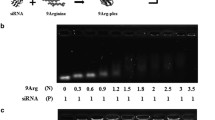
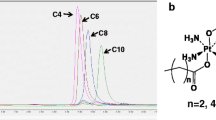
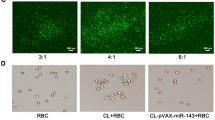
Abstract
Anti-apoptosis plays an important role in tumour formation and development. Survivin is a member of the inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) family, which is a target for anti-cancer drug exploitation was replaced as development. We investigated the role of the homo dominant-negative mutant Survivin-T34A in suppressing human lung adenocarcinomas (A549). The anti-tumour activity of HSurvivinT34A plasmid was evaluated in the A549 cell line and nude mice bearing A549 subcutaneous tumours. Low-dose systemic administration was continuously used. The HSurvivinT34A plasmid (5 µg/one) complexed with a cationic liposome (DOTAP/Chol) significantly inhibited tumour growth in our model. We observed microvessel density degradation by CD31 immunohistochemistry and apoptotic cell increase by TUNEL assay, PI staining and flow cytometric analysis in the treated group. The present findings suggest that the HSurvivinT34A plasmid complexed with a cationic liposome may provide an effective approach to inhibit the growth of human lung adenocarcinomas in vitro and in vivo.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
analysis of variance
- FBS:
-
foetal bovine serum
- H&E:
-
haematoxylin and eosin
- IAP:
-
inhibitor of apoptosis
- MVD:
-
microvessel density
- NSCLC:
-
non-small cell lung cancer
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- PI:
-
propidium iodine
- P-S:
-
penicillin/streptomycin
- TAL:
-
Tachypleus amebocyte lysate
- TUNEL:
-
terminal eoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labelling
- VEGF:
-
vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Altieri D C 2001 The molecular basis and potential role of survivin in cancer diagnosis and therapy; Trends. Mol. Med. 7 542–547
Altieri D C and Marchisio C 1999 Survivin apoptosis: an interloper between cell death and cell proliferation in cancer; Lab. Invest. 79 1327–1333
Blanc-Brude O P, Mesri M, Wall N R, Plescia J, Dohi T and Altieri D C 2003 Therapeutic targeting of the survivin pathway in cancer: initiation of mitochondrial apoptosis and suppression of tumor-associated angiogenesis; Clin. Cancer Res. 9 2683–2692
Bo L, Yi M, Carolyn C, Fenghua Z, Sylke S, Jiahui T, Jim P, Jun C et al. 2004 Survivin as a therapeutic target for radiation sensitization in lung cancer; Cancer Res. 64 2840–2845
Branko Z 2007 Report 2007 12th World Conference on Lung Cancer. Seoul, Korea.
Chakravarti A, Noll E, Black P M, Finkelstein D F, Finkelstein D M, Dyson N J and Loeffler J S 2002 Quantitatively determined survivin expression levels are of prognostic value in human gliomas; J. Clin. Oncol. 20 1063–1068
Connor D S, Grossman G, Plescia J, Li F, Zhang H, Villa A, Tognin S, Marchisio P C et al. 2000 Regulation of apoptosis at cell division by p34cdc2 phosphorylation of survivin; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97 13103–13107
Connor D S, Schechner J S, Adida C, Mesri M, Rothermel A L, Li F, Nath A K, Pober J S et al. 2000 Control of apoptosis during angiogenesis by survivin expression in endothelial cells; Am. J. Pathol. 156 393–398
Connor D S, Wall N R, Porter A C G and Altieri D C 2002 A p34cdc2 survival checkpoint in cancer; Cancer Cell 2 43–54
Deveraux Q L and Reed J C 1999 IAP family proteins: suppressors of apoptosis; Genes. Dev. 13 239–252
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L and Wang X 2000 Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition; Cell 102 33–42
Grossman D, Kim P J, Schechner J S and Altieri D C 2001 Inhibition of melanoma tumor growth in vivo by survivin targeting; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98 635–640
Grossman D, McNiff J M, Li F and Altieri D C 1999 Expression and targeting of the apoptosis inhibitor, survivin, in human melanoma; J. Invest. Dermatol. 113 1076–1081
Harfouche R, Hassessian H M, Guo Y, Faivre V, Srikant C B, Yancopoulos G D and Hussain S N 2002 Mechanisms which mediate the antiapoptotic effects of angiopoietin-1 on endothelial cells; Microvasc. Res. 64 135–147
Ito I, Began G, Mohiuddin I, Saeki T, Saito Y, Branch C D, Vaporciyan A, Stephens L C et al. 2003 Increased uptake of liposome-DNA complexes by lung metastases following intravenous administration; Mol. Ther. 7 409–418
Jiang G, Li J, Zeng Z and Xian L 2006 Lentivirus-mediated gene therapy by suppressing survivin in BALB/c nude mice bearing oral squamous cell carcinoma; Cancer Biol. Ther. 5 435–440
Kanwar J R, Shen W P, Kanwar R K, Berg R W and Krissansen G W 2001 Effects of survivin antagonists on growth of established tumors and B7-1 immunogene therapy; J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 93 1541–1552
Kennedy S M, Driscoll L, Purcell R, Fitz-Simons N, McDermott E W, Hill A D, Higgins N J, Parkinson M et al. 2003 Prognostic importance of survivin in breast cancer; Br. J. Cancer 88 1077–1083
Lu B, Gonzalez A, Massion P P, Shyr Y, Shaktour B, Carbone D P and Hallahan D E 2004 Nuclear survivin as a biomarker for nonsmall-cell lung cancer; Br. J. Cancer 91 537–540
Mehdi M, Nathan R, Jia L, Richard W. Kim and Dario C 2001 Cancer gene therapy using a survivin mutant adenovirus; J. Clin. Invest. 108 981–990
Mesri M, Morales-Ruiz M, Ackermann E J, Bennett C F, Pober J S, Sessa W C and Altieri D C 2001 Suppression of vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated endothelial cell protection by survivin targeting; Am. J. Pathol. 158 1757–1765
Mohamed S, Yasufuku K, Nakajima T, Hiroshima K, Chiyo M, Sekine Y, Shibuya K, Agamy G et al. 2009 Nuclear survivin in pN2 nonsmall cell lung cancer: prognostic and clinical implications; Eur. Respir. 33 127–133
Muzio L, Staibano S, Pannone G, Mignogna M D, Mariggio A, Salvatore G, Chieffi P, Tramontano D et al. 2001 Expression of the apoptosis inhibitor survivin in aggressive squamous cell carcinoma; Exp. Mol. Pathol. 70 249–254
Papapetropoulos A, Fulton D, Mahboubi K, Kalb R G, Connor D S, Li F, Altieri D C and Sessa W C 2000 Angiopoietin-1 inhibits endothelial cell apoptosis via the Akt/survivin pathway; J. Biol. Chem. 275 9102–9105
Peng X C, Yang L, Yang L P, Mao Y Q, Yang H S, Liu J Y, Zhang D M, Chen L J et al. 2008 Efficient inhibition of murine breast cancer growth and metastasis by gene transferred mouse survivin Thr34→Ala mutant; J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 27 46–59
Pennati M, Colella G, Folini M, Citti L, Daidone M G and Zaffaroni N 2002 Ribozyme-mediated attenuation of survivin expression sensitizes human melanoma cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis; J. Clin. Invest. 109 285–286
Pisarev V, Yu B, Salup R, Sherman S and Gabrilovich D I 2003 Fulllength dominant-negative survivin for cancer immunotherapy; Clin. Cancer Res. 9 6523–6533
Ramesh R, Saeki T, Templeton N S, Ji L, Stephens L C, Ito I, Wilson D R, Wu Z et al. 2001 Successful treatment of primary and disseminated human lung cancers by systemic delivery of tumor suppressor genes using an improved liposome vector; Mol. Ther. 22 11–16
Reed J C 1999 Dysregulation of apoptosis in cancer; J. Clin. Oncol. 17 2941–2953
Robert A, Olie A, Paula S, Bettina B, Sian H L, Doriano F, Rolf A and Stahel U 2000 A Novel antisense oligonucleotide targeting survivin expression induces apoptosis and sensitizes lung cancer cells to chemotherapy; Cancer Res. 60 2805–2809
Rudin C M and Thompson C B 1997 Apoptosis and disease: regulation and clinical relevance of programmed cell death; Annu. Rev. Med. 48 267–281
Shen C X, Liu W J, Andreas K B and Sven N R 2009 Pro-apoptosis and anti-proliferation effects of a recombinant dominantnegative survivin-t34a in human cancer cells; Anticancer Res. 29 1423–1428
Shi Y 2002 Mechanisms of caspase activation and inhibition during apoptosis; Mol. Cell. 9 459–470
Thurston G, Mclean J W, Rizen M, Baluk P, Haskell A, Murphy T J, Hanahan D and McDonald D M 1998 Cationic liposome target angiogenic endothelial cells in tumors and chronic inflammation in mice; J. Clin. Invest. 101 1401–1413
Tsuruma T, Hata F, Torigoe T, Furuhata T, Idenoue S, Kurotaki T, Yamamoto M, Yagihashi A et al. 2004 Phase I clinical study of antiapoptosis protein, surviving derived peptide vaccine therapy for patients with advanced or recurrent colorectal cancer; J. Transl. Med. 2 19–30
Verdecia M A, Huang H, Dutil E, Kaiser D A, Hunter T and Noel J P 2000 Structure of the human anti-apoptotic protein survivin reveals a dimeric arrangement; Nat. Struct. Biol. 7 602–608
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this research.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shan, Y., Wang, C., Yang, L. et al. Inhibition of human lung adenocarcinoma growth using survivint34a by low-dose systematic administration. J Biosci 35, 209–216 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-010-0025-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-010-0025-3