Abstract
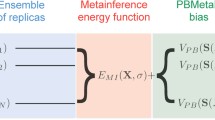
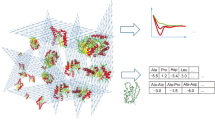
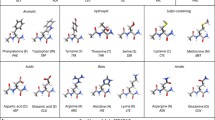
The computational identification of all the low energy structures of a peptide given only its sequence is not an easy task even for small peptides, due to the multiple-minima problem and combinatorial explosion. We have developed an algorithm, called the MOLS technique, that addresses this problem, and have applied it to a number of different aspects of the study of peptide and protein structure. Conformational studies of oligopeptides, including loop sequences in proteins have been carried out using this technique. In general the calculations identified all the folds determined by previous studies, and in addition picked up other energetically favorable structures. The method was also used to map the energy surface of the peptides. In another application, we have combined the MOLS technique, using it to generate a library of low energy structures of an oligopeptide, with a genetic algorithm to predict protein structures. The method has also been applied to explore the conformational space of loops in protein structures. Further, it has been applied to the problem of docking a ligand in its receptor site, with encouraging results.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LS:
-
Latin square
- MFT:
-
mean field technique
- MOLS:
-
mutually orthogonal Latin squares
- PES:
-
potential energy surface
References
Anfinsen C B 1973 Principles that Govern the Folding of Protein Chains; Science 181 223–230
Anfinsen C B, Robert R R, Warren I C, Juanita P and William R C 1954 Studies on the Gross Structure, Cross-Linkages, and Terminal Sequences in Ribonuclease; J. Biol. Chem. 207 201–210
Arunachalam J, Kanagasabai K and Gautham N 2006 Protein structure prediction using mutually orthogonal Latin squares and a genetic algorithm; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 342 424–433
Betancourt M R and Skolnick J 2001 Finding the needle in a haystack: deducing native folds from ambiguous ab initio protein structure predictions; J. Comp. Chem. 22 339–353
Böhm G 1996 New approaches in molecular structure prediction; Biophys. Chem. 59 1–32
Bowie J U and Eisenberg D 1994 An evolutionary approach to folding small a-helical proteins that uses sequence information and an empirical guiding fitness function; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91 4436–4440
Brooks B R, Bruccoleri R E, Olafson B D, States D J, Swaminathan S and Karplus M 1983 CHARMM: A program for macromolecular energy, minimization, and dynamics calculations; J. Comput. Chem. 4 187–217
Bujnicki J M 2006 Protein-Structure Prediction by Recombination of Fragments; Chem. Biol. Chem. 7 19–27
Chung S Y and Subbiah S 1996 Pac. Symp. Biocomput. (Hawaii) 126–141
Clark M, Cramer III R D and van Opdenhosch N 1989 Validation of the General Purpose Tripose 5.2 Force Field; J. Comp. Chem. 10 982–1012
Crivelli S, Eskow E, Bader B, Lamberti V, Byrd R, Schnabel R and Head G T 2002 A physical approach to protein structure prediction; Biophys. J. 82 36–49
Daisuke K, Hui L, Andrzej K and Jeffrey S 2001 TOUCHSTONE: An ab initio protein structure prediction method that uses threading-based tertiary restraints; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98 10125–10130
Damm W A, Frontera J, Tirado-Rives and Jorgensen W L 1997 OPLS All-Atom Force Field for Carbohydrates; J. Comp. Chem. 18 1955–1970
Dandekar T and Argos P 1994 Folding the main chain of small proteins with the genetic algorithm; J. Mol. Biol. 236 844–861
Dandekar T and Argos P 1996 Identifying the tertiary fold of small proteins with different topologies from sequence and secondary structure using the genetic algorithm and extended criteria for strand regions; J. Mol. Biol. 256 645–660
Deane M C and Blundell T L 2000 A novel exhaustive search algorithm for predicting the conformation of polypeptide segments in proteins; Prot. Struct. Funct. Genet. 40 135–144
DePristo M A, de Bakker P I, Lovell S C and Blundell T L 2003 Ab initio construction of polypeptide fragments: efficient generation of accurate, representative ensembles; Prot. Struct. Funct. Genet. 51 41–55
Dill K A and Chan H S 1997 From Levinthal to pathways to funnels; Nat. Struct. Biol. 4 10–19
Duan Y and Kollman P A 2001 Computational protein folding: From lattice to all-atom; IBM Systems J. 40 297–309
Efimov A V 1993 Patterns of loop regions in proteins; Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 3 379–384
Eisenhaber F, Persson B and Argos P 1995 Protein structure prediction: Recognition of primary, secondary, and tertiary structural features from amino acid sequence; Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 30 1–94
Finney D J 1955 Randomized blocks and Latin squares; in Experimental design and its statistical basis (London: Cambridge University Press) pp 45–67
Fiser A, Gian D K R and Sali R 2000 Modeling of loops in protein structures. Protein Sci. 9 1753–1773
Fisher R A 1960 The Latin square; in The design of experiments (London: Oliver and Boyd pp 70–92
Floudas C A, Klepeis J L and Pardalos, P M 1999 Global optimization approaches in protein folding and peptide docking. In DIMACS Series in discrete mathematics and theoretical computer science (eds) M Farach-Colton et al (New Jersey: American Mathematical Society) vol 47, pp 141–171
Gehlhaar D K, Verkhivker G M, Rejto P A, Sherman C J, Fogel D B, Fogel L J and Freer S T 1995 Molecular recognition of the inhibitor AG-1343 by HIV-1 protease: conformationally flexible docking by evolutionary programming; Chem. Biol. 2 317–324
Ginalski K, Grishin N V, Godzik A and Rychlewski L 2005 Practical lessons from protein structure prediction; Nuceic Acids Res. 33 1874–1891
Goldberg D E 1999 Genetic algorithms, in search, optimization and machine learning (Singapore: Pearson Education)
Griffin J F, Langs D A, Smith G D, Blundell T L, Tickle I J and Bedarkar S 1986 The crystal structures of [Met5]enkephalin and a third form of [Leu5]enkephalin: Observations of a novel pleated b-sheet; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83 3272–3276
Hansmann U H E, Okamoto Y, and Onuchic J N 1999 The folding funnel landscape for the peptide Met-enkephalin; Prot. Struct. Funct. Genet. 34 472–483
Hardin C, Pogorelov T V and Luthey-Schulten Z 2002 Ab initio protein structure prediction; Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 12 176–81
Howard A E and Kollman P A 1988 An analysis of current methodologies for conformational searching of complex molecules; J. Med. Chem. 31 1669–1675
Isogai Y, Nemethy G, and Scheraga H A 1977 Enkephalin: conformational analysis by means of empirical energy calculations; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74 414–418
Kanagasabai V, Arunachalam J, Arun Prasad P and Gautham N 2007 Exploring the Conformational Space of Protein Loops Using A Mean Field Technique With MOLS Sampling; Prot. Struct. Funct. Bioinfo. 67 (in press)
Klepeis J L and Floudas C A 2003 Ab initio Tertiary Structure Prediction of Proteins; J. Glob. Optim. 25 113–140
Koehl P and Delarue M 1994 Application of a self-consistent mean field theory to predict protein side-chains conformation and estimate their conformational entropy; J. Mol. Biol. 239 249–75
Koehl P and Delarue M 1996 Mean-field minimization methods for biological macromolecules; Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 6 222–226
Leach A R 1991 A survey of methods for searching the conformational space of small and medium-sized molecules; in Reviews in computational chemistry (eds) K B Lipkowitz and D B Boyd (New York: VCH Publishers) vol 2, pp 1–55
Leszczynski J F and Rose G D 1986 Loops in globular proteins: a novel category of secondary structure; Science 234 849–855
Levy Y and Becker O M 2001 Energy landscapes of conformationally constrained peptides; J. Chem. Phys 14 993–1009
Li Z and Scheraga H A 1987 Monte Carlo-minimization approach to the multiple-minima problem in protein folding; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84 6611–6615
Lii, J H and Allinger N L 1991 The MM3 Force Field for Amides, Polypeptides and Proteins; J. Comp. Chem. 12 186–199
Montgomery D C 2000 Randomized blocks, Latin squares, and related designs; in Design and analysis of experiments (New York: John Wiley) pp 126–169
Moult J, Fidelis K, Zemla A and Hubbard T 2003 Critical assessment of methods of protein structure prediction (CASP)-round V; Proteins (Suppl.) 53 334–339
Natasja B and Kuntz I D 2003 Molecular Recognition and Docking Algorithms; Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 32 335–373
Nemethy G, Gibson K D, Palmer K A, Yoon C N, Paterlini G, Zagari A, Rumsey S and Scheraga H A 1992 Energy parameters in polypeptides. 10. Improved geometric parameters and nonbonded interactions for use in the ECEPP/3 algorithm, with application to proline-containing peptides; J. Phys. Chem. 96 6472–6484
Neumaier A 1997 Molecular modeling of proteins and mathematical prediction of protein structure; SIAM Rev. 39 407–460
Onuchic J, Luthey S A, and Wolynes P G 1997 Theory of protein folding: the energy landscape perspective; Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 48 545–600
Plotkin S S and Onuchic J N 2002 Understanding protein folding with energy landscape theory Part II: Quantitative aspects; Q. Rev. Biophys. 35 205–286
Richard B and David B 2001 AB INITIO PROTEIN STRUCTURE PREDICTION: Progress and Prospects; Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 30 173–189
Ring C S, Kneller D G, Langridge R and Cohen F E 1992 Taxonomy and conformational analysis of loops in proteins; J. Mol. Biol. 224 685–699
Rost B and O’Donoghue S 1997 Sisyphus and protein structure prediction; Bioinformatics 13 345–356
Rost B and Sander C 1994 Structure prediction of proteins — where are we now?; Curr. Opin. Biotech. 5 372–380
Schulze K S 2000 Genetic algorithm and protein folding; in Protein structure prediction — methods and protocols (ed.) D M Webster (New Jersey: Humana press) pp 175–222
Sudarsanam S, DuBose R F, March C J and Srinivasan S 1995 Modelling protein loops using a ϕ i+1,Φ i dimer database; Protein Sci. 4 1412–1420
Sun S 1995 A genetic algorithm that seeks native states of proteins; Biophys. J. 69 340–355
Takada S 2001 Protein Folding Simulation With Solvent-Induced Force Field: Folding Pathway Ensemble of Three-Helix-Bundle Proteins; Prot. Struct. Funct. Genet. 42 85–98
Taylor R D, Jewsbury P J and Essex J W 2002 A review of protein-small molecule docking methods; J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 16 151–166
Taylor R D, Jewsbury P J, Essex W J 2003 FDS: Flexible Ligand and Receptor Docking with a Continuum Solvent Model and Soft-Core Energy Function; J. Comput. Chem. 24 1637–1656
Unger R and Moult J 1993 Genetic algorithms for protein folding simulations; J. Mol. Biol. 231 75–81
Van Vlijmen T W H and Karplus M 1997 PDB based protein loop prediction: parameters for election and methods for optimization; J. Mol. Biol. 267 975–1001
Vásquez M, Némethy G and Scheraga H A 1994 Conformational energy calculations on polypeptides and protein; Chem. Rev. 94 2183–2239
Vengadesan K and Gautham N 2003 Enhanced sampling of the molecular potential energy surface using mutually orthogonal Latin squares: Application to peptide structures; Biophys. J. 84 2897–2906
Vengadesan K and Gautham N 2004a Conformational studies on enkephalins using the MOLS technique; Biopolymers 74 476–494
Vengadesan K and Gautham N 2004b The energy landscape of Metenkephalin and Leu-enkephalin drawn using mutually orthogonal Latin squares sampling; J. Phys. Chem. B 108 11196–11205
Wales D J, Doye J P K, Miller M A, Mortenson P N, and Walsh T A 2000 Energy landscapes: From clusters to biomolecules; Adv. Chem. Phys. 115 1–111
Weiner S J, Kollman P A, Nguyen D T and Case D A 1986 An all atom force field for simulations of proteins and nucleic acids; J. Comput. Chem. 7 230–252
Wojcik J, Mornon J and Chomilier J 1999 New efficient statistical sequence-dependent structure prediction of short to medium sized protein loops based on an exhaustive loop classification; J. Mol. Biol. 289 1469–1490
Youxing Q, Jun-tao G, Victor O and Ying X 2004 Protein structure prediction using sparse dipolar coupling data; Nuceic Acids Res. 32 2551–2561
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prasad, P.A., Kanagasabai, V., Arunachalam, J. et al. Exploring conformational space using a mean field technique with MOLS sampling. J Biosci 32 (Suppl 1), 909–920 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-007-0091-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-007-0091-3