Abstract
In response to hypoxia, tissues have to implement numerous mechanisms to enhance oxygen delivery, including the activation of angiogenesis. This work investigates the angiogenic response of the hypoxic caudate putamen after several recovery times.
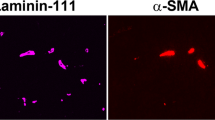
Adult Wistar rats were submitted to acute hypoxia and analysed after 0 h, 24 h and 5 days of reoxygenation. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alfa (HIF-1α) and angiogenesis-related genes including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), adrenomedullin (ADM) and transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1) was determined by both RT-PCR and ELISA. For vessel labelling, lectin location and expression were analysed using histochemical and image processing techniques (fractal dimension).
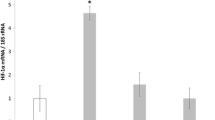
Expression of Hif-1α, Vegf, Adm and Tgf-β1 mRNA rose immediately after hypoxia and this increase persisted in some cases after 5 days post-hypoxia. While VEGF and TGF-β1 protein levels increased parallel to mRNA expression, ADM remained unaltered. The quantification of the striatal vessel network showed a significant augmentation at 24 h of reoxygenation.
These results reveal that not only short-term hypoxia, but also the subsequent reoxygenation period, up-regulate the angiogenic pathway in the rat caudate putamen as a neuroprotective mechanism to hypoxia that seeks to maintain a proper blood supply to the hypoxic tissue, thereby minimizing the adverse effects of oxygen deprivation.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Eid E and Landini G 2003 Quantification of the global and local complexity of the epithelial-connective ti ssue interface of normal, dysplastic, and neoplastic oral mucosae using digital imaging. Pathol. Res. Pract. 199 475–482
Autelitano DJ, Tang F and Little PJ 1999 Rapid regulation of adrenomedullin in metabolically compromised vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Hypertens. 17 373–379
Bani Hashemi S, Braun J, Bernhardt WM, Rascher W, Dötsch J and Trollmann R 2008 HIF-1alpha subunit and vasoactive HIF-1-dependent genes are involved in carbon monoxide-induced cerebral hypoxic stress response. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 104 95–102
Berse B, Hunt JA, Diegel RJ, Morganelli P, Yeo K, Brown F and Fava RA 1999 Hypoxia augments cytokine (transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) and IL-1)-induced vascular endothelial growth factor secretion by human synovial fibroblasts. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 115 176–182
Bradford MM 1976 A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72 248–254
Bright RT, Salvaterra CG, Rubin LJ and Yuan X-J 1995 Inhibition of glycolysis by 2- DG increases [Ca2+]i in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. 269 L203–L208
Cañuelo A, Siles E, Martínez-Romero R, Peinado MA and Martínez-Lara E 2007 The nitric oxide system response to hypoxia/reoxygenation in the aged cerebral cortex. Exp. Gerontol. 42 1137–1145
Cassavaugh J and Lounsbury KM 2011Hypoxia-mediated biological control. J. Cell Biochem. 112 735–744
Chávez JC, Agani F, Pichiule P and LaManna JC 2000 Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in the brain of rats during chronic hypoxia. J. Appl. Physiol. 89 1937–1942
Di Ieva A, Grizzi F, Ceva-Grimaldi G, Russo C, Gaetani P, Aimar E, Levi D, Pisano P, et al. 2007 Fractal dimension as a quantitator of the microvasculature of normal and adenomatous pituitary tissue. J. Anat. 211 673–680
Dickson MC, Martin JS, Cousins FM, Kulkarni AB, Karlsson S and Akhurst RJ 1995 Defective haematopoiesis and vasculogenesis in transforming growth factor- β 1 knock out mice. Development 121 1845–1854
Erecinska M and Silver IA 1996 Calcium handling by hippocampal neurons under physiologic and pathologic conditions. Adv. Neurol. 71 119–136
Ferrara N and Davis-Srnyth T 1997 The biology of vascular endothelial growth factor. Endocr. Rev. 18 4–25
Huang RQ, Cheng HL, Zhao XD, Dai W, Zhuang Z, Wu Y, Liu Y and Shi JX 2010 Preliminary study on the effect of trauma-induced secondary cellular hypoxia in brain injury. Neurosci. Lett. 473 22–27
Hwang IS, Fung ML, Liong EC, Tipoe GL and Tang F 2007 Age-related changes in adrenomedullin expression and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 activity in the rat lung and their responses to hypoxia. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 62 41–49
Iimuro S, Shindo T, Moriyama N, Amaki T, Niu P, Takeda N, Iwata H, Zhang Y, et al. 2004 Angiogenic effects of adrenomedullin in ischemia and tumor growth. Circ. Res. 95 415–423
Janssens, J P, Pautex, S, Hilleret, H and Michel, J P 2000 Sleep disordered breathing in the elderly. Aging (Milano) 12 417–429
Jussila L and Alitalo K 2002 Vascular growth factors and lymphangiogenesis. Physiol. Rev. 82 673–700
Kaur C, Sivakumar V, Zhang Y and Ling EA 2006 Hypoxia-Induced Astrocytic Reaction and Increased Vascular Permeability in the Rat Cerebellum. Glia 54 826–839
Kitamuro T, Takahashi K, Nakayama M, Murakami O, Hida W, Shirato K and Shibahara S 2000 Induction of adrenomedullin during hypoxia in cultured human glioblastoma cells. J. Neurochem. 75 1826–1833
Klempt ND, Sirimanne E, Gunn AJ, Klempt M, Singh K, Williams C and Gluckman PD 1992 Hypoxia-ischemia induces transforming growth factor beta 1 mRNA in the infant rat brain. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 13 93–101
Knowles HJ, Tian YM, Mole DR and Harris AL 2004 Novel mechanism of action for hydralazine: induction of hypoxia-inducible factor-1a, vascular endothelial growth factor, and angiogenesis by inhibition of prolyl hydroxylases. Circ. Res. 95 162–169
Krock B, Skuli N and Simon MC 2011 Hypoxia-induced angiogenesis: good and evil. Genes Cancer 2 1117–1133
Krupinski J, Kaluza J, Kumar P, Kumar S and Wang JM 1994 Role of angiogenesis in patients with cerebral ischemic stroke. Stroke 25 1794–1798
Kuo NT, Benhayon D, Przybylski RJ, Martin RJ and LaManna JC 1999 Prolonged hypoxia increases vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA and protein in adult mouse brain J. Appl. Physiol. 86 260–264
LaManna JC, Vendel LM and Farrell RM 1992 Brain adaptation to chronic hypobaric hypoxia in rats. J. Appl. Physiol. 72 2238–2243
Li H, Witte K, August M, Brausch I, Godtel-Armbrust U, Habermeier A, Closs EI, et al. 2006 Reversal of endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling and up-regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression lowers blood pressure in hypertensive rats. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 47 2536–2544
Lopez-Ramos JC, Martinez-Romero R, Molina F, Cañuelo A, Martinez-Lara E, Siles E and Peinado MA 2005 Evidence of a decrease in nitric oxide-storage molecules following acute hypoxia and/or hypobaria, by means of chemiluminescence analysis. Nitric Oxide 13 62–67
Mammen A, Kubin J, Greeley WJ, Schears GJ, Pastuszko P, F Wilson D and Pastuszko A 2011 Effect of hypoxia on expression of selected proteins involved in regulation of apoptotic activity in striatum of newborn piglets. Neurochem. Res. 36 746–753
Martínez-Romero R, Cañuelo A, Martínez- Lara E, Hernández R, Del Moral ML, Pedrosa JA, Peinado MA and Siles E 2006 Aging affects but does not eliminate the enzymatic antioxidative response to hypoxia/reoxygenation in cerebral cortex. Exp. Gerontol. 41 25–31
Mathur R, Cox IJ, Oatridge A, Shephard DT, Shaw RJ and Taylor-Robinson SD 1999 Cerebral bioenergetics in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 160 1994–1999
Mazzetti S, Frigerio S, Gelati M, Salmaggi A, Vitellaro-Zuccarello L 2004 Lycopersicon esculentum lectin: an effective and versatile endothelial marker of normal and tumoral blood vessels in the central nervous system. Eur. J. Histochem. 48 423–428
McMahon S, Charbonneau M, Grandmont S, Richard DE and Dubois CM 2006 Transforming growth factor beta1 induces hypoxia-inducible factor-1 stabilization through selective inhibition of PHD2 expression. J. Biol. Chem. 281 24171–24181
Nagelkerke A, Mujcic H, Wouters B and Span PN 2010 18S is an appropriate housekeeping gene for in vitro hypoxia experiments. Br. J. Cancer 103 590
Nakanishi K, Osada H, Uenoyama M, Kanazawa F, Ohrui N, Masaki Y, Hayashi T, Kanatani Y, et al. 2004 Expressions of adrenomedullin mRNA and protein in rats with hypobaric hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Physiol Heart Circ. Physiol. 286 H2159– H2168
Patt S, Sampaolo S, Théallier-Jankó A, Tschairkin I and Cervós-Navarro J 1997 Cerebral angiogenesis triggered by severe chronic hypoxia displays regional differences. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 17 801–806
Peebles KC, Richards AM, Celi L, McGrattan K, Murrell CJ and Ainslie PN 2008 Human cerebral arteriovenous vasoactive exchange during alterations in arterial blood gases. J. Appl. Physiol. 105 1060–1068
Pettersson A, Nagy JA, Brown LF, Sundberg C, Morgan E, Jungles S, Carter R, Krieger JE, et al. 2000 Heterogeneity of the angiogenic response induced in different normal adult tissues by vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor. Lab. Invest. 80 99–115
Pichiule P and LaManna JC 2002 Angiopoietin-2 and rat brain capillary remodeling during adaptation and deadaptation to prolonged mild hypoxia. J. Appl. Physiol. 93 1131–1139
Renner U, Lohrer P, Schaaf L, Feirer M, Schmitt K, Onofri C, Arzt E and Stalla GK 2002 Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates vascular endothelial growth factor production by folliculostellate pituitary cells. Endocrinology 143 3759–3765
Rus A, Del Moral ML, Molina F and Peinado MA 2011 Upregulation of cardiac NO/NOS system during short-term hypoxia and the subsequent reoxygenation period. Eur. J. Histochem. 55 e17
Rus A, Peinado MA, Castro L and Del Moral ML 2010a Lung eNOS and iNOS are reoxygenation time-dependent upregulated after acute hypoxia. Anat. Rec. (Hoboken) 293 1089–1098
Rus A, Molina F, Peinado MA, del Moral ML 2010b Endothelial NOS-derived nitric oxide prevents injury resulting from reoxygenation in the hypoxic lung. Free Radic. Res. 44 1027–1035
Sanford LP, Ormsby I, Gittenberger-de Groot AC, Sariola H, Friedman R, Boivin GP, Cardell EL and Doetschman T 1997 TGF β2 knockout mice have multiple developmental defects that are non-overlapping with other TGF β knockout phenotypes. Development 124 2659–2670
Serrano J, Fernández AP, Sánchez J, Rodrigo J and Martínez A 2008 Adrenomedullin expression is up-regulated by acute hypobaric hypoxia in the cerebral cortex of the adult rat. Brain Pathol. 18 434–442
Singh N, Sharma G, Mishra V and Raghubir R 2012 Hypoxia inducible factor-1: Its potential role in cerebral ischemia. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 32 491–507
Wang Y, Kilic E, Kilic U, Weber B, Bassetti CL, Marti HH and Hermann DM 2005 VEGF overexpression induces post-ischaemic neuroprotection, but facilitates haemodynamic steal phenomena. Brain 128 52–63
Wenger RH 2002 Cellular adaptation to hypoxia: O2-sensing protein hydroxylases, hypoxia-inducible transcription factors, and O2-regulated gene expression. FASEB J. 16 1151–1162
Wiener CM, Booth G and Semenza GL 1996 In vivo expression of mRNAs encoding hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 225 485–488
Withers DJ, Coppock HA, Seufferlein T, Smith DM, Bloom SR and Rozengurt E 1996 Adrenomedullin stimulates DNA synthesis and cell proliferation via elevation of cAMP in Swiss 3T3 cells. FEBS Lett. 378 83–87
Yuan X-J, Tod ML, Rubin LJ and Blaustein MP 1994 Deoxyglucose and reduced glutathione mimic effects of hypoxia on K+ and Ca2+ conductances in pulmonary arterial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 267 L52–L63
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank to Dr Rafael Lomas for his statistic assistance. This work was supported by Instituto de Salud Carlos III (PI081222), University of Jaén (RFC/PP2008/UJA_08_16_20), Junta de Andalucía (BIO-0184), and Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: NEERAJ JAIN
MS received 26 June 2012; accepted 02 April 2013
Corresponding editor: Neeraj Jain
[Molina F, Rus A, Peinado MA and del Moral ML 2013 Short-term hypoxia/reoxygenation activates the angiogenic pathway in rat caudate putamen. J. Biosci. 38 1–9] DOI 10.1007/s12038-013-9327-6
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molina, F., Rus, A., Peinado, M. et al. Short-term hypoxia/reoxygenation activates the angiogenic pathway in rat caudate putamen. J Biosci 38, 363–371 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-013-9327-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-013-9327-6