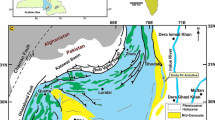
The Kachchh Mainland Fault (KMF) is a major E–W trending seismically active fault of the Kachchh palaeorift basin whose neotectonic evolution is not known. The present study deals with the eastern part of the KMF zone where the fault is morphologically expressed as steep north facing scarps and is divisible into five morphotectonic segments. The Quaternary sediments occurring in a narrow zone between the E–W trending KMF scarps and the flat Banni plain to the north are documented. The sediments show considerable heterogeneity vertically as well as laterally along the KMF zone. (The Quaternary sediments for a northward sloping and are exposed along the north flowing streams which also show rapid decrease in the depth of incision in the same direction.) The deposits, in general, comprise coarse as well as finer gravelly deposits, sands and aeolian and fluvial miliolites. The Quaternary sediments of the KMF zone show three major aggradation phases. The oldest phase includes the colluvio-fluvial sediments occurring below the miliolites. These deposits are strikingly coarse grained and show poor sorting and large angular clasts of Mesozoic rocks. The sedimentary characteristics indicate deposition, dominantly by debris flows and sediment gravity flows, as small coalescing alluvial fans in front of the scarps. These deposits suggest pre-miliolite neotectonic activity along the KMF. The second aggradation phase comprises aeolian miliolites and fluvially reworked miliolites that have been previously dated from middle to late Pleistocene. The youngest phase is the post-miliolite phase that includes all deposits younger than miliolite. These are represented by comparatively finer sandy gravels, gravelly sands and sand. The sediment characteristics suggest deposition in shallow braided stream channels under reduced level of neotectonic activity along the KMF during post-miliolite time evidenced by vertical dips of miliolites and tilting of gravels near the scarps. The tectonically controlled incision and dissection of the Quaternary deposits is the result of neotectonic activity that continues at present day. The overall nature, sedimentary characteristics and geomorphic setting of the sediments suggest that the KMF remained neotectonically active throughout the Quaternary period.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aziz H A, Rubio E S, Calvo J P, Hilgen F J and Krijgsman W 2003 Palaeoenvironmental reconstruction of a middle Miocene alluvial fan to cyclic shallow lacustrine depositional system in the Calatayud Basin (NE Spain); Sedimentology 50 211–236.
Baskaran M, Deshpande S V, Rajaguru S N and Somayajulu B L K 1989 Geochronology of miliolite rocks of Kutch, western India; J. Geol. Soc. India 33 588–593.
Bilham R 1998 Slip parameters of the Rann of Kachchh, India, 16 June 1819 earthquake quantified from contemporary accounts; In: Coastal Tectonics (eds) Stewart I S, Vita-Finzi C; Geol. Soc London 146 295–318.
Biswas S K 1971 The miliolite rocks of Kutch and Kathiawar; Sedim. Geol. 5 147–164.
Biswas S K 1974 Landscape of Kutch – A morphotectonic analysis; Indian J. Earth Sci. 1(2) 177–190.
Biswas S K 1987 Regional tectonic framework, structure and evolution of western marginal basins of India; Tectonophys. 135 307–327.
Biswas S K 1993 Geology of Kutch; K.D. Malaviya Institute of Petroleum Exploration, Dehradun, 2 450p.
Biswas S K and Khattri K N 2002 A geological study of earthquakes in Kachchh, Gujarat, India; J. Geol. Soc. India 60 131–142.
Blair T C and Mcpherson J G 1992 The Trollheim alluvial fan and facies model revisited; Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 104 762–769.
Bull W B 1997 Discontinuous ephemeral streams; Geomorphology 19 227–276.
Chakrabarti A, Somayajulu B L K, Baskaran M and Kumar B 1993 Quaternary miliolites of Kutch and Saurashtra, western India: Depositional environments in the light of physical sedimentary structures, biogenic structures and geochronological setting of the rocks; Senckenbergina Maritima 23 7–28.
Chen Y, Li Y, Zhang Y, Zhang M, Zhang J, Yi C and Liu G 2011 Late Quaternary deposition and incision sequences of the Golmud River and their environmental implications; Quat. Int. 236 48–56.
Chung W Y and Gao G 1995 Source parameters of the Anjar earthquake of July 21, 1956, India and its seismotectonic implications for the Kutch rift basin; Tectonophys. 242 281–292.
Coltorti M, Fazia J D, Rios F P and Tito G 2010 The Nuagapua alluvial fan sequence: Early and Late Holocene human-induced changes in the Bolivian Chaco?; Proc. Geologists’ Assoc. 121 218–228.
Deynoux M, Ciner A, Monod O, Karabıyıkoglu M, Manatschal G and Tuzcu S 2005 Facies architecture and depositional evolution of alluvial fan to fan-delta complexes in the tectonically active Miocene Koprucay Basin, Isparta Angle, Turkey; Sedim. Geol. 173 315–343.
Dorsey R J and Roering J J 2006 Quaternary landscape evolution in the San Jacinto fault zone, peninsular ranges of southern California: Transient response to strike-slip fault initiation; Geomorphology 73 16–32.
Garcia A F, Zhu Z, Ku T L, Galdeano C S, Chadwick O A and Chacón Montero J 2003 Tectonically driven landscape development within the eastern Alpujarran Corridor, Betic Cordillera, SE Spain (Almería); Geomorphology 50 83–110.
Garzione C N, DeCelles P G, Hodkinson D G, Ojha T P and Upreti B N 2003 East-west extension and Miocene environmental change in the southern Tibetan plateau: Thakkhola graben, central Nepal; Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 115 3–20.
Hein F J and Walker R G 1977 Bar evolution and development of stratification in the gravelly braided Kicking Horse River, British Columbia; Canadian J. Earth Sci. 14 562–570.
Humphrey N F and Konrad S K 2000 River incision or diversion in reponse to bedrock uplift; Geology 28 43–46.
Kallmeier E, Breitkreuz C, Kiersnowski H and Geißler M 2010 Issues associated with the distinction between climatic and tectonic controls on Permian alluvial fan deposits from the Kotzen and Barnim Basins (North German Basin); Sedim. Geol. 223 15–34.
Leeder M R, Seger M J and Stark C P 1991 Sedimentation and tectonic geomorphology adjacent to major active and inactive normal faults, southern Greece; J. Geol. Soc. London 148 331–343.
Mcpherson J G, Shanmugam G and Moiola R J 1987 Fan-deltas and braid deltas: Varieties of coarse-grained deltas; Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 99 331–340.
Maurya D M, Thakkar M G and Chamyal L S 2003a Implications of transverse fault system on tectonic evolution of Mainland Kachchh, western India; Curr. Sci. 85 661–667.
Maurya D M, Bhandari S, Thakkar M G and Chamyal L S 2003b Late Quaternary fluvial sequences of southern Mainland Kachchh, western India; Curr. Sci. 84 1056–1064.
Maurya D M, Thakkar M G, Patidar A K, Bhandari S, Goyal B and Chamyal L S 2008 Late Quaternary geomorphic evolution of the coastal zone of Kachchh, western India; J. Coastal Res. 24 746–758.
Miall A D 1977 A review of the braided-river depositional environment; Earth Sci. Rev. 13 1–62.
Miall A D 1996 The geology of fluvial deposits; Springer, Berlin, 582p.
Merh S S 2005 The Great Rann of Kachchh: Perception of a field geologist; J. Geol. Soc. India 65 9–25.
Patidar A K, Maurya D M, Thakkar M G and Chamyal L S 2007 Fluvial geomorphology and neotectonic activity based on field and GPR data, Katrol hill range, Kachchh, western India; Quat. Int. 159 74–92.
Patidar A K, Maurya D M, Thakkar M G and Chamyal L S 2008 Evidence of neotectonic reactivation of the Katrol Hill Fault during late Quaternary and its GPR characterization; Curr. Sci. 94 338–346.
Pope R, Wilkinson K, Skourtsos E, Triantaphyllou M and Ferrier G 2008 Clarifying stages of alluvial fan evolution along the Sfakian piedmont, southern Crete: New evidence from analysis of post-incisive soils and OSL dating; Geomorphology 94 206–225.
Rust B R 1978 Depositional models for braided alluvium, In: Fluvial Sedimentology (ed.) Miall A D, Can. Soc. Petrol. Geol. Mem. 5 605–625.
Smith G A 1986 Coarse-grained nonmarine volcaniclastic sediment and depositional processes; Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 97 1–10.
Somayajulu B L K 1993 Age and mineralogy of the miliolites of Saurashtra and Kachchh, Gujarat; Curr. Sci. 64 926–928.
Stokes M and Mather A E 2000 Response of Plio-Pleistocene alluvial systems to tectonically induced base-level changes, Vera Basin, SE Spain; J. Geol. Soc. London 157 303–316.
Thakkar M G, Maurya D M, Rachna R and Chamyal L S 1999 Quaternary tectonic history and terrain evolution of the area around Bhuj, Mainland Kachchh, western India; J. Geol. Soc. India 53 601–610.
Wells S G and Harvey A M 1987 Sedimentologic and geomorphic variations in storm-generated alluvial fans Howgill Fells, northwest England; Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 98 182–198.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
CHOWKSEY, V., MAURYA, D.M., JOSHI, P. et al. Lithostratigraphic development and neotectonic significance of the Quaternary sediments along the Kachchh Mainland Fault (KMF) zone, western India. J Earth Syst Sci 120, 979–999 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-011-0123-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-011-0123-0