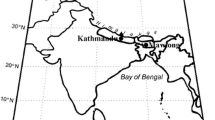
Isotopic composition of monthly composite precipitation samples from Kozhikode (n = 31), a wet tropic station and Hyderabad (n = 25), a semi-arid station across southern India were studied for a period of four years from 2005 to 2008. During the study period, the Kozhikode station recorded an average rainfall of 3500 mm while the Hyderabad station showed an average rainfall of 790 mm. The average stable isotope values in precipitation at the Kozhikode station were δ 18O = −3.52‰, d-excess = 13.72‰; δ 18O = −2.94‰, d-excess = 10.57‰; and δ 18O = −7.53‰, d-excess = 13.79‰, respectively during the pre-monsoon (March–May), monsoon (June–September) and post-monsoon (October–February) seasons. For the Hyderabad station, the average stable isotope values were δ 18O = −5.88‰, d-excess = 2.34‰; δ 18O = −4.39‰, d-excess = 9.21‰; and δ 18O = −8.69‰, d-excess = 14.29‰, respectively for the three seasons. The precipitation at the two stations showed distinctive isotopic signatures. The stable isotopic composition of precipitation at the Hyderabad station showed significant variations from the global trend while the Kozhikode station almost followed the global value. These differences are mainly attributed to the latitudinal differences of the two stations coupled with the differences in climatic conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Argiriou A A and Lykoudis S 2006 Isotopic composition of precipitation in Greece; J. Hydrol. 327 486–495.
Alyamani M S 2001 Isotopic composition of rainfall and ground water recharge in the western province of Saudi Arabia; J. Arid Environ. 49 751–760.
Buechler S J, Devi G and Raschid L 2002 Livelihoods and wastewater irrigated agriculture along the Musi River in Hyderabad city, Andhra Pradesh, India; Urban Agriculture 8 14–17.
Clark I D and Fritz P 1997 Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology; Boca Raton, Lewis Publishers, pp. 40–108.
Craig H 1961 Isotopic variation in meteoric waters; Science 133 1702–1703.
Dansgaard W 1964 Stable isotopes in precipitation; Tellus 16 436–468.
Datta P S, Tyagi S K and Chandrasekharan H 1991 Factors controlling the stable isotopic composition of rainfall in New Delhi, India; J. Hydrol. 128 223–236.
Delaygue G, Bard E, Rollion C, Jouzel J, Stiévenard M, Duplessy J C and Ganssen G 2001 Oxygen isotope/ salinity relationship in the northern Indian Ocean; J. Geophys. Res. 106(C3) 4565–4574, doi: 10.1029/ 1999JC000061.
Deshpande R D, Bhattacharya S K, Jani R A and Gupta S K 2003 Distribution of oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in shallow groundwaters from Southern India: Influence of a dual monsoon system; J. Hydrol. 271 226–239.
Epstein S and Mayeda T 1953 Variation of 18O content of water from natural sources; Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 4 213–214.
Fontes J Ch 1980 Environmental isotopes in groundwater hydrology; In: Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry; Fritz P and Fontes J Ch (eds) Vol. 1, The Terrestrial Environment (Amsterdam: Elsevier), pp. 75–140.
Gonfiantini R 1978 Standards for stable isotope measurements in natural compounds; Nature 271 534–536.
Gonfiantini R 1986 Environmental isotopes in lake studies; In: Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry; (eds) Fritz P and Fontes J Ch (New York: Elsevier) 2 113–168.
Hendry M J 1988 Hydrogeology of clay till in a prairie region in Canada; Ground Water 26 607–614.
International Atomic Energy Agency 1981 Guidebook on Nuclear Techniques in Hydrology; Technical Report Series Vienna.
Kadorkar M S 2009 WWDR3 side publication on Ecosystem Management; United Nations Environment Programme-UNEP, pp. 56–59.
Katiyar V S 1990 The Indian Monsoon and its Frontiers; (New Delhi: Inter-India Publications), pp. 227–228.
Kondoh A and Shimada J 1997 The origin of precipitation in eastern Asia by deuterium excess; J. Japan Soc. Hydrol. & Water Resour. 10(6) 627–629.
Krabbenhoft D P, Bowser C J, Anderson M P and Valley J W 1990 Estimating groundwater exchange with lakes: The stable isotope mass balance method; Water Resour. Res. 26 2445–2453.
Kulkarni K M, Navada S V, Nair A R, Rao S M, Shivanna K, Sinha U K and Sharma S 1997 Drinking water salinity problem in coastal Orissa, India – Identification of past transgression of sea water by isotope investigation; In: Isotope Techniques in the Study of Past and Current Environmental Change, Proc. Intl. Symp. IAEA Vienna, pp. 293–306.
Kumar B, Rai S P, Saravana Kumar U, Verma S K, Garg P, Vijaya Kumar S V, Jaiswal R, Purendra B K, Kumar S R and Pande N G 2010 Isotopic characteristics of Indian precipitation; Water Resour. Res. 46 W12548, doi: 10.1029/2009WR008532.
Lawrence R J and Gedzelman D S 1996 Low stable isotope ratios of tropical cyclone rains; Geophys. Res. Lett. 23(5) 527–530.
Mathieu R and Bariac T 1996 An isotopic study on water movements in clayey soils under semiarid climate; Water Resour. Res. 32 779–789.
Mazor E 1991 Chemical and Isotopic Groundwater Hydrology; The Applied Approach, 2nd edn; Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, 413p.
Menon P A and Rajan C K 1989 Climate of Kerala; Classic Publishing House Cochin, pp. 5–35.
Rozanski K, Sonntag G and Munnich K O 1982 Factors controlling the stable isotopic composition of European precipitation; Tellus 34 142–150.
Rozanski K, Araguas A L and Gonfiantini R 1993 Isotopic patterns in modern global precipitation; Geophys. Monogr. 78 1–37.
Saravana Kumar U, Suman S, Navada S V and Deodhar A S 2009 Environmental isotopes investigation on recharge processes and hydrodynamics of the coastal sedimentary aquifers of Tiruvadanai, Tamil Nadu State, India; J. Hydrol. 364 23–39.
Sengupta S and Sarkar A 2006 Stable isotope evidence for dual (Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal) vapour sources in monsoonal precipitation over north India; Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 250 511–521.
Unnikrishnan Warrier C, Praveen Babu M, Manjula P, Velayudhan K T, Shahul Hameed A and Vasu K 2010 Isotopic characterisation of dual monsoon precipitation-evidence from Kerala, India; Curr. Sci. 98 1487– 1495.
Yadava M G, Ramesh R and Pandarinath K 2007 A positive ‘amount effect’ in the Sahayadri (Western Ghats) rainfall; Curr. Sci. 93(4) 560–564.
Yurtsever Y and Gat G R 1971 Atmospheric waters; In: Stable Isotope Hydrology Deuterium and Oxygen-18 in the Water Cycle (eds) Gat J R and Gonfiantini R, IAEA Technical Report Series Vienna, pp. 103–142.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WARRIER, C.U., BABU, M.P. A comparative study on isotopic composition of precipitation in wet tropic and semi-arid stations across southern India. J Earth Syst Sci 120, 1085–1094 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-011-0121-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-011-0121-2