Abstract
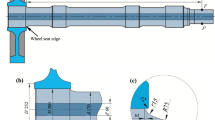
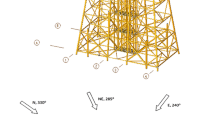
Structural fatigue property of Shanghai 65-m fully-steerable antenna structure is analysed. According to the active fully-steerable working pattern, the typical fatigue stress piece is put forward based on simple sampling and decomposed by real-time rain flow counting algorithms. Subsequently, the fatigue lives of pitch mechanism bearings were computed by miner linear accumulative damage criterion. What’s more, in a complete cycle of dynamic observation, the shear force and axial force of high strength friction grip bolts for all of the supporting nodes are extracted and counted aiming at each pitching angle. As a result, fatigue analysis is carried out on the supporting nodes of the back-frame structure connected with the pitching mechanism. Last but not the least, finite element refinement model is conducted for the contact part between antenna wheels and the rail. Based on contact fatigue curve spectrum, the contact fatigue existing between the antenna structure roller and the track is analysed. The results show that the fatigue life of the whole antenna structure can meet the safety requirements in the design reference period which is intended to be 30 years. This systematic fatigue analysis procedure, method and results can provide valuable references for design, construction and maintenance of such similar fully-steerable antenna structures in future.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao S. S., Lei Q. J. 2016, Fatigue life prediction of steel structure considering interval uncertainty, J. Jilin University Press, 03, 804
Fan F., Jin X. F. 2010, Fatigue analysis of FAST cable-net structure under long-term active shape-changing work, J. Building Structures, 12, 19
Fan F., Qian H. L. 2010, Report of Shanghai 65-m Radio Telescope Structure Analysis, Space Structure Research Center in Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China
Fu L. 2009, Verification scheme for mechanics analysis of Shanghai 65-meter radio telescope structure, Chinese Acad. Sci., 11, 23
Fu G. Y., Tong W. L., Liu B. 2016, Beach marking method in checking fatigue crack propagation of steel structures, Engineering & Mechanics, 08, 93
Huang K., Shen S. S., Zhang Y. F. 2016, Random vibration and fatigue analysis of array antenna structure, Guidance & Fuze, 02, 25
Liao F. F., Wang W., Li C. W. 2016, Review on research status of connection fracture of steel structures, J. Architecture and Civil Engineering, 01, 67
Li B., Wang L. X., Lang S. S. 2018, Steel structure with changing cross section fatigue life estimation, Steel Structure, 01, 17
Liu Y. 2016, Non-uniform solar temperature field on large aperture, fully-steerable telescope structure, J. Astrophys. Astron., 37, 19
Liu C., Fan S. J., Nie G. J. 2017a, Fatigue performance research of headed studs in steel and ultra-high performance concrete composite deck, China J. Highway and Transport, 03, 134
Liu Y., Qian H. L., Fan F. 2017b, Reflector wind load characteristics of the large all-movable antenna and its effect on reflector surface precision, Int. J. Advanced Steel Construction, 01, 1
Wang H. Q., Gu M. 2008, Comparison between methods of structural fatigue life estimation, J. Vibration and Shock, 02, 77
Weng W. X. 2017, Study on Static and Fatigue Performance of the Short Studs in Steel-UHPC Lightweight Composite Bridge Deck, Southwest Jiaotong University Press, Chengdu, pp. 12–29
Wu Z. X. 2016, Study on Bonding and Fatigue Properties of CFRP Reinforcing Cracked Steel Plate, Hunan University Press, Changsha, pp. 35–56
Xu J., Zhan J. J. 2017, Research on Fatigue Accumulative Damage of Steel Structure Transmission Tower, Supervision Test and Cost of Construction, vol. 04, pp. 11–14
Zhang B. X., Zhang N. J. 2014, Fatigue life prediction of riveted structure with damage mechanics and finite element method, Aeronautical Computing Technique, 05, 66
Zhao N. E., Qu L. W., Zhou Q. 2016, Low-cycle fatigue experiments of structural steel and its related welded metal under multi-axial loading, J. Building Structures, 12, 153
Zhong J. et al. 2016, An estimate of the time-varying temperature field of the main reflector and sub reflector of the Shanghai 65 m radio telescope under solar illumination, Int. J. Steel Structures, 01, 115
Zhou C. Y., Li Q. A., Fang Z. 2017, Experimental study on low cycle fatigue properties of Q345 steel butt joint, J. Southeast University, 04, 738
Zhou Y., Pu H. Q., Shi Z. 2015, Study on Mechanics Behavior and fatigue performance of steel-concrete composite joints of railway hybrid girder cable-stayed bridges, China Civil Engineering J., 11, 77
Acknowledgements
This project was financially supported by the Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (Program No. 2019JM-499).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y. Rotational fatigue analysis on Shanghai 65-m fully-steerable antenna structure during its normal operation. J Astrophys Astron 40, 30 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12036-019-9599-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12036-019-9599-9