Abstract
The trans-\(\hbox {Mn}^{{\mathrm{III}}}\)(Salophen)(\({\hbox {OH}_{2})_{2}}^{+}\) and bioxalate (\(\hbox {HOX}^{-})\) in aqueous medium equilibrate rapidly to trans-\(\hbox {Mn}^{{\mathrm{III}}}\)(Salophen)(\(\hbox {OH}_{2})\)(HOX) followed by the acid dissociation equilibrium to the (aqua) mono oxalato complex. The slow redox reactions of trans-\(\hbox {Mn}^{{\mathrm{III}}}\)(Salophen)(\(\hbox {OH}_{2})\)(HOX/OX)\(^{0/-}\) with \(\hbox {H}_{2}\hbox {OX}\), \(\hbox {HOX}^{-}\),\(\hbox {OX}^{2-}\) obey second order kinetics satisfying 2:1 stoichiometry \(([\hbox {Mn}^{{\mathrm{III}}}]_{\mathrm{T}}/[\hbox {OX}]_{\mathrm{T}} = 2/1)\). The products are \(\hbox {Mn}^{{\mathrm{II}}}\) and \(\hbox {CO}_{2}\). Acrylamide monomer has no effect on the rate constant and the reaction does not induce its polymerization. The rate and activation parameters for the various rate limiting paths are reported. The intramolecular reduction of \(\hbox {Mn}^{{\mathrm{III}}}\) by the coordinated \(\hbox {HOX}^{-}\) and \(\hbox {OX}^{2-}\) in trans-\(\hbox {Mn}^{{\mathrm{III}}}\)(Salophen)(\(\hbox {OH}_{2})(\hbox {HOX/OX})^{0/-}\) could not be detected. Contrary to our expectation, it is observed that \(\hbox {H}_{2}\hbox {OX}\) is a better reducing agent than \(\hbox {HOX}^{-}\) for trans-\(\hbox {Mn}^{{\mathrm{III}}}\)(Salophen)(\(\hbox {OH}_{2})(\hbox {HOX})\), the slowest being the redox reaction of \(\hbox {OX}^{2-}\) with trans-\(\hbox {Mn}^{{\mathrm{III}}}\)(Salophen)(\(\hbox {OH}_{2})(\hbox {OX})^{-}\). The molecular modelling by DFT depicts the structural trans effect in the oxalato complexes, it being maximum for trans-\(\hbox {Mn}^{{\mathrm{III}}}\)(Salophen)(\(\hbox {OH}_{2})(\hbox {OX})^{-}\). The observed sequence of the redox activity of the oxalato complexes reflects the potential role of non-covalent interaction i.e. H-bonding, governing the proton controlled electron transfer process (PCET). The \(\hbox {Mn}^{{\mathrm{III}}}\)(Salophen/Salen) complexes may turn out to be good substitute candidates for Oxalo Oxidase (OXO) enzyme in alleviating the oxalate overload in plants and animal biochemistry.
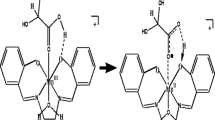
Graphical Abstract
The trans-\(\hbox {Mn}^{{\mathrm{III}}}\)(Salophen)(\(\hbox {OH}_{2})_{2}^{+}\) undergoes equilibrium pre-association in aqueous medium with bioxalate forming \(\hbox {Mn}^{{\mathrm{III}}}\)(Salophen)(HOX)\((\hbox {OH}_{2})\) and \(\hbox {Mn}^{{\mathrm{III}}}\)(Salophen)(OX)\((\hbox {OH}_{2})^{-}\) which are inert to intramolecular reduction but undergo reduction via second-order paths by \(\hbox {H}_{2}\hbox {OX}\), \(\hbox {HOX}^{-}\) and \(\hbox {OX}^{2-}\) with decreasing reactivity sequence implying proton controlled process.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kar A K, Acharya A N, Pradhan G C and Dash A C 2014 Glyoxylate as a reducing agent for manganese(III) in salen scaffold: A Kinetics and Mechanistic study J. Chem. Sci. 126 547
Kar A K, Acharya A N, Mundlapati V R, Pradhan G C, Biswal H S and Dash A C 2014 Ligand substitution and electron transfer reactions of trans-(diaqua)(salen)manganese(III) with oxalate: an experimental and computational study RSC Adv. 4 58867
Huynh M H V and Meyer T J 2007 Proton-coupled electron transfer Chem. Rev. 107 5004
Lane B G 1994 Oxalate, germin and the extracellular matrix of higher plants FASEB J. 8 294
(a) Sugiura M, Yamamura H, Hirano K, Sasaki M, Morikawa M and Tsuboi M 1979 Purification and properties of Oxalate Oxidase from Barley Seedlings Chem. Pharm. Bull. 27 2003; (b) Aguilar C, Urzua U, Koenig C and Vicuna R 1999 Oxalate Oxidase from Ceriporiopsis subvermispora: biochemical and cytochemical studies Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 366 275
Koyama H 1988 Purification and characterization of Oxalate Oxidase from pseudomonas Sp. Ox-53 Agri. Biol. Chem. 52 743
Yuan M, Zhao F, Zhang W, Wang Z-Ming and Gao S 2007 Azide–bridged one-dimensional \(\text{ Mn }^{III }\) polymers: effects of side group of schiff base ligands on structure and magnetism Inorg. Chem. 46 11235
Ciringh Y, Gordon-Wylie Scott W, Norman R E, Clark G R, Weintraub S T and Horwitz C P 1997 Multinuclear paramagnetic NMR spectra and solid state X-ray crystallographic characterization of manganese(III) Schiff-base complexes Inorg. Chem. 36 4968
Bonadies J A, Maroney M J and Pecoraro V L 1989 Structurally diverse manganese(III) Schiff base complexes: solution speciation via paramagnetic proton NMR spectroscopy and electrochemistry Inorg. Chem. 28 2044
Sawyer D T and Roberts Jr. J L 1974 Experimental Electrochemistry for Chemists (New York: Wiley-Intersc.) p. 42
Perrin D D and Dempsey B 1974 Buffers for pH and Metal Ion control (London: Chapman and Hall) p. 120
Irving H M, Miles M G and Pettit L D 1967 A study of some problems in determining the stoichiometric proton dissociation constants of complexes by potentiometric titrations using a glass electrode Anal. Chim. Acta 38 475
Mcgravey B R 1966 In Transition Metal Chemistry, R L Carlin (Ed.) (New York: Marcel Dekker Inc.) Vol. 3 p. 89
Jones T J and Noyes R M 1983 Mechanistic details of the oxidation of oxalate by Manganese(III) J. Phys. Chem. 87 4686
Kovács B, Vizvári B, Riedel M and Tóth J 2004 Decomposition of the permanganate/oxalic acid overall reaction to elementary steps on integer programming theory Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 6 1236
Alrichs R, Bär M, Häser M, Horn H and Kölmel C 1989 Electronic Structure Calculations on Workstation computers: The program system turbomole Chem. Phys. Lett. 162 165
Treutlor O and Ahlrichs R 1995 Efficient molecular numerical integration schemes J. Chem. Phys. 102 346
Vahtras O, Almlöf J and Feyereisen M W 1993 Integral approximation for LCAO-SCF Calculations Chem. Phys. Lett. 213 514
Eichkorn K, Treutlor O, Öhm H, Häser M and Alrichs R 1995 Auxiliary basis sets to approximate coulomb potentials Chem. Phys. Lett. 240 283
Eichkorn K, Treutlor O, Öhm H, Häser M and Alrichs R 1995 Auxiliary basis sets to approximate coulomb potential Chem. Phys. Lett. 242 652
Fukuda T, Sakamoto F, Sato M, Nakano Y, Tan X Shi and Fujii Y 1998 Photopromoted oxidative cyclization of an o-phenylene-bridged Schiff base via manganese(III) complex, leading to fluorescent compound, 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)benzimidazole Chem. Commun. 1391
McAuliffe C A, Nabhan A, Pritchard R G, Watkinson M, Bermejo M and Sousa A 1994 [Mn(Salphen)(EtOH)\(_{2}\)](\(\text{ BH }_{4}\)) [\(\text{ SalphenH }_{2}=N\), \(N^{\prime \prime }\)-bis(salicylidene)-1,2-diaminobenzene], a further example of photosyntheic model compound forming dimers linked by hydrogen and \(\pi \) bonds Acta Cryst. C 50 1676
Requena L and Bornemann S 1999 Barley (Horeum vulgare) oxalate oxidase is a manganese-containing enzyme Biochem. J. 343 185
Opaleye O, Rose R-Sarah, Whittaker M M, Woo E J, Whittaker J W and Pickersgill R W 2006 Structural and spectroscopic studies shed light on the mechanism of oxalate oxidase J. Biol. Chem. 281 6428
Noritke Y, Umezawa N, Kato N and Higuchi T 2013 Manganese Salen complexes with acid-base catalytic auxiliary: Functional mimetics of catalase Inorg. Chem. 52 3653
Lanza V and Vechhio G 2009 New Conjugates of Superoxide dismutases/Catalases mimetics with cyclodextrins J. Inorg. Biochem. 102 381
Olivera V and Vecchio G 2011 A novel artificial superoxide dismutase: Non covalent conjugation of albumin with a \(\text{ Mn }^{{\text{ III }}}\)-Salophen type complex Eur. J. Med. Chem. 46 961
Liu Shih-Yuan, Soper J D, Yang J Y, Rybak-Akimova E V and Nocera D G 2006 Mechanistic Studies of Hangman Salophen-mediated activation of O–O bonds Inorg. Chem. 45 7572
Riley D P 1999 Functional mimics of Superoxide Dismutase Enzymes as Therapeutic Agents Chem. Rev. 99 2573
(a) Dahiya T and Pundir C S 2013 In vivo oxalate degradation by liposome encapsulated oxalate oxidase in rat model of hyperoxaluria Indian J. Med. Res. 137 136; (b) Gibson M I, Chen P Yang-Ting, Johnson A C, Piera E, Can M, Ragsdale S W and Drennan C L 2016 One Carbon Chemistry of Oxalate Oxidoreductase Captured by X-ray Crystallography PNAS 113 320, and references cited therein
Signorella S, Palopoli C and Ledesma G 2018 Rationally designed mimics for antioxidant manganoenzymes: Role of structural features in the quest for catalysts with catalase and superoxide dismutase activity Coord. Chem. Rev. 365 75
Acknowledgements
P J is thankful to MHRD, Govt. of India for a fellowship under Technical Education Quality Improvement Program (TEQIP-II). Financial support to H S B and V R M from the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), Govt. of India is gratefully acknowledged. The authors are thankful to Dr. R. K. Behera of National Institute of Technology (NIT), Rourkela for NMR measurements and to Prof. Gautam K. Lahiri, Indian Institute of Technology, Mumbai for ESR measurement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This work is dedicated to Late Professor Rabindra Kumar Nanda (ex-Professor & Head of the Department of Chemistry, Utkal University, Bhubaneswar).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jena, P., Acharya, A.N., Mundlapati, V.R. et al. Kinetics and mechanistic study of the reduction of \(\hbox {Mn}^{\mathrm{III}}\) by oxalate in Salophen scaffold: relevance to oxalate oxidase. J Chem Sci 130, 123 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-018-1514-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-018-1514-4