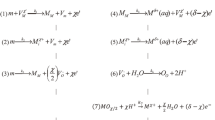Abstract
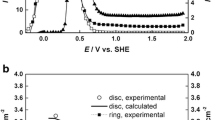
An impedance model for a metal surface corroding under a thin electrolyte layer is presented. The model describes the oxygen diffusion in the electrolyte, the cathodic current via the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) reaction and the anodic current via metal dissolution reaction (MDR) at the metal/electrolyte interface under the pseudo-steady approximation. The results for the impedance are obtained in terms of the thickness of electrolyte, the diffusion coefficient of oxygen, the concentration of dissolved oxygen and the anodic/cathodic reaction rates. The impedance characteristic are analysed through Bode and Nyquist plots which unveils six distinctive frequency regimes viz., (i) purely oxygen diffusion controlled regime, (ii) electrolyte film thickness controlled regime, (iii) activation controlled regime, (iv) mixed diffusion-kinetic controlled regime, (v) capacitive electric double layer controlled regime and (vi) solution Ohmic controlled regime. The impedance response shows two asymmetrical depressed arc on the Nyquist plots indicating the Faradaic charge transfer controlled regime and purely electrolyte thickness diffusion controlled regime with an intervening straight Warburg line. The arc at low frequencies is strongly dependent on the concentration and diffusion coefficient of dissolved oxygen indicative of pseudo-steady state behaviour of interface whereas the high frequency arc represents Faradaic regimes due to MDR and ORR which is indicative of the dynamic nature of corrosion reaction rates at the interface. At thick electrolyte layer, the interface shows a mass transport controlled kinetic regime with a finite length Warburg type impedance whereas at thin electrolyte layer the interface is activation controlled with a finite diffusion Randles type impedance response. A comparison of the model with the experimental data of corroding metal shows reasonable agreement.
Graphical abstract
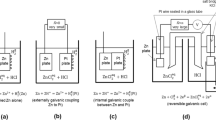
Atmospheric corrosion of metal in contact with a thin electrolyte film via diffusion of dissolved oxygen coupled with oxygen reduction reaction and metal dissolution reaction in pseudosteady state.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(\omega \) :
-
Frequency
- \(\omega _{\text {D}}\) :
-
Characteristic diffusion frequency
- \(\omega _C\) :
-
Characteristic Faradaic frequency
- \(\alpha _{{O_{2}/OH^{-}}}\) :
-
Transfer coefficient of ORR
- \(\alpha _{{M/M^{n_{1}^{+}}}}\) :
-
Transfer coefficient of MDR
- \({\Delta }C\) :
-
Deviation of oxygen concentration from steady state concentration \(C_{\text {st}}\)
- F :
-
Faraday’s constant
- \(Z_{\text {FLW}}(\omega )\) :
-
Finite length Warburg impedance
- \(R_{{\Omega }}\) :
-
Resistance of electrolyte
- \(R_{\text {ct}}\) :
-
Charge transfer resistance
- \(C_{\text {dl}}\) :
-
Capacitance of EDL
- D :
-
Diffusion constant of species
- T :
-
Temperature in Kelvin
- \(\Phi \) :
-
Phase of impedance
- E :
-
Potential
- \(E^{0}_{{M/M^{n_{1}^{+}}}}\) :
-
Reduction potential of MDR
- \( E^{0}_{{O_{2}/OH^{-}}}\) :
-
Reduction potential of ORR
- R :
-
Universal gas constant
- \(Z'(\omega )\) :
-
Real component of impedance
- \(Z''(\omega )\) :
-
Imaginary component of impedance
- \(|Z(\omega )|\) :
-
Magnitude of impedance
References
Cole I S, Azmat N S, Kanta A and Venkatraman M S 2009 What really controls the atmospheric corrosion of zinc? Effect of marine aerosols on atmospheric corrosion of zinc Int. Mater. Rev. 54 117
Cole I S, Muster T H, Azmat N S, Venkatraman M S and Cook A 2011 Multiscale modelling of the corrosion of metals under atmospheric corrosion Electrochim. Acta 56 1856
Gunasegaram D R, Venkatraman M S and Cole I S 2014 Towards multiscale modelling of localised corrosion Inter. Mat. Rev. 59 84
Simillion H, Dolgikh O, Terryn H and Deconinck J 2014 Atmospheric corrosion modeling Corr. Rev. 32 73
McCafferty E 2010 Introduction to Corrosion Science (Springer: New York) p. 8
Muster T H, Bradbury A, Trinchi A, Cole I S, Markley T, Lau D, Dligatch S, Bendavid A and Martin P 2011 The atmospheric corrosion of zinc: The effects of salt concentration, droplet size and droplet shape Electrochim. Acta 56 1866
Leygraf C, Wallinder I.O, Tidblad J and Graedel T 2016 Atmospheric Corrosion (Wiley: Hoboken) p. 22
Schweitzer P A 2007 Fundamentals of Metallic Corrosion: Atmospheric and Media Corrosion of Metals (CRC Pres: Taylor and Francis group) p. 39
Tomashov N D 1964 Development of the electrochemical theory of metallic corrosion Corros. 20 7t
Stratmann M and Streckel H 1990 On the atmospheric corrosion of metals which are covered with thin electrolyte layers- I. Verification of the experimental technique Corros. Sci. 30 681
Stratmann M and Streckel H 1990 On the atmospheric corrosion of metals which are covered with thin electrolyte layers- II. Experimental results Corros. Sci. 30 697
Stratmann M, Streckel H, Kim T and Crockett S 1990 On the atmospheric corrosion of metals which are covered with thin electrolyte layers- III. Measurements of polarization curves on metal surfaces which are covered by thin electrolyte layers Corros. Sci. 30 715
Tsuru T, Nishikata A and Wang J 1995 Electrochemical studies on corrosion under a water film Mater. Sci. Eng. A 198 161
Nishikata A, Ichihara Y and Tsuru T 1995 An application of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy to atmospheric corrosion study Corros. Sci. 37 897
Nishikata A, Ichihara Y and Tsuru T 1996 Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of metals covered with a thin electrolyte layer Electrochem. Acta 41 1057
Nishikata A, Ichihara Y, Hayashi Y and Tsuru T 1997 Influence of electrolyte layer thickness and pH on the initial stage of the atmospheric corrosion of iron J. Electrochem. Soc. 144 1244
Shi Y, Tada E and Atsushi Nishikata A 2015 A method for determining the corrosion rate of a metal under a thin electrolyte film J. Electrochem. Soc. 162 C135
Nishikata A, Yamashita Y, Katayama H, Tsuru T, Usami A, Tanabe K and Mabuchi H 1995 An electrochemical impedance study on atmospheric corrosion of steel in a cyclic wet-dry conditions Corros. Sci. 37 2059
Chung K W and Kim K B 2000 A study of the effect of concentration build-up of electrolyte on the atmospheric corrosion of carbon steel during drying Corros. Sci. 42 517
Frankel G S, Stratmann M, Rohwerder M, Michalik A, Maier B, Dora J and Wicinski M 2007 Potential control under thin aqueous layers using a Kelvin Probe 2007 Corros. Sci. 49 2021
Liu C, Srinivasan J and Kelly R G 2017 Electrolyte film thickness effects on the cathodic current availability in a galvanic couple J. Electrochem. Soc. 164 C845
Katona R M, Carpenter J C, Knight A W, Marshall R S, Nation B L, Schindelholz E J, Schaller R F and Kelly R G 2021 Natural convection boundary layer thickness at elevated chloride concentrations and temperatures and the effects on a galvanic couple J. Electrochem. Soc. 168 031512
Zhang S H and Lyon S B 1994 Anodic process on iron covered by thin dilute electrolyte layer (II) A. C. impedance measurements Corros. Sci. 36 1309
Zhang T, Chen C, Shao Y, Meng G, Wang F, Li X and Dong C 2008 Corrosion of pure magnesium under thin electrolyte layers Electrochim. Acta 53 7921
Liao X, Cao F, Zheng L, Liu W, Chen A, Zhang J and Cao C 2011 Corrosion behaviour of copper under chloride-containing thin electrolyte layer Corros. Sci. 53 3289
Liu W, Cao F, Chen A, Chang L, Zhang J and Cao C 2010 Corrosion behaviour of AM60 magnesium alloys containing Ce or La under thin electrolyte layers. Part 1: Microstructural characterization and electrochemical behaviour Corros. Sci. 52 627
Cheng Y L, Zhang Z, Cao F H, Li J F, Zhang J Q, Wang J M and Cao C N 2004 A study of the corrosion of aluminum alloy 2024-T3 under thin electrolyte layers Corros. Sci. 46 1649
Xing S, Li Y, Wu J and Yan Y 2010 Electrochemical methods study on corrosion of 5% Al-Zn alloy-coated steel under thin electrolyte layers Mater. Corros. 61 428
Xiao K, Dong C F, Luo H, Lui Q and Li X G 2012 Investigation on the electrochemical behaviour of copper under HSO\(^{-}_{3}\) containing thin electrolyte layers Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 7 7503
Huang H, Guo X, Zhang G and Dong Z 2011 Effect of direct current electric field on atmospheric corrosion behaviour of copper under thin electrolyte layer Corros. Sci. 53 3446
Ingelgem Y V, Hubin A and Vereecken J 2008 Application of multisine impedance spectroscopy, FE-AES and FE-SEM to study the early stages of copper corrosion Electrochim. Acta 53 7523
Ingelgem Y V, Tourwe E, Vereecken J and Hubin A 2008 Application of multisine impedance spectroscopy, FE-AES and FE-SEM to study the early stages of copper corrosion Electrochim. Acta 53 7523
El-Feki A A, Broadbridge P and Walter G W 1999 Exact solutions of potentiostatic current transients for a corrosion reaction under mixed charge transfer and diffusion control Math. Comput. Modell. 29 27
El-Feki A A, Broadbridge P and Walter G W 1999 Potential Transients for an electrochemical corrosion reaction under constant current conditions Math. Comput. Modell. 30 111
Cruz R P V, Nishikata A and Tsuru T 1998 Pitting corrosion mechanism of stainless steels under wet-dry exposure in chloride-containing environment Corros. Sci. 40 125
den Steen N V, Simillion H, Dolgikh O, Terryn H and Deconinck J 2016 An integrated modeling approach for atmospheric corrosion in presence of a varying electrolyte film Electrochim. Acta 187 714
Venkatraman M S, Cole I S and Emmanuel B 2011 Model for corrosion of metals covered with thin electrolyte layers: Pseudo-steady state diffusion of oxygen Electrochim. Acta 56 7171
Venkatraman M S, Cole I S and Emmanuel B 2011 Corrosion under a porous layer: A porous electrode model and its implications for self-repair Electrochim. Acta 56 8192
Gabriel I B, Venkatraman M S, Cole I S, Moorthy C G and Emmanuel B 2011 Metallic corrosion under a thin electrolyte layer controlled by oxygen diffusion: depressed nyquist arcs without the constant phase element, CSIRO e-publication, Manuscript/Document Number EP106760
Gabriel I B, Venkatraman M S, Cole I S and Emmanuel B (2011) Model for corrosion of metals covered with thin electrolyte layers: Pseudo- steady state diffusion of oxygen Electrochim. Acta 56 7171
Venkatraman M S, Bosco I G, Cole I S and Emmanuel B 2011 Models for corrosion of metals under thin electrolyte layers ECS Trans. 35 1
Dolgikh O, Bastos AC, Oliveira A, Dan C and Deconinck J 2016 Influence of the electrolyte film thickness and NaCl concentration on the oxygen reduction current on platinum Corros. Sci. 102 338
Simillion H, den Steen N V, Terryn H and Deconinck J 2016 Geometry influence on corrosion in dynamic thin film electrolytes Electrochim. Acta 209 149
Thebault F, Vuillemina B, Oltra R, Ogle K and Allely C 2008 Investigation of self-healing mechanism on galvanized steels cut edges by coupling SVET and numerical modeling Electrochim. Acta 53 5226
Thebault F, Vuillemin B, Oltra R, Allely C and Ogle K 2011 Modeling bimetallic corrosion under thin electrolyte films Corros. Sci. 53 201
Koushik B G, den Steen N V, Mamme M H, Van Ingelgem Y and Terryn H 2021 Review on modelling of corrosion under droplet electrolyte for predicting atmospheric corrosion rate J. Mater. Sci. Tech. 62 254
Saeedikhani M and Blackwood D J 2020 Finite element method for thin film corrosion modelling: Where we advanced and where we would like to advance? Corros. Mater. Degrad. 1 273
Cole I S 2017 Recent progress and required developments in atmospheric corrosion of galvanised steel and zinc Materials 10 1288
Oldham K B and Myland J C 1994 Fundamentals of Electrochemical Science (Academic Press Inc., San Diego, CA) p. 175
Smith J M, Ness H C V and Abbott M 2017 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics (McGraw-Hill Companies) p. 614
Garcia H E and Gordon L I 1992 Oxygen solubility in seawater: Better fitting equations Limnol. Oceanogr. 37 1307
Bard A J and Faulkner L R 2001 Electrochemical Methods, Fundamentals and Applications (Wiley) p. 99
Calvo E J 2014 The kinetics of oxygen electroreduction: A long way from iron rust to lithium-air batteries Mater. Corr. 65 4
Franceschetti D R, Macdonald J R and Buck R P 1991 Interpretation of Finite-Length-Warburg-Type Impedances in Supported and Unsupported Electrochemical Cells with Kinetically Reversible Electrodes J. Electrochem. Soc. 138 368
Barsoukov E and Macdonald J R 2018 Impedance Spectroscopy Theory, Experiment, and Applications (John Wiley & Sons, Inc) pp. 57–70
Lasia A Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy and its Applications (Springer) p. 88
Randles J E B 1947 Kinetics of rapid electrode reactions Disc. Faraday Soc. 1 11
Kant R and Singh M B 2015 Generalization of Randles-Ershler admittance for an arbitrary topography electrode: application to random nite fractal roughness Electrochim. Acta 163 310
Oragem M E and Tribollet B 2008 Elecrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (John Wiley and Sons, Inc.) p. 333
Warburg E 1899 Ueber das verhalten sogenannter unpolarisirbarer elektro-den gegen wechselstrom Ann. Phys. Chem. (Ser. 3) 67 493
Warburg E 1901 Uber die Polarizationscapacitat des Platins Ann. Phys. (Leipzig) 6 125
Nagy Z, Hernes P J, Minkoff M, Leaf G F and and R H 1989 Effect of Diffusion Layer Structure on the Determination of Corrosion Rates from DC Transient Measurements J. Electrochem. Soc. 136 2816
Bosco E 2008 Constant phase elements, depressed arcs and analytic continuation: A critique J. Electroanal. Chem. 624 14
Bisquert J, Belmonte G G, Santiago F F and Bueno P R 1999 Theoretical models for ac impedance of finite diffusion layers exhibiting low frequency dispersion J. Electroanal. Chem. 475 152
Singh M B and Kant R 2011 Debye-Falkenhagen dynamics of electric double layer in presence of electrode heterogeneities J. Electroanal. Chem. 704 197
Singh M B and Kant R 2014 Theory of anomalous dynamics of electric double layer at heterogeneous and rough electrodes J. Phys. Chem. C 118 5122
Stern M and Geary A L 1957 Electrochemical polarization I. A theoretical analysis of the shape of polarization curves J. Electrochem. Soc. 104 56
Toloei A, Stoilov V and Northwood D O 2015 WIT Transactions on Engineering Sciences C A Brebbia (Ed.) 90 p 355
Bassach P, Quintana G, Ferrer I and Ciurana J 2012 Studying the relation between corrosion and surface roughness AIP Conf. Proc. 1431 319
Acknowledgements
MBS acknowledges the DST, New Delhi, India for the award of DST Inspire Faculty. MBS also acknowledges CSIRO (Australia) where initial part of research was carried out as Visiting Scientist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial/commercial interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, M.B., Gabriel, B.I., Venkatraman, M.S. et al. Theory of impedance for initial corrosion of metals under a thin electrolyte layer: a coupled charge transfer-diffusion model. J Chem Sci 134, 32 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-021-02025-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-021-02025-x