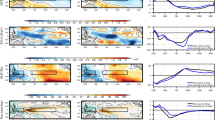
The Indian subcontinent witnessed a severe monsoon drought in the year 2009. India as a whole received 77% of its long period average during summer monsoon season (1 June to 30 September) of 2009, which is the third highest deficient all India monsoon season rainfall year during the period 1901–2009. Therefore, an attempt is made in this paper to study the characteristic features of summer monsoon rainfall of 2009 over the country and to investigate some of the possible causes behind the anomalous behaviour of the monsoon.
Presence of El Niño like conditions in the Pacific and warming over the equatorial Indian Ocean altered the circulation patterns and produced an anomalous low level convergence and ascending motion over the Indian Ocean region and large scale subsidence over the Indian landmass. Furthermore, the cross-equatorial flow was weak, the monsoon was dominated by the slower 30–60 day mode, and the synoptic systems, which formed over the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea, did not move inland. All the above features resulted in less moisture supply over the Indian landmass, resulting in subdued rainfall activity leading to a severe monsoon drought during 2009.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya N, Kar S C, Mohanty U C, Kulkarni M A and Dash S K 2011 Performance of GCMs for seasonal prediction over India – A case study for 2009 monsoon; Theor. Appl. Climatol., doi:10.1007/s00704-010-0396-2.
Ashok K, Guan Z and Yamagata T 2001 Impact of Indian Ocean Dipole on the relationship between the Indian monsoon rainfall and ENSO; Geophys. Res. Lett. 28 4499–4502.
Behera S K, Krishnan R and Yamagata T 1999 Unusual Ocean-atmosphere conditions in the tropical Indian Ocean during 1994; Geophys. Res. Lett. 26 3001–3004.
Francis P A and Gadgil S 2009 The aberrant behaviour of the Indian monsoon in June 2009; Curr. Sci. 85 1291–1295.
Francis P A and Gadgil S 2010 Towards understanding the unusual Indian monsoon in 2009; J. Earth Syst. Sci. 119 397–415.
Gadgil S, Abrol Y P and Seshagiri Rao P R 1999 On growth and fluctuation of Indian foodgrain production; Curr. Sci. 76 548–556.
Gadgil S 2000 Monsoon ocean coupling; Curr. Sci. 97 309–323.
Gadgil S, Vinayachandran P N and Francis P A 2003 Droughts of Indian summer monsoon: Role of clouds over Indian Ocean; Curr. Sci. 85 1713–1719.
Gadgil S, Vinayachandran P N, Francis P A and Gadgil S 2004 Extremes of the Indian summer monsoon rainfall, ENSO and Equatorial Indian Ocean Oscillation; Geophys. Res. Lett., doi: 10.1029/2004GL019733.
Joseph P V 1976a Monsoon rainfall and cyclone tracks in relation to 500 hPa altitudes, 1955–1974; Proceedings of Symposium on Tropical Monsoons, Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune, pp. 494–504.
Joseph P V 1976b Climate change in monsoon and cyclones 1891 to 1974; Proceedings of Symposium on Tropical Monsoons, Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune, pp. 378–387.
Kalnay E et al 1996 The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project; Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 77 437–470.
Koteswaram P 1958 The easterly jet stream in the tropics; Tellus 10 43–56.
Kripalani R H and Kulkarni A 1996 Assessing the impacts of El Niño and non-El Niño related droughts over India; Drought Network News 8 11–13.
Kripalani R H and Kulkarni A 1999 Climatology and variability of historical Soviet snow depth: Some new perspectives in snow-Indian monsoon teleconnections; Climate Dynamics 15 475–489.
Kripalani R H, Kulkarni A, Sabade S S, Revadekar J V, Patwardhan S K and Kulkarni J R 2004 Intra-seasonal oscillations during monsoon 2002 and 2003; Curr. Sci. 87 327–331.
Kripalani R H, Kulkarni A and Singh S V 1997 Association of the Indian summer monsoon with the Northern Hemisphere midlatitude circulation; Int. J. Climatol. 17 1055–1067.
Krishnamurti T N 1973 Tibetan high and upper tropospheric tropical circulation during northern summer; Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 54 1234–1249.
Krishnamurti T N, Thomas A, Simon A and Vinay Kumar 2010 Desert air incursions, an overlooked aspect, for the dry spells of the Indian summer monsoon; J. Atmos. Sci. 67 3423–3441.
Krishnan R, Vinay Kumar, Sugi M and Yoshimura J 2009 Internal feedbacks from monsoon–midlatitude interactions during droughts in the Indian summer monsoon; J. Atmos. Sci. 66 553–578.
Li T and Zhang Y 2002 Processes that determine the quasi-biennial and lower-frequency variability of the South Asian monsoon; J. Meteor. Soc. Japan 80 1149–1163.
Mujumdar M, Vinay Kumar and Krishnan R 2007 Indian summer monsoon drought of 2002 and its linkage with tropical convective activity over northwest Pacific; Climate Dynamics 28 743–758.
Nanjundiah R S 2009 A quick-look assessment of forecasts for the Indian summer monsoon rainfall in 2009; 2009- AS-2, CAOS Technical Report, Centre for Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, India.
Neena J M, Suhas E and Goswami B N 2011 Leading role of internal dynamics in the 2009 Indian summer monsoon drought; J. Geophys. Res., doi: 10.1029/2010JD015328.
Pai D S and Sreejith O P 2010 Global and regional circulation anomalies. Monsoon 2009; A report. IMD Met Monograph No: Synoptic Meteorology No. 09/2010, National Climate Centre, India Meteorological Department, Pune, India.
Parthasarathy B and Pant G B 1985 Seasonal relationship between Indian summer monsoon rainfall and southern oscillation; J. Climate 5 369–378.
Parthasarathy B, Sontakke N A, Munot A A and Kothawale D R 1987 Droughts/floods in summer monsoons season over different meteorological sub-divisions of India for the period 1871–1980; J. Climatol. 7 57–70.
Parthasarathy B, Rupa Kumar K and Munot A A 1992 Forecast of rainy season foodgrain production based on monsoon rainfall; Indian J. Agri. Sci. 62 1–8.
Preethi B, Revadekar J V and Munot A A 2011 Extremes in precipitation over India during 2001–2009 using CPC high resolution data; Int. J. Remote Sens. 32 717–735.
Ramaswamy C 1962 Breaks in the Indian summer monsoon as a phenomenon of interaction between the easterly and the subtropical westerly jet streams; Tellus 14A 337–349.
Rasmussen E M and Carpenter T H 1983 The relationship between eastern equatorial Pacific SSTs and rainfall over India and Sri Lanka; Mon. Weather Rev. 111 517–528.
Ratnam J V, Behera S K, Masumoto Y, Takahashi T and Yamagata T 2010 Pacific ocean origin for the 2009 Indian summer monsoon failure; Geophys. Res. Lett. 37 L07807, doi: 10.1029/2010GL042798.
Saji N H, Goswami B N, Vinayachandran P N and Yamagata T 1999 A dipole mode in the tropical Indian ocean; Nature 401 360–363.
Sikka D R 1980 Some aspects of large-scale fluctuations of summer monsoon rainfall over India in relation to fluctuations in the planetary and regional scale circulation parameters; Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet. Sci.) 89 179–195.
Sikka D R and Gadgil S 1980 On the maximum cloud zone and the ITCZ over India longitude during the southwest monsoon; Mon. Weather Rev. 108 1840–1853.
Smith T M, Reynolds R W, Peterson T C and Lawrimore J 2007 Improvements to NOAA’s historical merged land–ocean surface temperature analysis (1880–2006); J. Climate 21 2283–2296.
Yanai M and Wu G-X 2006 Effects of the Tibetan Plateau; The Asian–Monsoon (ed.) Wang B, Springer-Praxis, pp. 513–549.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
PREETHI, B., REVADEKAR, J.V. & KRIPALANI, R.H. Anomalous behaviour of the Indian summer monsoon 2009. J Earth Syst Sci 120, 783–794 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-011-0112-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-011-0112-3