Abstract
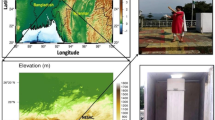
In this paper, a comparison of two methods for the calculation of the height of atmospheric boundary layer (ABL), using balloon-borne GPS radiosonde data is presented. ABL has been characterized using vertical profiles of meteorological parameter. The gradient of virtual potential temperature (𝜃 v ) profile for the determination of mixed layer heights (MLH) and the mean value of turbulent flow depth (TFD) obtained from the vertical profile of Bulk Richardson Number (R i B ) have been used in this study. One-year data have been used for the study. There is large seasonal variability in MLH with a peak in the summer and winter whereas the TFD remained steady throughout the year. Results from the present study indicate that the magnitudes of TFD are often larger than the MLH.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angevine Wayne M, Bakwin Peter S, and Davis Kenneth J 1998 Wind profiler and RASS measurements compared with measurements from a 450-m tall tower; J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 15 818–825.
Ao C O et al. 2008 Planetary boundary layer information from GPS radio occultation measurements; GRAS SAF Workshop on Applications of GPSRO Measurements, 16–18 June 2008, pp. 123–131 (http://www.grassaf.org/Workshops/agrom_prog/Ao.pdf).
Eresmaa N et al. 2006 Mixing height determination by ceilometers; Atmos. Chem. Phys. 6 1485–1493.
Hennemuth B and Lammert A 2006 DeterminationQ2 of the atmospheric boundary layer height from radiosonde and lidar backscatter; Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1 181–200, doi: 10.1007/s10546-005-9035-3.
Holzworth G C 1964 Estimates of mean maximum mixing depths in the contiguous United States; Mon. Wea. Rev. 92 235–242.
Holzworth G C 1967 Mixing depths, wind speeds and air pollution potential for selected locations in the United States; J. Appl. Meteorol. 6 1039–1044.
Nair Sandhya K et al. 2011 Characterization of the Vertical Structure of Coastal Atmospheric Boundary Layer over Thumba (8.5∘N, 76.9∘E) during Different Seasons; Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Meteorology Volume, Article ID 390826, doi: 10.1155/2011/390826.
Oke T R 1988 Boundary Layer Climates; Halsted Press, New York, 435p.
Russell Philip B and Uthe Edward E 1978 Regional patterns of mixing depth and stability: Sodar network measurements for input to air quality models; Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 59 1275–1287, doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1978)059<1275:RPOMDA>2.0.CO;2.
Seibert P, Beyrich F, Gryning S E, Joffre S, Rasmussen A, and Tercier P 2000 Review and intercomparison of operational methods for the determination of the mixing height; Atmos. Environ. 34 1001–1027.
Seibert P et al. 2000 Review and intercomparison of operational methods for the determination of the mixing height; Atmos. Environ. 34 1001–1027.
Sørensen J H 1998 Sensitivity of the derma long-range Gaussian dispersion model to meteorological input and diffusion parameters; Atmos. Environ. 32 4195– 4206.
Srivastava S et al. 2010 Seasonal variability in mixed layer height and its impact on trace gas distribution over a tropical urban site: Ahmedabad; Atmos. Res. 96 79–87.
Stull R B 1988 An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 666p
Subrahamanyam D B and Ramachandran R 2003 Structural characteristics of marine atmospheric boundary layer and its associated dynamics over the central Arabian Sea during INDOEX, IFP-99 campaign; Curr. Sci. 85 1334–1340.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the SPL, VSSC, ISRO for their logistical and technical support in smooth functioning of balloon borne GPS ascents for the study under ISRO (IGBP)–NOBLE project. Sagarika Chandra is thankful to the Birla Institute of Technology for sponsoring a fellowship for her PhD research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandra, S., Dwivedi, A.K. & Kumar, M. Characterization of the atmospheric boundary layer from radiosonde observations along eastern end of monsoon trough of India. J Earth Syst Sci 123, 1233–1240 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-014-0458-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-014-0458-4