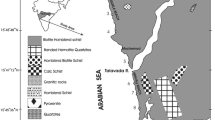
In this study, environmental magnetic, heavy metal and statistical analyses were conducted on 21 surface sediments collected from Chennai coast, India, to examine the feasibility of heavy metal pollution using magnetic susceptibility. The Chennai coastal sediment samples are dominated by ferrimagnetic minerals corresponding to magnetite-like minerals. The percentage of frequency dependent magnetic susceptibility reflects the presence of super-paramagnetic/single domain magnetic minerals in Chennai harbour, Cooum and Adayar rivers sediments. High pollution load index in sample E1, E2, CH7, C11, C12 and A16 is mainly due to anthropogenic activities such as, harbour activities, Cooum and Adayar rivers input and industrial effluent. Factor analysis shows that the magnetic concentration dependent parameters (χ, χ ARM and SIRM) covary with the heavy metal concentrations, suggesting that the input of magnetic minerals and heavy metals in Chennai coastal sediments are derived from the same anthropogenic sources. Strong correlation obtained between pollution load index (PLI) and concentration dependent parameters (χ, χ ARM and SIRM) for the polluted samples with magnetic susceptibility excess of 50×10 − 8 m3kg − 1. Significant correlations between heavy metals and magnetic susceptibility point out the potential of magnetic screening/monitoring for simple and rapid proxy indicator of heavy metal pollution in marine sediments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahim G M S and Parker R J 2008 Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary, Auckland, New Zealand; Environ. Monit. Assess. 136 227–238.
Alagarsamy R 2009 Environmental magnetism and application in the continental shelf sediments of India; Mar. Environ. Res. 68 49–58.
Angulo E 1996 The Tomlinson pollution load index applied to heavy metal ‘Mussel-Watch’ data: A useful index to assess coastal pollution; Sci. Total Environ. 187 19–56.
Bityukova L, Scholger R and Birke M 1999 Magnetic susceptibility as indicator of environmental pollution of soils in Tallinn; Phys. Chem. Earth 24 829–835.
Canbay M, Aydin A and Kurtulus C 2010 Magnetic susceptibility and heavy-metal contamination in topsoils along the Izmit Gulf coastal area and IZAYTAS (Turkey); J. Appl. Geophys. 70 46–57.
Chan L S, Ng S L, Davis A M, Yim W W S and Yeung C H 2001 Magnetic properties and heavy metal contents of contaminated seabed sediments of Penny’s Bay, Hong Kong; Mar. Pollut. Bull. 42 569–583.
Chan L S, Yeung C H, Yim W W S and Or O L 1998 Correlation between magnetic susceptibility and distribution of heavy metals in contaminated sea-floor sediments of Hong Kong harbour; Environ. Geol. 36 1–2.
Dearing J A 1994 Environmental magnetic susceptibility: Using the Bartington MS2 system; Chi Publishing, Kenilworth, U.K.
Flanders P J 1994 Collection, measurement, and analysis of airborne magnetic particulates from pollution in the environment; J. Appl. Phys. 75 5931–5936.
Hay K L, Dearing J A, Baban S M J and Loveland P 1997 A preliminary attempt to identify atmospherically-derived pollution particles in English topsoils from magnetic susceptibility measurements; Phys. Chem. Earth 22 207–210.
Higgitt S R, Oldfield F and Appleby P G 1991 The record of land use change and soil erosion in the late Holocene sediment of the Petit Lac d’Annecy, eastern France; The Holocene 1 14–28.
Horng C-S, Huh C-A, Chen K-H, Huang P-R, Hsiung K-H and Lin H-L 2009 Air pollution history elucidated from anthropogenic spherules and their magnetic signatures in marine sediments offshore of southwestern Taiwan; J. Mar. Syst. 76 468–478.
Karlin R, Lyle M and Ross Heath G 1987 Authigenic magnetite formation in suboxic marine sediments; Nature 326 490–493.
Lovley D R, Stolz J F, Nord J G L and Phillips E J P 1987 Anaerobic production of magnetite by a dissimilatory iron reducing microorganism; Nature 330 252–255.
Maher B A 1988 Magnetic properties of some synthetic sub-micron magnetites; Geophys. J. 94 83–96.
Maher B A 1998 Magnetic properties of modern soils and Quaternary loessic paleosols: Paleoclimatic implications; Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 137 25–54.
Maher B A and Taylor R M 1988 Formation of ultrafine grained magnetite in soils; Nature 336 368–370.
Maher B A and Thompson R 1999 Quaternary climates, environments and magnetism; Cambridge University Press, p. 383.
Maher B A, Thompson R and Hounslow M W 1999 Introduction; In: Quaternary Climate, Environments and Magnetism (eds) Maher B A and Thompson R (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press), pp. 1–48.
Matzka J and Maher B A 1999 Magnetic biomonitoring of roadside tree leaves: Identification of spatial and temporal variations in vehicle-derived particulates; Atmos. Environ. 33 4565–4569.
Oldfield F and Richardson N 1990 Lake sediment magnetism and atmospheric deposition; Philos. Trans. Roy. Soc. London B 327 325–330.
Peters C and Dekkers M J 2003 Selected room temperature magnetic parameters as a function of mineralogy, concentration and grain size; Phys. Chem. Earth 28 659–667.
Taylor S R and McLennan S M 1995 The geochemical evolution of the continental crust; Rev. Geophys. 33 241–265.
Thompson R and Oldfield F 1986 Environmental Magnetism, Allen and Unwin, London.
Venkatachalapathy R, Veerasingam S, Basavaiah N and Ramkumar T 2010 Comparison between petroleum hydrocarbon concentrations and magnetic properties in Chennai coastal sediments, Bay of Bengal, India; Mar. Petrol. Geol. 27 1927–1935.
Walden J, Smith J P and Oldfield F 1999 Environmental magnetism: A practical guide, Quaternary Research Association Technical Guide, vol. 6, 243p.
Zhou L P, Oldfield F, Wintle A G, Robinson S G and Wang J T 1990 Partly pedogenic origin of magnetic variations in Chinese loess; Nature 346 737–739.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
VENKATACHALAPATHY, R., VEERASINGAM, S., BASAVAIAH, N. et al. Environmental magnetic and geochemical characteristics of Chennai coastal sediments, Bay of Bengal, India. J Earth Syst Sci 120, 885–895 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-011-0108-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-011-0108-z