Abstract
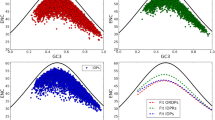
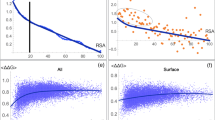
The relationship between the synonymous codon usage and different protein secondary structural classes were investigated using 401 Homo sapiens proteins extracted from Protein Data Bank (PDB). A simple Chi-square test was used to assess the significance of deviation of the observed and expected frequencies of 59 codons at the level of individual synonymous families in the four different protein secondary structural classes. It was observed that synonymous codon families show non-randomness in codon usage in four different secondary structural classes. However, when the genes were classified according to their GC3 levels there was an increase in non-randomness in high GC3 group of genes. The non-randomness in codon usage was further tested among the same protein secondary structures belonging to four different protein folding classes of high GC3 group of genes. The results show that in each of the protein secondary structural unit there exist some synonymous family that shows class specific codon-usage pattern. Moreover, there is an increased non-random behaviour of synonymous codons in sheet structure of all secondary structural classes in high GC3 group of genes. Biological implications of these results have been discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adzhubei A A, Adzhubei I A, Krasheninnikov I A and Neidle S 1996 Non-random usage of ‘degenerate’ codons is related to protein three-dimensional structure; FEBS Lett. 399 78–82
Alvarez F, Robello C and Vignali M 1994 Evolution of codon usage and base contents in kinetoplastid protozoans; Mol. Biol. Evol. 11 790–802
Arhondakis S, Anletta F, Torelli G and D’Onofrio G 2004 Base composition and expression level of human genes; Gene 325 165–169
Basak S, Banerjee T, Gupta S K and Ghosh T C 2004 Investigation on the causes of codon and amino acid usages variation between thermophilic Aquifex aeolicus and mesophilic Bacillus subtilis; J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 22 205–214
Basak S and Ghosh T C 2006 Temperature adaptation of synonymous codon usage in different functional categories of genes: a comparative study between homologous genes of Methanococcus jannaschii and Methanococcus maripaludis; FEBS Lett. 580 3895–3899
Berman H M, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat T N, Weissig H, Shindyalov I N and Bourne P E 2000 The Protein Data Bank; Nucleic Acids Res. 28 235–242
Bernardi G 2004 Structural and evolutionary genomics. Natural selection in genome evolution (Amsterdam: Elsevier)
Brenner S E, Koehl P and Levitt M 2000 The ASTRAL compendium for protein structure and sequence analysis; Nucleic Acids Res. 28 254–256
Chiapello H, Ollivier E, Landes-Devauchelle C, Nitschke P and Risler J L 1999 Codon usage as a tool to predict the cellular location of eukaryotic ribosomal proteins and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases; Nucleic Acids Res. 27 2848–2851
Conte L L, Brenner S E, Hubbard T J P, Chothia C and Murzin A G 2002 SCOP database in 2002: refinements accommodate structural genomics; Nucleic Acids Res. 30 264–267
D’Onofrio G 2002 Expression patterns and gene distribution in the human genome; Gene 300 155–160
D’Onofrio G, Ghosh T C and Bernardi G 2002 The base composition of the human genes is correlated with the secondary structures of the encoded proteins. Gene 300 179–187
Ellis J T and Morrison D A 1995 Schistosoma mansoni: patterns of codon usage and bias. Parasitology 110 53–60
Grantham R, Gautier C, Gouy M, Mercier R and Pave A 1980 Codon catalog usage and the genome hypothesis; Nucleic Acids Res. 8 r49–r62
Gupta S K, Majumdar S, Bhattacharya T K and Ghosh T C 2000 Studies on the relationships between the synonymous codon usage and protein secondary structural units; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 269 692–696
Gu W, Zhou T, Ma J, Sun X and Lu Z 2004 The relationshiP between synonymous codon usage and protein structure in Escherichia coli and Homo sapiens; Biosystems 73 89–97
Ikemura T 1985 Codon usage and tRNA content in unicellular and multicellular organisms; Mol. Biol. Evol. 2 13–34
Kabsch W and Sander C 1983 Dictionary of protein secondary structure: pattern recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features; Biopolymers 12 2577–2637
Karlin S and Mrazek J 1996 What drives codon choices in human genes?; J. Mol. Biol. 262 459–472
Kahali B, Basak S and Ghosh T C 2007 Reinvestigating the codon and amino acid usage of S. cerevisiae genome: A new insight from protein secondary structure analysis; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 354 693–699
Lynn D J, Singer G A and Hickey D A 2002 Synonymous codon usage is subject to selection in thermophilic bacteria; Nucleic Acids Res. 30 4272–4277
Majumdar S, Gupta S K, Sundararajan V S and Ghosh T C 1999 Compositional correlation studies among the three different codon positions in 12 bacterial genomes; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 266 66–71
Oresic M and Shalloway D 1998 Specific correlations between relative synonymous codon usage and protein secondary structure; J. Mol. Evol. 281 31–48
Pouwels P H and Leunissen J A 1994 Divergence in codon usage of Lactobacillus species; Nucleic Acids Res. 22 929–936
Siemion I Z and Siemion P J 1994 The informational context of the third base in amino acid codons; Biosystems 33 139–148
Tao X and Dafu D 1998 The relationship between synonymous codon usage and protein Structure; FEBS Lett. 434 93–96
Taylor F and Coates D 1989 The code within the codons; Biosystems 22 177–187
Thanaraj T A and Argos P 1996a Protein secondary structural types are differentially coded on messenger RNA; Protein Sci. 5 1973–1983
Thanaraj T A and Argos P 1996b Ribosome-mediated translational pause and protein domain organization; Protein Sci. 5 1594–1612
Volkenstein M V 1966 The genetic coding of protein structure; Biochim. Biophys. Acta 119 421–424
Zhang S, Zubay G and Goldman E 1991 Low-usage codons in Escherichia coli, yeast, fruit fly and primates; Gene 105 61–72
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukhopadhyay, P., Basak, S. & Ghosh, T.C. Synonymous codon usage in different protein secondary structural classes of human genes: Implication for increased non-randomness of GC3 rich genes towards protein stability. J Biosci 32 (Suppl 1), 947–963 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-007-0095-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-007-0095-z