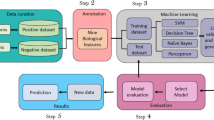
Abstract
Functional classification of proteins is central to comparative genomics. The need for algorithms tuned to enable integrative interpretation of analytical data is felt globally. The availability of a general, automated software with built-in flexibility will significantly aid this activity. We have prepared ARC (Automated Resource Classifier), which is an open source software meeting the user requirements of flexibility. The default classification scheme based on keyword match is agglomerative and directs entries into any of the 7 basic non-overlapping functional classes: Cell wall, Cell membrane and Transporters (C), Cell division (

), Information (I), Translocation (\( \mathcal{L} \)), Metabolism (

), Stress (

), Signal and communication(S) and 2 ancillary classes: Others (O) and Hypothetical (

). The keyword library of ARC was built serially by first drawing keywords from Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli K12. In subsequent steps, this library was further enriched by collecting terms from archaeal representative Archaeoglobus fulgidus, Gene Ontology, and Gene Symbols. ARC is 94.04% successful on 6,75,663 annotated proteins from 348 prokaryotes. Three examples are provided to illuminate the current perspectives on mycobacterial physiology and costs of proteins in 333 prokaryotes. ARC is available at http://arc.igib.res.in .
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams M D, Kerlavage A R, Fleischmann R D, Fuldner R A, Bult C J, Lee N H, Kirkness E F, Weinstock K G et al 1995 Initial assessment of human gene diversity and expression patterns based upon 83 million nucleotides of cDNA sequence; Nature (London) (Suppl.) 377 3–174
Akashi H and Gojobori T 2002 Metabolic efficiency and amino acid composition in the proteomes of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99 3695–3700
Andrade M A, Ouzounis C, Sander C, Tamames J and Valencia A 1999 Functional classes in the three domains of life; J. Mol. Evol. 49 551–557
Auffray C, Imbeaud S, Roux-Rouquié M and Hood L 2003 Self-organized living systems: conjunction of a stable organization with chaotic fluctuations in biological space-time; Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 361 1125–1139
Blattner F R, Plunket III G, Bloch C A, Perna N T, Burland V, Riley M, Collado-Vides J, Glasner J D et al 1997 The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12; Science 277 1453–1474
Cole S T, Brosch R, Parkhill J, Garnier T, Churcher C, Harris D, Gordon S V, Eiglmeier K et al 1998 Deciphering the biology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the complete genome sequence; Nature (London) 393 537–544
Cole S T, Eiglmeier K, Parkhill J, James K D, Thomson N R, Wheeler P R, Honore N, Garnier T et al 2001 Massive gene decay in the leprosy bacillus; Nature (London) 409 1007–1011
Gao Q, Kripke K E, Saldanha A J, Yan W, Holmes S and Small P M 2005 Gene expression diversity among Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical isolates; Microbiology 151 5–14
Grunewald J and Marahiel M A 2006 Chemoenzymatic and template-directed synthesis of bioactive macrocyclic peptides; Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 70 121–146
Harris M A, Clark J, Ireland A, Lomax J, Ashburner M, Foulger R, Eilbeck K, Lewis S et al 2004 The Gene Ontology (GO) database and informatics resource; Nucleic Acids Res. 32 D258–D261
Klenk H P, Clayton R A, Tomb J F, White O, Nelson K E, Ketchum K A, Dodson R J, Gwinn M et al 2003 The complete genome sequence of Mycobacterium bovis; Nature (London) 100 7877–7882
Klenk H P, Clayton R A, Tomb J F, White O, Nelson K E, Ketchum K A, Dodson R J, Gwinn M et al 1997 The complete genome sequence of the hyperthermophilic, sulphate-reducing archaeon Archaeoglobus fulgidus; Nature (London) 390 364–370
Kondrashov F A, Rogozin I B, Wolf Y I and Koonin E V 2002 Selection in the evolution of gene duplications; Genome Biol. 3 research 0008.1–0008.9
Kunst F, Ogasawara N, Moszer I, Albertini A M, Alloni G, Azevedo V, Bertero M G, Bessieres P et al 1997 The complete genome sequence of the gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis; Nature (London) 390 249–256
Madan Babu M 2003 Did the loss of sigma factors initiate pseudogene accumulation in M leprae?; Trends Microbiol. 11 59–61
Pillet V, Zehnder M, Seewald A K, Veuthey A L and Petrak J 2004 GPSDB: a new database for synonyms expansion of gene and protein names; Bioinformatics 21 1743–1744
Riley M 1993 Functions of the Gene Products of Escherichia coli; Microbiol. Rev. 54 862–952
Subramanyam M B, Gnanamani M and Ramachandran S 2006 Simple sequence proteins in prokaryotic proteomes; B.M.C. Genomics 11 141
Uitenbroek D G 1997 SISA Binomial. Southampton http://home.clara.net/sisa/binomial.htm
Van Regenmortel M H 2004 Reductionism and complexity in molecular biology. Scientists now have the tools to unravel biological and overcome the limitations of reductionism; EMBO Rep. 5 1016–1020
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Additional material pertaining to this article is available with authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gnanamani, M., Kumar, N. & Ramachandran, S. ARC: Automated Resource Classifier for agglomerative functional classification of prokaryotic proteins using annotation texts. J Biosci 32 (Suppl 1), 937–945 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-007-0094-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-007-0094-0