolds R W 2003 Interdecadal changes of 30-yr SST normals during 1871-2000; J. Climate 16 1601–1612.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) for providing the Seasonal Ensemble Prediction System (EPS) hindcast datasets for a period of 32 years from 1979 to 2010 for use in the present study. Authors are thankful to the Additional Director General of Meteorology (Research), ADGM (R), India Meteorological Department, Pune for the encouragement and facilities provided to carry out this study. Thanks are also due to the anonymous reviewers for their very useful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sonawane, K., Sreejith, O.P., Pattanaik, D.R. et al. Simulation of Indian summer monsoon using the Japan Meteorological Agency’s seasonal ensemble prediction system. J Earth Syst Sci 124, 321–333 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-015-0537-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-015-0537-1