Abstract
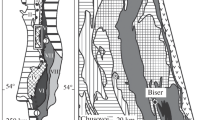
Cretaceous phosphorites from the onshore of Tamil Nadu have been investigated for their origin and compared with those in the offshore. Cretaceous phosphorites occur as light brown to yellowish brown or white nodules in Karai Shale of the Uttatur Group in the onshore Cauvery basin. Nodules exhibit phosphatic nucleus encrusted by a chalky shell of carbonate. The nucleus of the nodules consists of light and dark coloured laminae, phosphate peloids/coated grains and detrital particles interspersed between the laminae. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) studies reveal trapping and binding activity of microbial filaments. A mat structure with linearly arranged microbial filaments and hollow, cell-based coccoid cyanobacterial mat are present. Nodules contain abundant carbonate fluorapatite, followed by minor calcite, quartz and feldspar. The P2O5 content of the phosphorites ranges from 18 to 26%. The CaO/P2O5, Sr and F contents are higher than that of pure carbonate fluorapatite. Concentrations of Si, Al, K, Fe, and Ti are low. We suggest that the nuclei of the nodules represent phosphate clasts related to phosphate stromatolites formed at intertidal conditions. At high energy levels the microbial mats were disintegrated into phosphate clasts, coated with carbonate and then reworked into Karai Shale. On the other hand, Quaternary phosphorites occur as irregular to rounded, grey coloured phosphate clasts at water depths between 180 and 320m on the continental shelf of Tamil Nadu. They exhibit grain-supported texture. Despite Quaternary in age, they also resemble phosphate stromatolites of intertidal origin and reworked as phosphate clasts onto the shelf margin depressions. Benthic microbial mats probably supplied high phosphorus to the sediments. Availability of excess phosphorus seems to be a pre-requisite for the formation of phosphate stromatolites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azad H C and Borchardt J A 1970 Variations in phosphorus uptake by algae; Environ. Sci. Technol. 4 737–743.
Baioumy H and Tada R 2005 Origin of late Cretaceous phosphorites in Egypt; Cre. Res. 26 261–275.
Banerjee D M 1986 Proterozoic and Cambrian phosphorites regional review: India subcontinent; In: Phosphate deposits of the world, Proterozoic and Cambrian phosphorites (eds) Cook P J and Shergold J H (Cambridge University Press) 1 70–90.
Baturin G N 1981 Phosphorites on the seafloor, origin, composition and distribution; Developments in Sedimentology 33 (Elsevier), 343 p.
Berner R A, Ruttenburg K C, Ingall E D and Rao J L 1993 The nature of phosphorus burial in modern marine sediments; In: Interactions of C, N, P, and S biogeochemical cycles and global change (eds) Wollast R, Mackenzie E T and Chou L (Springer-Verlag) 365–378.
Bertrand-Sarfati J, Flicoteaux R, Moussine-Pouchkine A and Ahmed A A K 1997 Lower Cambrian apatite stromatolites and phospharenites related to glacio-eustatic cratonic rebound (Sahara, Algeria); J. Sediment. Res. 67 957–974.
Blanford H F 1862 Cretaceous and other rocks of South Arcot and Trichinopoly districts, Madras; Geol. Surv. India Memoir 4 217.
Burnett W C and Riggs S R 1986 Phosphate Deposits of the World, v. 3, Neogene to Modern phosphorites (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) 3 464 p.
Cook P J and Shergold J H 1986 Phosphate deposits of the World, Proterozoic and Cambrian phosphorites (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) 1 386 p.
Follomi K B 1989 Evolution of the Mid-Cretaceous triad: platform carbonates, phosphatic sediments and pelagic carbonates along the northern Tethys margin; Lecture notes in Earth Sciences (Berlin: Springer-Verlag) 23 153 p.
Follomi K B 1990 Condensation and phosphogenesis: example of the Helvetic mid-Cretaceous (northern Tethyan margin); In: Phosphorite Research and Development, (eds) Notholt A J G and Jarvis I, Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 52 237–252.
Follomi K B 1994 Concepts and controversies in phosphogenesis; Eclo. Geol. Helv. 87 639–788.
Glenn C R 1990 Depositional sequences of the Duwi, Sibaiya and phosphate formation, Egypt: phosphogenesis and glauconitization in a late Cretaceous epeiric sea; In: Phosphorite Research and Development (eds) Notholt A J G and Jarvis I, Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 52 205–222.
Glenn C R and Arthur M A 1990 Anatomy and origin of a Cretaceous phosphorite-Greensand giant, Egypt; Sediment. 37 123–154.
Govindan A, Yadagiri K, Ravindran C N and Kalyanasundar R 1998 A field guide on Cretaceous sequences of Tiruchirapalli Area, Cauvery Basin, India; Oil and Natural Gas Corporation Limited, 53 p.
Krajewski K P 1981 Phosphate microstromatolites in the High-Tatric Albian limestones in the Polish Tatra Mountains; Bull. Acad. Pol. Sci. Ser. Sci. Terre 29 175–183.
Krajewski K P, Van Cappellen P, Trichet J, Kuhn O, Lucas J, Martin-Algarra A, Prevot L, Tewari V V, Gasper I, Knight R I and Lamboy M 1994 Biological processes and apatite formation in sedimentary environments; Eclo. Geol. Helvet. 87 701–745.
Krumbien W E 1986 Biotransfer of minerals by microbes and microbial mats; In: Biomineralization in Lower Plants and Animals (eds) Leadbeater B S C and Riding R (Oxford University Press) 55–72.
Laskar B and Narasimhan A S 1968 Rock phosphate deposits in the Cretaceous rocks of South India; Geol. Soc. India Memoir 2 105–119.
Lamboy M 1990 Microbial mediation in phosphogenesis: new data from the Cretaceous phosphatic chalks of northern France; In: Phosphorite Research and Development (eds) Notholt A J G and Jarvis I, Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 52 157–167.
Mani G, Srinivasan K R, Nair K B and Selvan T A 1966 A preliminary note on the occurrence of phosphorite in the Uttatur beds of Cretaceous age, Tiruchinoploy district, Madras State; Geological Survey of India report, 30 p.
Martin-Algarra A and Sanchez-Navas A 1995 Phosphate stromatolites from condensed cephalopod limestones, Upper Jurassic Southern Spain; Sediment. 42 893–919.
Monty C L V 1976 The origin and development of cryptalgal structures; In: Stromatolites (ed.) Walter M R, Developments in Sedimentology (Elsevier) 20 193–250.
Notholt A J G and Jarvis I 1990 Phosphorite Research and Development; Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 52 326 p.
Notholt A J G, Sheldon R P and Davidson D F 1986 Phosphate Deposits of the World, V. 2, Phosphate Rock Resources (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press) 566 p.
Pevear D R 1966 The estuarine formation of United States Atlantic coastal plain phosphorites; Econ. Geol. 61 251–256.
Rama Rao L 1958 Fossil Algae in India; Nature 181 544–545.
Rao V P and Nair R R 1988 Microbial origin of phosphorites of the western continental margin of India; Mar. Geol. 84 105–110.
Rao V P, Rao K M and Raju D S N 2000 Quaternary phosphorites from the continental margin off Chennai, southeast India: Analogs of ancient phosphate stromatolites; J. Sediment. Res. 70 1197–1209.
Rao V P, Rao K M, Vora K H, Almeida F, Subramaniam M M and Souza C G A 1998 A potential phosphorite deposit on the continental margin off Chennai; Curr. Sci. 74 577–579.
Rao V P, Michard A, Naqvi S W A, Bottcher M E, Krishnaswamy R, Thamban M, Natarajan R and Borole D V 2002 Quaternary phosphorites off the southeast coast of India; Chem. Geol. 182 483–502.
Sastry V V, Raju A T R, Sinha R N and Venkatachala B S and Banerjee R K 1977 Biostratigraphy and evolution of the Cauvery Basin, India; J. Geol. Soc. India 18 355–377.
Soudry D and Champetier Y 1983 Microbial processes in the Negev phosphorites (southern Israel); Sediment. 30 411–423.
Soudry D and Panczer G 1994 Stromatolitic phosphorites in the Eocene of the Negev (Southern Israel); In: Phanerozoic stromatolites II (eds) Bertrand-Sarfati J and Monty C L V (The Netherlands: Kluwer) 255–276.
Taberner C, Marshall J D, Hendry J P, Pierre C and Thirlwall M F 2002 Celestite formation, bacterial sulphate reduction and carbonate cementation of Eocene reefs and basinal sediments (Igualada, NE Spain); Sediment. 49 171–190.
Valdiya K S 1972 Origin of phosphorite of the late Precambrian Gangolihat dolomites of Pithoragarh, Kumaun Himalaya, India; Sediment. 17 115–128.
Vaz G G 1995 Phosphatic nodules in the outer continental shelf off Madras, Bay of Bengal; Indian J. Mar. Sci. 24 8–12.
Vaz G G, Vijay Kumar P and Rao B L 1999 Phosphorites from the continental margin off Madras, Bay of Bengal; Mar. Georesour. Geotechnol. 17 33–48.
Walter M R 1976 Stromatolites; Development in Sedimentology (Amsterdam: Elsevier) 20 790 p.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Purnachandra Rao, V., Kessarkar, P.M., Nagendra, R. et al. Origin of Cretaceous phosphorites from the onshore of Tamil Nadu, India. J Earth Syst Sci 116, 525–536 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-007-0048-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-007-0048-9