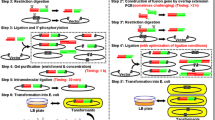
Abstract
The Klenow fragment (KF) has been used to make the blunt end as a tool enzyme. Its 5′-3′ polymerase activity can extend the 5′ overhanging sticky end to the blunt end, and 3′-5′ exonuclease activity can cleave the 3′ overhanging sticky end to the blunt end. The blunt end is useful for cloning. Here, we for the first time determined that a sticky end can be made by using the 3′-5′ exonuclease activity of KF. We found that KF can cleave the blunt end into certain sticky ends under controlled conditions. We optimized enzyme cleavage conditions, and characterized the cleaved sticky ends to be mainly 2 nt 5′ overhang. By using these sticky ends, we realized ligation reaction in vitro, and accomplished cloning short oligonucleotides directionally with high cloning efficiency. In some cases, this method can provide sticky end fragments in large scale for subsequent convenient cloning at low cost.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DTT:
-
dithiothreitol
- IPTG:
-
Isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside
- KF:
-
Klenow fragment
- KPB:
-
potassium phosphate buffer
- ODN:
-
oligodeoxyribonucleotide
- PAGE:
-
polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- TdT:
-
terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
References
An Y, Wu W and Lv A 2010 A PCR-after-ligation method for cloning of multiple DNA inserts. Anal. Biochem. 402 203–205
Beese LS and Steitz TA 1991 Structural basis for the 3'-5' exonuclease activity of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I: a two metal ion mechanism. EMBO J 10 25–33
Berrow NS, Alderton D and Owens RJ 2009 The precise engineering of expression vectors using high-throughput In-Fusion PCR cloning. Methods Mol. Biol. 498 75–90
Brutlag D and Kornberg A 1972 Enzymatic synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid. 36. A proofreading function for the 3' leads to 5' exonuclease activity in deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases. J. Biol. Chem. 247 241–248
Carver TE Jr, Hochstrasser RA and Millar DP 1994 Proofreading DNA: recognition of aberrant DNA termini by the Klenow fragment of DNA polymerase I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91 10670–10674
Clark JM 1988 Novel non-templated nucleotide addition reactions catalyzed by procaryotic and eucaryotic DNA polymerases. Nucleic Acids Res. 16 9677–9686
Clark JM, Joyce CM and Beardsley GP 1987 Novel blunt-end addition reactions catalyzed by DNA polymerase I of Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 198 123–127
Eger BT, Kuchta RD, Carroll SS, Benkovic PA, Dahlberg ME, Joyce CM and Benkovic SJ 1991 Mechanism of DNA replication fidelity for three mutants of DNA polymerase I: Klenow fragment KF(exo+), KF(polA5), and KF(exo-). Biochemistry 30 1441–1448
Freemont PS, Friedman JM, Beese LS, Sanderson MR and Steitz TA 1988 Cocrystal structure of an editing complex of Klenow fragment with DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85 8924–8928
Howland SW, Poh C-M and Renia L 2011 Directional, seamless, and restriction enzyme-free construction of random-primed complementary DNA libraries using phosphorothioate-modified primers. Anal. Biochem. 416 141–143
Hu G 1993 DNA polymerase-catalyzed addition of nontemplated extra nucleotides to the 3' end of a DNA fragment. DNA Cell Biol. 12 763–770
Kaluz S, Kolble K and Reid KB 1992 Directional cloning of PCR products using exonuclease III. Nucleic Acids Res. 20 4369–4370
Liu X-P and Liu J-H 2010 The terminal 5 ' phosphate and proximate phosphorothioate promote ligation-independent cloning. Protein Sci. 19 967–973
Motea EA and Berdis AJ 2010 Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase: The story of a misguided DNA polymerase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteomics 1804 1151–1166
Ranjan RK and Rajagopal K 2010 Efficient ligation and cloning of DNA fragments with 2-bp overhangs. Anal. Biochem. 402 91–92
Stoker AW 1990 Cloning of PCR products after defined cohesive termini are created with T4 DNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 18 4290
Yang S, Li X, Ding D, Hou J, Jin Z, Yu X, Bo T, Li W and Li M 2005 A method for filling in the cohesive ends of double-stranded DNA using Pfu DNA polymerase. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 42 223–226
Yang YS, Watson WJ, Tucker PW and Capra JD 1993 Construction of recombinant DNA by exonuclease recession. Nucleic Acids Res. 21 1889–1893
YunHua LU, LiXin MA and SiJing J 2006 A Universal high-throughput novel method of constructing the vectors. Hereditas (Beijing) 28 212–218
Zhang J, Li K, Pardinas JR, Sommer SS and Yao KT 2005 Proofreading genotyping assays mediated by high fidelity exo+ DNA polymerases. Trends Biotechnol. 23 92–96
Zhao G and Guan Y 2010 Polymerization behavior of Klenow fragment and Taq DNA polymerase in short primer extension reactions. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai) 42 722–728
Zhao Y 2009 Construction of a high efficiency PCR Products cloning T vector using Avicenna. J. Med. Biotechnol. 1 37–39
Zhou MY and Gomez-Sanchez CE 2000 Universal TA cloning. Curr. Iss. Mol. Biol. 2 1–7
Zhao G, Wei H and Guan Y 2013 Identification of a premature termination of DNA polymerization in vitro by Klenow fragment mutants. J. Biosci. 38 1–11
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31070705).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: B Jagadeeshwar Rao
[Zhao G, Li J, Hu T, Wei H and Guan Y 2013 Realizing directional cloning using sticky ends produced by 3′-5′ exonuclease of Klenow fragment. J. Biosci. 38 1-10] DOI 10.1007/s12038-013-9389-5
Supplementary materials pertaining to this article are available on the Journal of Biosciences Website at http://www.ias.ac.in/jbiosci/dec2013/supp/Zhao.pdf
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, G., Li, J., Hu, T. et al. Realizing directional cloning using sticky ends produced by 3′-5′ exonuclease of Klenow fragment. J Biosci 38, 857–866 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-013-9389-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-013-9389-5