Abstract
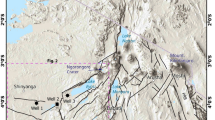
Giant quartz veins (GQVs; earlier referred to as ‘quartz reefs’) occurring in the Archean Bundelkhand Craton (29,000 km2) represent a gigantic Precambrian (∼2.15 Ga) silica-rich fluid activity in the central Indian shield. These veins form a striking curvilinear feature with positive relief having a preferred orientation NE-SW to NNE-SSW in the Bundelkhand Craton. Their outcrop widths vary from ≤1 to 70m and pervasively extend over tens of kilometers along the strike over the entire craton. Numerous younger thin quartz veins with somewhat similar orientation cut across the giant quartz veins. They show imprints of strong brittle to ductile-brittle deformation, and in places are associated with base metal and gold incidences, and pyrophyllite-diaspore mineralization. The geochemistry of giant quartz veins were studied. Apart from presenting new data on the geology and geochemistry of these veins, an attempt has been made to resolve the long standing debate on their origin, in favour of an emplacement due to tectonically controlled polyphase hydrothermal fluid activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basu A K 1986 Geology of parts of the Bundelkhand Craton, central India; Rec. Geol. Surv. India 101 61–124.
Brown C and Thomas L 1960 The effect of impurities on the growth of synthetic quartz; J. Phys. Chem. Solids 13 337.
Cohen A 1960 Substitutional and interstitial aluminium impurity in quartz: structure, and colour centre interrelationships; J. Phys. Chem. Solids 13 321–325.
Dong G, Morrison G and Jaireth S 1995 Quartz textures in epithermal veins, Queensland-classification, origin and implication; Econ. Geol. 90 1841–1856.
Gaines RV, Skinner H C W, Foord E E, Mason B and Rosenzweig A 1997 Dana’s New Mineralogy (New York: John Wiley & Sons) 1819 p.
Jhingran A G 1958 The problem of Bundelhkand granites and gneisses. Presidential Address; Proc. 45 th Indian Sci. Cong., Madras 98–120.
Kerrich R and Feng R 1992 Archean geodynamics and the Abitibi-Pontiac collision: implications for advection of fluids at transpressive collisional boundaries and the origin of giant quartz vein systems; Earth Sci. Rev. 23 33–60.
Malviya V P, Arima M, Pati J K and Kaneko Y 2004 First report of metamorphosed pillow lava in central part of Bundelkhand craton-an island arc setting of possible late Archaean age; Gondwana Res. 7 1338–1340.
Malviya V P, Arima M, Pati J K and Kaneko Y 2006 Petrology and geochemistry of metamorphosed basaltic pillow lava and basaltic komatiite in the Mauranipur area: subduction related volcanism in the Archaean Bundelkhand craton, central India; J. Mineral. Petrol. Sci. 101 199–217.
Mishra R C 1960 Quartz reefs of Bundelkhand and their origin; Proc. Indian Sci. Cong., III 241–242.
Mishra R C and Sharma R P 1975 New data on the geology the Bundelkhand Complex of central India; Recent Researches in Geology (New Delhi: Hindustan Publishing Corporation) 311–346.
Mondal M E A, Goswami J N, Deomurari M P and Sharma K K 2002 Ion microprobe 207Pb/206Pb ages zircons from Bundelkhand craton, north India: implications for crustal evolution of the Bundelkhand-Aravalli protocontinent; Prec. Res. 117 85–100.
Monecke T, Kempe U and Götze J 2002 Genetic significance of the trace element content in metamorphic and hydrothermal quartz: a reconnaissance study; Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 202 709–724.
Müller A 2000 Cathodoluminescence and characterisation of defect structures in quartz with applications to the study of granitic rocks (A dissertation zur Erlangung des Doktorgrades der Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Fakultäten der Georg August-Universität zu Götingen) 219 p.
Pascoe E H 1950 A Manual of the Geology of India and Burma. Part I (3rd edn.) (Geol. Surv. India) 486 p.
Passchier C W and Trouw R A J 1996 Microtectonics (Berlin: Springer-Verlag) 289 p.
Pati J K 1998 Specialized thematic studies of quartz reefs and mylonite zones in parts of Bundelkhand Granitoid Complex, southern U.P.; Rec. Geol. Surv. India 130(8) 88–89.
Pati J K 1999 Study of granitoid mylonites and reef/vein quartz in parts of Bundelkhand Granitoid Complex (BGC); Rec. Geol. Surv. India 131(8) 95–96.
Pati J K, Raju S, Mamgain V D and Shankar R 1997 Record of gold mineralization in parts of Bundelkhand Granitoid Complex (BGC); J. Geol. Soc. India 50 601–606.
Prasad M H, Hakim A and Krishna Rao B 1999 Metavolcanic and metasedimentary inclusions in the Bundelkhand Granitic Complex in Tikamgarh district, Madhya Pradesh; J. Geol. Soc. India 54 359–368.
Rao M J, Poornachandra Rao G V S, Widdowson M and Kelley S P 2005 Evolution of Proterozoic mafic dyke swarms of the Bundelkhand Granite Massif, central India; Curr. Sci. 88 502–506.
Roday P P, Diwan P and Singh S 1995 A synkinematic model of emplacement of quartz reefs and subsequent deformation patterns in the central Indian Bundelkhand batholith; Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet. Sci.) 104 465–468.
Sarkar A, Bhalla J K, Bishui P K, Gupta S N, Singhai R K and Upadhaya T P 1994 Tectonic discrimination of granitic rocks: studies on the early Proterozoic Bundelkhand Complex, central India; Indian Minerals 45 103–112.
Saxena M N 1961 Bundelkhand granites and associated rocks from Kabrai and Mauranipur area of Hamirpur and Jhansi District, Uttar Pradesh. Res. Bull (N.S). Punjab Univ. 12(1–2) 85–107.
Senthiappan M 1976 Geology of the area along the Raksa Shear zone, Jhansi district, Uttar Pradesh; Symposium on the Archaean of central India, GSI, Nagpur, Nov. 30–Dec. 1 (Abstract), 22 p.
Senthiappan M 1981 Geology of the area along the Raksa Shear zone, Jhansi district, Uttar Pradesh; Spec. Publ. Geol. Surv. India 3 73–76.
Sharma R P 1979 Origin of the pyrophyllite-diaspore deposits of the Bundelkhand Complex, central India; Mineral Deposita 14 343–352.
Sharma R P 1982 Lithostratigraphy, structure and petrology of the Bundelkhand Group; In: Geology of Vindhyachal (eds) K S Valdiya, S B Bhatia and V K Gaur (New Delhi: Hindustan Publishing Corporation) 30–46.
Sharma K K and Rahman A 1996 Bundelkhand Craton, Northern Indian Shield geochemistry, petrogenesis and tectonomagmatic environments; DST Newsletter 6 12–17.
Siebers F B 1986 Inhomogene verteilung von verunreinigungen in gezüchteten und natürlichen quarzen als funktion der Wachstumsbedingungen und ihr Einfluauf kristallphysikalische eigenschaften (Thesis, Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Germany) 133 p.
Siebers F B and Klapper H 1984 Zelluläres wachstum und verunreinigungsverteilung im zuchtquarz, aufgezeigt mit röntgentopographie; Zeitschrift für Kristallographie 167 177–178.
Stipp M, Stunitz H, Heilbronner R and Schmid S M 2002 The eastern Tonale fault zone: a ‘natural laboratory’ for crystal plastic deformation of quartz over a temperature range from 250 to 700°C; J. Struct. Geol. 24 1861–1884.
Sun Ss-and McDonough W F 1989 Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts implications for mantle composition and process. In: Magmatism in Ocean Basins (eds) A D Saunders and M J Norry; Geological Society Special Publication (Netherlands: Kluwer Academic).
Taylor S R and McLennan S M 1985 The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution (Oxford: Blackwell Scientific) 311 p.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pati, J.K., Patel, S.C., Pruseth, K.L. et al. Geology and geochemistry of giant quartz veins from the Bundelkhand Craton, central India and their implications. J Earth Syst Sci 116, 497–510 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-007-0046-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-007-0046-y