Abstract
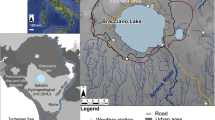
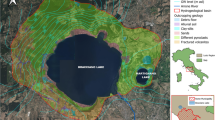
The subject of this paper is the detailed hydrological simulation of two playa lakes located in southern Spain from January 2011 to March 2012 on a daily basis. These playas are placed over a 400-km 2 shallow aquifer, which is exposed to an increasing stress caused by agricultural activities, mainly olive grove plantations. The objective of the paper is to elaborate a detailed numeric model that simulates the water regime of each playa lake on a daily scale. The simulation is compared to measured water level (WL) data of the playas in order to characterize the groundwater–surface interactions. The ultimate objective of this paper is to assess the environmental impact of the increasing anthropogenic water consumption within the area of research. The results of the GW–surface interaction were very consistent with previous works. One of the playa lakes is groundwater-dependent and the other one is presumably a perched playa lake. The GW discharge of the former playa (214 mm) during the research period stands in sharp contrast to no regional GW discharge in the latter. Water level data prove that the hydrological year (2011–2012) had a very negative water budget. The evapotranspiration estimation was almost as high as double the sum of the precipitation, the run-off, and the groundwater discharge. The simulation of an anthropologically altered water regime proves that water retrieval has a harmful impact on the WL of the playa lakes as well as on the aquifer.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beltran M, Moral F and Rodriguez-Rodriguez M 2012 Changes in the hydrological functioning of a playa-lake complex under increasing agricultural pressures (Andalusia, southern Spain); Water Environ. J. 26 212–223.
Castro J et al. 1999 Respuestas del olivar tradicional a diferentes estrategias y dosis de agua de riego (Response of the traditional olive grove to different strategies and irrigation dosis), Investigación agraria. Producción y protección vegetales 14 393–404.
Chen D, Gao G, Xu C-Y, Guo J and Ren G 2005 Comparison of the Thornthwaite method and pan data with the standard Penman–Monteith estimates of reference evapotranspiration in China; Clim. Res. 28 123–132.
Jensen M E, Burman R D and Allen R G 1990 Evapotranspiration and irrigation water requirements; American Society of Civil Engineers, New York.
Moral F, Rodriguez-Rodríguez M, Beltrán M, Benavente J and Cifuentes V J 2013 Water regime of playa-lakes from southern Spain. Conditioning factors and hydrological modeling; Water Environ. Res. 85(7) 632–642.
Moral F, Rodríguez-Rodríguez M, Benavente J and Beltrán M 2008 Hydrogeological relations of the Llanos de Osuna-La Lantejuela aquifer and the playa-lake complex of La Lantejuela, Guadalquivir River Authoritie, Seville.
Oroud I M 1995 Effects of salinity upon evaporation from pans and shallow lakes near the Dead Sea; Theor. Appl. Climatol. 52 231–240.
Padilla A, Delgado J and Castillo E 2005 Management and processing of hydrological time series. Alicante: Algibe Consulting.
Penman H L 1948 Natural evaporation from open water, bare soil and grass; Proc. Roy. Soc. London 193 120–145.
Rodríguez-Rodríguez M, Moral F and Benavente J 2007 Anthropogenic alterations and hydrological functioning of a semi-arid playa-lake complex and related detritic aquifer (Seville province, Spain); XXXV International Association of Hydrogeologists Congress, Groundwater and Ecosystems, Lisbon, September 2007, pp. 97–98.
Rodríguez-Rodríguez M, Moral F and Benavente J 2008 Hydrogeological characteristics of a groundwater dependant ecosystem (La Lantejuela, Seville, Spain); Water Environ. J. 22 137–147.
Rodriguez-Rodriguez M, Moral F, Bruque J M and Benavente J 2011 Modelización hidrológica en humedales de la Demarcación Hidrográfica del Guadalquivir (Hydrological modelling in wetlands of the Guadalquivir River Basin), Seville.
Thornthwaite C W and Mather J R 1955 The water balance; Drexel Institute of Technolog; Publ. Climatol. 8 1–104.
Acknowledegments
This work has been carried out in the framework of an academic exchange between the Carl von Ossietzky University Oldenburg and Pablo de Olavide University Seville. The collaboration was established, thanks to the close contact of G Massmann (Carl von Ossietzky University Oldenburg) andC Kohlfahl (Spanish Geological Survey). Authors would like to thank them for having made this collaboration possible. Furthermore, they would like to thank J M Bruque Carmona, who is staff member of the Pablo de Olavide University for his helpful advices and everlasting patience. They are also grateful to the reviewers whose comments and suggestions have improved both the quality and the explicitness of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miguel, RR., Malte, S. A hydrological simulation of the water regime in two playa lakes located in southern Spain. J Earth Syst Sci 123, 1295–1305 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-014-0464-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-014-0464-6