Abstract
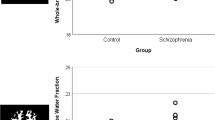
Several studies have reported compromised white matter integrity, and that some inflammatory mediators may underlie this functional dysconnectivity in the brain of patients with schizophrenia. The immune-inflammatory response system and compensatory immune-regulatory reflex system (IRS/CIRS) are novel biomarkers for exploring the role of immune imbalance in the pathophysiological mechanism of schizophrenia. This study aimed to explore the little-known area regarding the composite score of peripheral cytokines, the IRS/CIRS, and its correlation with white matter integrity and the specific microstructures most affected in schizophrenia. First-episode patients with schizophrenia (FEPS, n = 94) and age- and sex-matched healthy controls (HCs, n = 50) were enrolled in this study. Plasma cytokine levels were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and psychopathology was assessed using the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS). The whole brain white matter integrity was measured by fractional anisotropy (FA) from diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) using a 3-T Prisma MRI scanner. The IRS/CIRS in FEPS was significantly higher than that in HCs (p = 1.5 × 10−5) and Cohen’s d effect size was d = 0.74. FEPS had a significantly lower whole-brain white matter average FA (p = 0.032), which was negatively associated with IRS/CIRS (p = 0.029, adjusting for age, sex, years of education, BMI, and total intracranial volume), but not in the HCs (p > 0.05). Among the white matter microstructures, only the cortico-spinal tract was significantly correlated with IRS/CIRS in FEPS (r = − 0.543, p = 0.0009). Therefore, elevated IRS/CIRS may affect the white matter in FEPS.



Similar content being viewed by others

Data Availability
The datasets generated during the current study will be made available from the corresponding author on reasonable request once the dataset has been fully exploited by the authors.
References
Marder SR, Cannon TD (2019) Schizophrenia. N Engl J Med 381(18):1753–1761
Adamczyk P, Plonka O, Kruk D, Jani M, Bladzinski P, Kalisz A et al (2021) On the relation of white matter brain abnormalities and the asociality symptoms in schizophrenia outpatients - a DTI study. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 81(1):80–95
Stahl SM (2018) Beyond the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia to three neural networks of psychosis: dopamine, serotonin, and glutamate. CNS Spectr 23(3):187–191
Watkins CC, Andrews SR (2016) Clinical studies of neuroinflammatory mechanisms in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 176(1):14–22
Lizano P, Lutz O, Xu Y, Rubin LH, Paskowitz L, Lee AM et al (2021) Multivariate relationships between peripheral inflammatory marker subtypes and cognitive and brain structural measures in psychosis. Mol Psychiatry 26(7):3430–3443
Michalczyk A, Tyburski E, Podwalski P, Waszczuk K, Rudkowski K, Kucharska-Mazur J et al (2022) Serum inflammatory markers and their associations with white matter integrity of the corpus callosum in schizophrenia patients and healthy controls. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 116:110510
Malashenkova IK, Krynskiy SA, Ogurtsov DP, Mamoshina MV, Zakharova NV, Ushakov VL et al (2018) A role of the immune system in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. Zhurnal nevrologii i psikhiatrii imeni SS Korsakova 118(12)
Najjar S, Pearlman DM (2015) Neuroinflammation and white matter pathology in schizophrenia: systematic review. Schizophr Res 161(1):102–112
Lee EE, Hong S, Martin AS, Eyler LT, Jeste DV (2017) Inflammation in schizophrenia: cytokine levels and their relationships to demographic and clinical variables. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 25(1):50–61
Lesh TA, Careaga M, Rose DR, McAllister AK, Van de Water J, Carter CS et al (2018) Cytokine alterations in first-episode schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: relationships to brain structure and symptoms. J Neuroinflammation 15(1):165
Wu ZW, Yu HH, Wang X, Guan HY, Xiu MH, Zhang XY (2021) Interrelationships between oxidative stress, cytokines, and psychotic symptoms and executive functions in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Psychosom Med 83(5):485–491
Dahan S, Bragazzi NL, Yogev A, Bar-Gad M, Barak V, Amital H et al (2018) The relationship between serum cytokine levels and degree of psychosis in patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 268:467–472
Goldsmith DR, Rapaport MH, Miller BJ (2016) A meta-analysis of blood cytokine network alterations in psychiatric patients: comparisons between schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depression. Mol Psychiatry 21(12):1696–1709
Maes M, Carvalho AF (2018) The compensatory immune-regulatory reflex system (CIRS) in depression and bipolar disorder. Mol Neurobiol 55(12):8885–8903
Noto MN, Maes M, Vargas Nunes SO, Ota VK, Rossaneis AC, Verri WA Jr et al (2019) Activation of the immune-inflammatory response system and the compensatory immune-regulatory system in antipsychotic naive first episode psychosis. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 29(3):416–431
Maes M, Berk M, Goehler L, Song C, Anderson G, Gałecki P et al (2012) Depression and sickness behavior are Janus-faced responses to shared inflammatory pathways. BMC Med 10:66
Maes M, Plaimas K, Suratanee A, Noto C, Kanchanatawan B (2021) First episode psychosis and schizophrenia are systemic neuro-immune disorders triggered by a biotic stimulus in individuals with reduced immune regulation and neuroprotection. Cells 10(11)
Moustafa SR, Al-Rawi KF, Stoyanov D, Al-Dujaili AH, Supasitthumrong T, Al-Hakeim HK et al (2020) The endogenous opioid system in schizophrenia and treatment resistant schizophrenia: increased plasma endomorphin 2, and kappa and mu opioid receptors are associated with interleukin-6. Diagnostics (Basel) 10(9)
Roomruangwong C, Noto C, Kanchanatawan B, Anderson G, Kubera M, Carvalho AF et al (2020) The role of aberrations in the immune-inflammatory response system (IRS) and the compensatory immune-regulatory reflex system (CIRS) in different phenotypes of schizophrenia: the IRS-CIRS theory of schizophrenia. Mol Neurobiol 57(2):778–797
Noto MN, Maes M, Vargas Nunes SO, Ota VK, Cavalcante D, Oliveira G et al (2021) BDNF in antipsychotic naive first episode psychosis: effects of risperidone and the immune-inflammatory response system. J Psychiatr Res 141:206–213
Chen W, Gou M, Wang L, Li N, Li W, Tong J et al (2023) Inflammatory disequilibrium and lateral ventricular enlargement in treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 72:18–29
Martins PLB, Moura IA, Mendes G, Ribeiro V, Arnaud A, Gama CS et al (2023) Immunoinflammatory and oxidative alterations in subjects with schizophrenia under clozapine: a meta-analysis. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 73:82–95
Wang Y, Wei Y, Edmiston EK, Womer FY, Zhang X, Duan J et al (2020) Altered structural connectivity and cytokine levels in schizophrenia and genetic high-risk individuals: associations with disease states and vulnerability. Schizophr Res
Prasad KM, Upton CH, Nimgaonkar VL, Keshavan MS (2015) Differential susceptibility of white matter tracts to inflammatory mediators in schizophrenia: an integrated DTI study. Schizophr Res 161(1):119–125
Tong J, Zhou Y, Huang J, Zhang P, Fan F, Chen S et al (2021) N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antibody and white matter deficits in schizophrenia treatment-resistance. Schizophr Bull 47(5):1463–1472
Kraguljac NV, Anthony T, Morgan CJ, Jindal RD, Burger MS, Lahti AC (2021) White matter integrity, duration of untreated psychosis, and antipsychotic treatment response in medication-naïve first-episode psychosis patients. Mol Psychiatry 26(9):5347–5356
Stapel B, Sieve I, Falk CS, Bleich S, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Kahl KG (2018) Second generation atypical antipsychotics olanzapine and aripiprazole reduce expression and secretion of inflammatory cytokines in human immune cells. J Psychiatr Res 105:95–102
Li F, Lui S, Yao L, Ji GJ, Liao W, Sweeney JA et al (2018) Altered white matter connectivity within and between networks in antipsychotic-naive first-episode schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 44(2):409–418
Chwa WJ, Tishler TA, Raymond C, Tran C, Anwar F, Villablanca JP et al (2020) Association between cortical volume and gray-white matter contrast with second generation antipsychotic medication exposure in first episode male schizophrenia patients. Schizophr Res 222:397–410
Kahn RS, Sommer IE (2015) The neurobiology and treatment of first-episode schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 20(1):84–97
Gou M, Pan S, Tong J, Zhou Y, Han J, Xie T et al (2021) Effects of microRNA-181b-5p on cognitive deficits in first-episode patients with schizophrenia: Mediated by BCL-2. J Psychiatr Res 136:358–365
Kochunov P, Huang J, Chen S, Li Y, Tan S, Fan F et al (2019) White matter in schizophrenia treatment resistance. Am J Psychiatry 176(10):829–838
Jahanshad N, Kochunov PV, Sprooten E, Mandl RC, Nichols TE, Almasy L et al (2013) Multi-site genetic analysis of diffusion images and voxelwise heritability analysis: a pilot project of the ENIGMA-DTI working group. Neuroimage 81:455–469
Cohen J (1992) A power primer. Psychol Bull 112(1):155–159
Eleni P, Georgia P, Constantine P, Efstratios K, Georgios V, Nikolaos K et al (2021) Functional brain imaging of speeded decision processing in Parkinson’s disease and comparison with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 314:111312
Erhardt S, Schwieler L, Imbeault S, Engberg G (2017) The kynurenine pathway in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Neuropharmacology 112(Pt B):297–306
Noyan H, Erdağ E, Tüzün E, Yaylım İ, Küçükhüseyin Ö, Hakan MT et al (2021) Association of the kynurenine pathway metabolites with clinical, cognitive features and IL-1β levels in patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorder and their siblings. Schizophr Res 229:27–37
Mendiola AS, Cardona AE (2018) The IL-1beta phenomena in neuroinflammatory diseases. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 125(5):781–795
Noto MN, Maes M, Nunes SOV, Ota VK, Rossaneis AC, Verri WA Jr et al (2019) Activation of the immune-inflammatory response system and the compensatory immune-regulatory system in antipsychotic naive first episode psychosis. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 29(3):416–431
Derecki NC, Cardani AN, Yang CH, Quinnies KM, Crihfield A, Lynch KR et al (2010) Regulation of learning and memory by meningeal immunity: a key role for IL-4. J Exp Med 207(5):1067–1080
Walker KA (2018) Inflammation and neurodegeneration: chronicity matters. Aging (Albany NY) 11(1):3–4
Benedetti F, Poletti S, Hoogenboezem TA, Mazza E, Ambree O, de Wit H et al (2016) Inflammatory cytokines influence measures of white matter integrity in bipolar disorder. J Affect Disord 202:1–9
Dietz AG, Goldman SA, Nedergaard M (2020) Glial cells in schizophrenia: a unified hypothesis. Lancet Psychiatry 7(3):272–281
Favrais G, van de Looij Y, Fleiss B, Ramanantsoa N, Bonnin P, Stoltenburg-Didinger G et al (2011) Systemic inflammation disrupts the developmental program of white matter. Ann Neurol 70(4):550–565
Seki Y, Kato TA, Monji A, Mizoguchi Y, Horikawa H, Sato-Kasai M et al (2013) Pretreatment of aripiprazole and minocycline, but not haloperidol, suppresses oligodendrocyte damage from interferon-γ-stimulated microglia in co-culture model. Schizophr Res 151(1–3):20–28
Zhou Y, Zhang J, Wang L, Chen Y, Wan Y, He Y et al (2017) Interleukin-1beta impedes oligodendrocyte progenitor cell recruitment and white matter repair following chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Brain Behav Immun 60:93–105
Pu H, Zheng X, Jiang X, Mu H, Xu F, Zhu W et al (2021) Interleukin-4 improves white matter integrity and functional recovery after murine traumatic brain injury via oligodendroglial PPARgamma. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 41(3):511–529
Fu G, Zhang W, Dai J, Liu J, Li F, Wu D et al (2019) Increased peripheral interleukin 10 relate to white matter integrity in schizophrenia. Front Neurosci 13(FEB)
Goudarzi S, Gilchrist SE, Hafizi S (2020) Gas6 induces myelination through anti-inflammatory IL-10 and TGF-beta upregulation in white matter and glia. Cells 9(8)
Zhang J, Yang L, Fang Z, Kong J, Huang Q, Xu H (2018) Adenosine promotes the recovery of mice from the cuprizone-induced behavioral and morphological changes while effecting on microglia and inflammatory cytokines in the brain. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 13(3):412–425
Devinsky O, Vezzani A, Najjar S, De Lanerolle NC, Rogawski MA (2013) Glia and epilepsy: excitability and inflammation. Trends Neurosci 36(3):174–184
Zhang C, Xue H, Lei Y, Xu W, K. CRC, Xin Y et al (2012) Motor coordination and white matter integrity in prefrontal lobe and corticospinal tract in first-episode schizophrenia. Chin Ment Health J 26(8):561-5
Matrone M, Kotzalidis GD, Romano A, Bozzao A, Cuomo I, Valente F et al (2022) Treatment-resistant schizophrenia: addressing white matter integrity, intracortical glutamate levels, clinical and cognitive profiles between early- and adult-onset patients. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 114:110493
Sui J, He H, Pearlson GD, Adali T, Kiehl KA, Yu Q et al (2013) Three-way (N-way) fusion of brain imaging data based on mCCA+jICA and its application to discriminating schizophrenia. Neuroimage 66:119–132
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all of the study participants and staff.
Funding
This work was supported by the capital health research and development of special (2022–1-2131); the National Natural Science Foundation of China grants 82171507, 81761128021, and 81771452; the National Institute of Health grant R01MH112180; the Estonian Research Council-European Union Regional Developmental Fund Mobilitas Plus Program No. MOBTT77 and the Estonian Research Council personal research funding team grant project No. PRG878; the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82001415); and the Capital’s Funds for Health Improvement and Research (CFH2020-2–2134).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Li Tian, Yunlong Tan, and L. Elliot Hong designed the project and obtained the funding for this study. Mengzhuang Gou, Wei Li, Jinghui Tong, Yanfang Zhou, Ting Xie, Ting Yu, Wei Feng, Yanli Li, Song Chen, Shujuan Pan, Ping Zhang, and Junchao Huang were responsible for recruiting patients, performing clinical ratings, neuroimaging, and collecting samples. Mengzhuang Gou analyzed all the data and wrote the paper. Yunlong Tan and Li Tian are responsible for the integrity of data and the accuracy of data analysis. Baopeng Tian, Zhiren Wang, Shuping Tan, Xingguang Luo, Chiang-Shan R. Li, and L. Elliot Hong were invited in evolving the ideas and editing the manuscript. All authors have contributed to and have approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
All study-related procedures were performed only after the participants enrolled in this study provided written informed consent. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Beijing Huilongguan Hospital.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
LEH has received or plans to receive research funding or consulting fees on research projects from Mitsubishi, Your Energy Systems LLC, Neuralstem, Taisho, Heptares, Pfizer, Luye Pharma, Sound Pharma, IGC Pharma, Takeda, and Regeneron. None was involved in the design, analysis, or outcomes of the study. All other authors declare no competing commercial and financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gou, M., Li, W., Tong, J. et al. Correlation of Immune-Inflammatory Response System (IRS)/Compensatory Immune-Regulatory Reflex System (CIRS) with White Matter Integrity in First-Episode Patients with Schizophrenia. Mol Neurobiol 61, 2754–2763 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03694-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03694-0