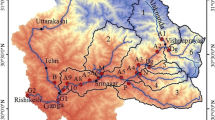
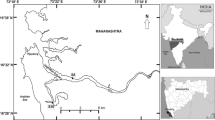
The present study is an attempt towards understanding the sediment routing system in the semi-arid margin of the Gulf of Kachchh, which is one of the largest macrotidal regimes in the northern Arabian Sea. Investigations based on heavy minerals, clay minerals, mineral magnetic properties and sediment geochemistry indicated that there are three major sources of sediments contributing to the Gulf of Kachchh basin: (1) Indus River, (2) Kachchh mainland coastal rivers and (3) the Saurashtra peninsular coastal rivers. The flanks of northern and southern coast of western Gulf of Kachchh show dominant signatures of Kachchh mainland/Saurashtra peninsular provenance. In contrast, the eastern Gulf of Kachchh coast bearing fine grained sediments shows dominant Indus River Provenance. Although ephemeral in nature, the small coastal rivers of Saurashtra and Kachchh contribute significant amount of sediments to the Gulf of Kachchh coastline because of their ‘dryland’ nature and thus they control the coarse grained sedimentation processes.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad T, Khanna P P, Chakrapani G J and Balakrishnan S 1998 Geochemical characteristics of water and sediment of the Indus River, Trans-Himalaya, India: Constraints on weathering and erosion; J. Asian Earth Sci. 16 333–346.
Alizai A, Hillier S, Clift P D and Giosan L 2012 Clay mineral variations in Holocene terrestrial sediments from the Indus basin: A response to SW Asian monsoon variability; Quat. Res. 77(3) 368–381.
Babu M T, Vethamony P and Desa E 2005 Modelling tide-driven currents and residual eddies in the Gulf of Kachchh: A marine environmental planning perspective; Ecol. Model. 184(2–4) 299–312.
Basavaiah N 2011 Geomagnetism: Solid Earth and Upper Atmosphere Perspectives (Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Springer), 410p.
Biscaye P E 1965 Mineralogy and sedimentation of recent deep sea clay in Atlantic ocean and adjacent seas and oceans; Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 76 803–832.
Biswas S K 1993 Geology of Kutch; K.D. Malaviya Institute of Petroleum Exploration, Dehradun, 2 450p.
Castelltort S and Van Den Driessche J 2003 How plausible are high-frequency sediment supply-driven cycles in the stratigraphic record?; Sedim. Geol. 157 3–13.
Chauhan O S 1994 Influence of macrotidal environment on shelf sedimentation, Gulf of Kachchh, India; Cont. Shelf Res. 14 1477–1493.
Chauhan O S, Jayakumar S, Menezes A A, Suneethi J, Shradha N, Rajawat A S, Nayak S R, Ramanamurthy M V and Subramanian B R 2004 Tidal currents as feeders of the river Indus flux into the macrotidal Gulf of Kachchh, India; 3rd Indian National Conference on Harbour and Ocean Engineering, NIO, Goa, pp. 174–183.
Chauhan O S, Jayakumar S, Menezes A A, Rajawat A S and Nayak S R 2006 Anomalous inland influx of River Indus, Gulf of Kachchh, India; Marine Geol. 229 91–100.
Folk R L 1974 Petrology of sedimentary rocks; Hemphill Publishing Co. Texas, 184p.
Garzanti E and Ando S 2007 Heavy mineral concentration in modern sands: Implications for provenance interpretation; Dev. Sedim. 58 517–545.
Garzanti E, Vezzoli G, Andó S, Paparella P and Clift P 2005 Petrology of Indus River sands: A key to interpret erosion history of the western Himalayan Syntaxis; Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 229 287–302.
Giosan L, Constantinescu C, Clift P D, Tabrez A R, Danish M and Inam A 2006 Recent morphodynamics of Indus delta shore and shelf; Marine Geol. 26(14) 1668–1684, doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2006.05.009.
Goodbred S L 2003 Response of Ganga dispersal system to climate change: A source-to-sink view since the last interstade; Sedim. Geol. 162 83–104.
Hashimi N H, Nair R R and Kidwai R M 1978 Sediments of Gulf of Kachchh – A high energy tide dominated environment; Indian J. Marine Sci. 7 1–7.
Horng C S and Huh C A 2011 Magnetic properties as tracers for source-to-sink dispersal of sediments: A case study in the Taiwan Strait; Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2011.07.002.
Jiang F, Li A and Li T 2011 Sediment pathway of East China Sea inferred from an R-mode factor analysis of surface sediments in Okinawa trough; Quat. Int. 230(1–2) 13–20.
Kar A 1993 Neotectonic influence on morphological variations along coastline of Kachchh, India; Geomorphology 8 199–219.
Kessarkar P M, Rao V P, Ahmad S M and Badu B A 2003 Clay minerals and Sr–Nd isotopes of the sediments along the western margin of India and their implication for sediment provenance; Marine Geol. 202 55–69.
Kolla V, Henderson L and Biscaye P E 1976 Clay mineralogy and sedimentation in the western Indian ocean; Deep Sea Research and Oceanagraphic abstracts 23(10) 949–961.
Kuehl S A, Brunskill G J, Burns K A, Fugate D C, Kniskern T and Meneghini L 2004 Nature of sediment dispersal off the Sepik River, Papua New Guinea: Preliminary sediment budget and implications for margin processes; Cont. Shelf Res. 24(19) 2417–2429.
Kunte P D, Wagle B G and Sugimori Y 2003 Sediment transport and depth variation study of Gulf of Kutch using remote sensing; Intl. J. Rem. Sen. 24(11) 2253–2263.
Lepland A and Stevens R L 1996 Mineral magnetic and textural interpretations of sedimentation in the Skagerrak, eastern North Sea; Marine Geol. 135 51–64.
Limmer D, Köhler C, Hillier S, Mauqoy D, Alizai A, Sothcott J, Giosan L, Ponton C, Tabrez A and Clift P D 2012a Temporal changes in physical properties and mineralogy of Holocene to Recent sediments from the Western Indus Shelf, Northern Arabian Sea; Marine Geol. 326–328 101–115.
Limmer D R, Boening P, Giosan L, Ponton C, Köhler C M, Cooper M J, Tabrez A R and Clift P D 2012b Geochemical record of Holocene to recent sedimentation on the western Indus continental shelf, Arabian Sea; Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 13(Q01008), doi: 10.1029/2011GC003845.
Liu S, Zhang W, He Q, Li D, Liu H and Yu L 2010 Magnetic properties of East China sea shelf sediments off Yangtze estuary: Influence of provenance and particle size; Geomorphology 119 212–220.
Maher B A, Watkins S J, Brunskill G, Alexander J and Fielding C R 2009 Sediment provenance in a tropical fluvial and marine context by magnetic ‘fingerprinting’ of transportable sand fractions; Sedimentology 56 841–861.
Mange M A and Maurer H F W 1991 Heavy Minerals in Colour; Chapman and Hall, London 1 160p.
MARGINS Office 2003 Source-to-Sink. NSF MARGINS Program Science Plans 2004, Lamont–Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University, New York, September 2003, 170p.
Maurya D M, Thakkar M G, Patidar A K, Bhandari S, Goyal B and Chamyal L S 2008 Late Quaternary geomorphic evolution of coastal zone of Kachchh, western India; J. Coast. Res. 24(3) 746–758.
Milliman J D, Quraishee G S and Beg M A A 1982 Sediment discharge from the Indus River to the ocean: Past, present and future; In: Marine Geology and Oceanography of Arabian Sea and Coastal Pakistan (eds) Haq B U and Milliman J D, Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, pp. 65–70.
Nair R R, Hashimi N H and Rao V P 1982 On the possibility of high velocity tidal streams as dynamic barrier to longshore sediment transport: Evidence from continental shelf off the Gulf of Kachchh, India; Marine Geol. 47 77–86.
Nechaev V P and Isphording W C 1993 Heavy-mineral assemblages of continental margins as indicators of plate-tectonic environments; J. Sedim. Res. 63(6) 1110–1117.
Oldfield F and Yu L 1994 The influence of particle size variations on the magnetic properties of sediments from the north-eastern Irish Sea; Sedimentology 41 1093–1108.
Petschick R, Kuhn G and Gingele F 1996 Clay mineral distribution in surface sediments of south Atlantic: Sources, transport and relation to oceanography; Marine Geol. 130 203–229.
Pettijohn F J, Potter P E and Siever R 1987 Sand and Sandstones; 2nd edn, Springer-Verlag, New York, 553p.
Prizomwala S P, Shukla S B and Bhatt N 2010 Geomorphic assemblage of the Gulf of Kachchh coast, western India: Implication in understanding the pathways of coastal sediments; Zeitschrift fur Geomorphologie 54(1) 31–46.
Prizomwala S P, Shukla S B and Bhatt N 2012 Distribution of Indus born mica along Gulf of Kachchh coast: Implications in understanding offshore dynamics; J. Geol. Soc. India 79 557–562.
Prizomwala S P, Shukla S B, Basavaiah N and Bhatt N 2013 Provenance discrimination studies on sediments of SW Kachchh coast, western India: Insights from heavy mineral and mineral magnetic analysis; J. Coast. Res. 29(1) 52–60.
Prizomwala S P, Bhatt N and Basavaiah N Provenance discrimination and source-to-sink studies from a dryland fluvial regime: An example from Kachchh, western India; Int. J. Sedim. Res. (in press).
Ramaswamy V, Nagender N B, Vethamony P and Illangovan D 2007 Source and dispersal of suspended sediment in macro-tidal Gulf of Kachchh; Marine Pollut. Bull. 54 708–719.
Rao V P and Rao B R 1995 Provenance and distribution of clay minerals sediments in sediments of the western continental shelf and slope of India; Cont. Shelf Res. 15(14) 1757–1771.
Shetye S R 1999 Tides in the Gulf of Kachchh, India; Cont. Shelf Res. 19 1771–1782.
Shukla S B, Prizomwala S P, Ukey V, Bhatt N and Chamyal L S 2010 Coastal geomorphology and tsunami hazard scenario along the Kachchh coast, western India; Indian J. Geo-Marine Sci. 39(4) 549–556.
Staubwasser M and Sirocko F 2001 On the formation of laminated sediments on the continental margin off Pakistan: The effects of sediment provenance and sediment redistribution; Marine Geol. 172 43–56.
Syvitski J P M, Kettner A J, Correggian A and Nelson B W 2005 Distributary channels and their impact on sediment dispersal; Marine Geol. 222–223 75–94.
Vethamony P, Reddy G S, Babu M T, Desa E and Sudheesh K 2005 Tidal eddies in a semi-enclosed basin: A model study; Marine Environ. Res. 59 519–532.
Vethamony P, Babu M T, Ramanamurty M V, Saran A K, Joseph A, Sudheesh K, Padgaonkar R S and Jayakumar S 2007 Thermohaline structure of an Inverse Estuary – the Gulf of Kachchh: Measurements and model simulations; Marine Pollut. Bull. 54(6) 697–707.
Vora K H, Chauhan O S and Rao B R 1987 Some geological processes in the macro-tidal regime of Gulf of Kachchh, Northwest coast of India; Indian J. Marine Sci. 16 230–234.
Wang Y, Dong H, Li G, Zhang W, Oguchi T, Bap M, Jiang H and Bishop M 2010 Magnetic properties of muddy sediments on the northeastern continental shelves of China: Implication for provenance and transportation; Marine Geol. 274 107–119.
Wasson R J 2003 A sediment budget for the Ganga–Brahmaputra catchment; Curr. Sci. 84(8) 1041–1047.
Worm H-U 1998 On the superparamagnetic-stable single domain transition for magnetite, and frequency dependency of susceptibility; Geophys. J. Int. 133 201–206.
Yang S Y, Jung H S, Lim D I and Li C X 2003 A review on provenance discrimination of sediments in Yellow sea; Earth Sci. Rev. 63 93–120.
Yang S, Wang Z, Guo Y, Li C and Cai J 2009 Heavy mineral composition of Changjiang (Tangtze river) sediments and their provenance tracing implication; J. Asian Earth Sci. 35 56–65.
Acknowledgements
This is a contribution to the DST, Government of India sponsored research programme on Science of Shallow Subsurface (DST No. SR/S4/ES21/ Kachchh Window/P6). Prof L S Chamyal of the M S University of Baroda is thankfully acknowledged for constant encouragement and fruitful discussions. A critical review by anonymous reviewers and editors of the JESS has helped in significant improvement of the earlier version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prizomwala, S.P., Bhatt, N. & Basavaiah, N. Understanding the sediment routing system along the Gulf of Kachchh coast, western India: Significance of small ephemeral rivers. J Earth Syst Sci 123, 121–133 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-013-0379-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-013-0379-7