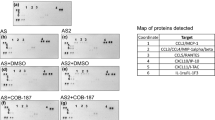
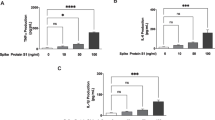
Abstract
SARS-CoV-2 infects cells via its spike (S) protein binding to its surface receptor angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) on target cells and results in acute symptoms involving especially the lungs known as COVID-19. However, increasing evidence indicates that SARS-CoV-2 infection produces neuroinflammation associated with neurological, neuropsychiatric, and cognitive symptoms persists well past the resolution of the infection, known as post-COVID-19 sequalae or long-COVID. The neuroimmune mechanism(s) involved in long-COVID have not been adequately characterized. In this study, we show that recombinant SARS-CoV-2 full-length S protein stimulates release of pro-inflammatory IL-1b, CXCL8, IL-6, and MMP-9 from cultured human microglia via TLR4 receptor activation. Instead, recombinant receptor-binding domain (RBD) stimulates release of TNF-α, IL-18, and S100B via ACE2 signaling. These results provide evidence that SARS-CoV-2 spike protein contributes to neuroinflammation through different mechanisms that may be involved in CNS pathologies associated with long-COVID.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ACE2:
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme-2
- DAMPS:
-
Damage-associated molecular patterns
- MMP9:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase 9
- RBD:
-
Receptor-binding domain
- S:
-
Spike protein
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
References
Tai W, He L, Zhang X, Pu J, Voronin D, Jiang S, Zhou Y, Du L (2020) Characterization of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of 2019 novel coronavirus: implication for development of RBD protein as a viral attachment inhibitor and vaccine. Cell Mol Immunol 17:613–620
Cai Y, Zhang J, Xiao T, Peng H, Sterling SM, Walsh RM Jr, Rawson S, Rits-Volloch S, Chen B (2020) Distinct conformational states of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Science 369:1586–1592
Walls AC, Park YJ, Tortorici MA, Wall A, McGuire AT, Veesler D (2020) Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Cell 181:281–292
Canna SW, Cron RQ (2020) Highways to hell: mechanism-based management of cytokine storm syndromes. J Allergy Clin Immunol 146:949–959
Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Netea MG, Rovina N, Akinosoglou K, Antoniadou A, Antonakos N, Damoraki G, Gkavogianni T, Adami ME, Katsaounou P, Ntaganou M, Kyriakopoulou M, Dimopoulos G, Koutsodimitropoulos I, Velissaris D, Koufargyris P, Karageorgos A, Katrini K, Lekakis V, Lupse M, Kotsaki A, Renieris G, Theodoulou D, Panou V, Koukaki E, Koulouris N, Gogos C, Koutsoukou A (2020) Complex immune dysregulation in COVID-19 patients with severe respiratory failure. Cell Host Microbe 27:992–1000
Moore JB, June CH (2020) Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19. Science 368:473–474
Ye Q, Wang B, Mao J (2020) The pathogenesis and treatment of the ‘Cytokine Storm’ in COVID-19. J Infect 80:607–613
Chen G, Wu D, Guo W, Cao Y, Huang D, Wang H, Wang T, Zhang X, Chen H, Yu H, Zhang X, Zhang M, Wu S, Song J, Chen T, Han M, Li S, Luo X, Zhao J, Ning Q (2020) Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019. J Clin Invest 130:2620–2629
Conti P, Ronconi G, Caraffa A, Gallenga CE, Ross R, Frydas I, Kritas SK (2020) Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and lung inflammation by coronavirus-19 (COVI-19 or SARS-CoV-2): anti-inflammatory strategies. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 34:327–331
Tang Y, Liu J, Zhang D, Xu Z, Ji J, Wen C (2020) Cytokine storm in COVID-19: the current evidence and treatment strategies. Front Immunol 11:1708
Paces J, Strizova Z, Smrz D, Cerny J (2020) COVID-19 and the immune system. Physiol Res 69:379–388
Ragab D, Salah EH, Taeimah M, Khattab R, Salem R (2020) The COVID-19 cytokine storm; what we know so far. Front Immunol 11:1446
Brodin P (2021) Immune determinants of COVID-19 disease presentation and severity. Nat Med 27:28–33
Copaescu A, Smibert O, Gibson A, Phillips EJ, Trubiano JA (2020) The role of IL-6 and other mediators in the cytokine storm associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. J Allergy Clin Immunol 146:518–534
Conti P, Caraffa A, Gallenga CE, Ross R, Kritas SK, Frydas I, Younes A, Ronconi G (2020) Coronavirus-19 (SARS-CoV-2) induces acute severe lung inflammation via IL-1 causing cytokine storm in COVID-19: a promising inhibitory strategy. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 34:1971–1975
Herold T, Jurinovic V, Arnreich C, Lipworth BJ, Hellmuth JC, von Bergwelt-Baildon M, Klein M, Weinberger T (2020) Elevated levels of IL-6 and CRP predict the need for mechanical ventilation in COVID-19. J Allergy Clin Immunol 146:128–136
Han H, Ma Q, Li C, Liu R, Zhao L, Wang W, Zhang P, Liu X, Gao G, Liu F, Jiang Y, Cheng X, Zhu C, Xia Y (2020) Profiling serum cytokines in COVID-19 patients reveals IL-6 and IL-10 are disease severity predictors. Emerg Microbes Infect 9:1123–1130
Mazzoni A, Salvati L, Maggi L, Capone M, Vanni A, Spinicci M, Mencarini J, Caporale R, Peruzzi B, Antonelli A, Trotta M, Zammarchi L, Ciani L, Gori L, Lazzeri C, Matucci A, Vultaggio A, Rossi O, Almerigogna F, Parronchi P, Fontanari P, Lavorini F, Peris A, Rossolini GM, Bartoloni A, Romagnani S, Liotta F, Annunziato F, Cosmi L (2020) Impaired immune cell cytotoxicity in severe COVID-19 is IL-6 dependent. J Clin Invest 130:4694–4703
Liu F, Li L, Xu M, Wu J, Luo D, Zhu Y, Li B, Song X, Zhou X (2020) Prognostic value of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and procalcitonin in patients with COVID-19. J Clin Virol 127:104370
Nalbandian A, Sehgal K, Gupta A, Madhavan MV, McGroder C, Stevens JS, Cook JR, Nordvig AS, Shalev D, Sehrawat TS, Ahluwalia N, Bikdeli B, Dietz D, Der-Nigoghossian C, Liyanage-Don N, Rosner GF, Bernstein EJ, Mohan S, Beckley AA, Seres DS, Choueiri TK, Uriel N, Ausiello JC, Accili D, Freedberg DE, Baldwin M, Schwartz A, Brodie D, Garcia CK, Elkind MSV, Connors JM, Bilezikian JP, Landry DW, Wan EY (2021) Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Nat Med 27:601–615
Baig AM (2021) Chronic COVID Syndrome: need for an appropriate medical terminology for long-COVID and COVID long-haulers. J Med Virol 93:2555–2556
Higgins V, Sohaei D, Diamandis EP, Prassas I (2021) COVID-19: from an acute to chronic disease? Potential long-term health consequences. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 58:297–310
Huang C, Huang L, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Gu X, Kang L, Guo L, Liu M, Zhou X, Luo J, Huang Z, Tu S, Zhao Y, Chen L, Xu D, Li Y, Li C, Peng L, Li Y, Xie W, Cui D, Shang L, Fan G, Xu J, Wang G, Wang Y, Zhong J, Wang C, Wang J, Zhang D, Cao B (2021) 6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: a cohort study. Lancet 397:220–232
Moreno-Perez O, Merino E, Leon-Ramirez JM, Andres M, Ramos JM, Renas-Jimenez J, Asensio S, Sanchez R, Ruiz-Torregrosa P, Galan I, Scholz A, Amo A, Gonzalez-dela Aleja P, Boix V, Gil J (2021) Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Incidence and risk factors: a Mediterranean cohort study. J Infect 82:378–83
Montagne A, Nation DA, Sagare AP, Barisano G, Sweeney MD, Chakhoyan A, Pachicano M, Joe E, Nelson AR, D’Orazio LM, Buennagel DP, Harrington MG, Benzinger TLS, Fagan AM, Ringman JM, Schneider LS, Morris JC, Reiman EM, Caselli RJ, Chui HC, Tcw J, Chen Y, Pa J, Conti PS, Law M, Toga AW, Zlokovic BV (2020) APOE4 leads to blood-brain barrier dysfunction predicting cognitive decline. Nature 581:71–76
Sudre CH, Murray B, Varsavsky T, Graham MS, Penfold RS, Bowyer RC, Pujol JC, Klaser K, Antonelli M, Canas LS, Molteni E, Modat M, Jorge CM, May A, Ganesh S, Davies R, Nguyen LH, Drew DA, Astley CM, Joshi AD, Merino J, Tsereteli N, Fall T, Gomez MF, Duncan EL, Menni C, Williams FMK, Franks PW, Chan AT, Wolf J, Ourselin S, Spector T, Steves CJ (2021) Attributes and predictors of long COVID. Nat Med 27:626–631
Dennis A, Wamil M, Alberts J, Oben J, Cuthbertson DJ, Wootton D, Crooks M, Gabbay M, Brady M, Hishmeh L, Attree E, Heightman M, Banerjee R, Banerjee A (2021) Multiorgan impairment in low-risk individuals with post-COVID-19 syndrome: a prospective, community-based study. BMJ Open 11:e048391
Helms J, Kremer S, Merdji H, Clere-Jehl R, Schenck M, Kummerlen C, Collange O, Boulay C, Fafi-Kremer S, Ohana M, Anheim M, Meziani F (2020) Neurologic features in severe SARS-CoV-2 infection. N Engl J Med 382:2268–2270
Fotuhi M, Mian A, Meysami S, Raji CA (2020) Neurobiology of COVID-19. J Alzheimers Dis 76:3–19
Najjar S, Najjar A, Chong DJ, Pramanik BK, Kirsch C, Kuzniecky RI, Pacia SV, Azhar S (2020) Central nervous system complications associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection: integrative concepts of pathophysiology and case reports. J Neuroinflammation 17:231
Singh AK, Bhushan B, Maurya A, Mishra G, Singh SK, Awasthi R (2020) Novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and neurodegenerative disorders. Dermatol Ther 33:e13591
Liotta EM, Batra A, Clark JR, Shlobin NA, Hoffman SC, Orban ZS, Koralnik IJ (2020) Frequent neurologic manifestations and encephalopathy-associated morbidity in Covid-19 patients. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 7:2221–2230
Koralnik IJ, Tyler KL (2020) COVID-19: a global threat to the nervous system. Ann Neurol 88:1–11
Nepal G, Rehrig JH, Shrestha GS, Shing YK, Yadav JK, Ojha R, Pokhrel G, Tu ZL, Huang DY (2020) Neurological manifestations of COVID-19: a systematic review. Crit Care 24:421
Favas TT, Dev P, Chaurasia RN, Chakravarty K, Mishra R, Joshi D, Mishra VN, Kumar A, Singh VK, Pandey M, Pathak A (2020) Neurological manifestations of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of proportions. Neurol Sci 41:3437–3470
Nazari S, Azari JA, Mirmoeeni S, Sadeghian S, Heidari ME, Sadeghian S, Assarzadegan F, Puormand SM, Ebadi H, Fathi D, Dalvand S (2021) Central nervous system manifestations in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Behav 11:e02025
Kempuraj D, Selvakumar GP, Ahmed ME, Raikwar SP, Thangavel R, Khan A, Zaheer SA, Iyer SS, Burton C, James D, Zaheer A (2020) COVID-19, mast cells, cytokine storm, psychological stress, and neuroinflammation. Neuroscientist 26:402–414
Levin SN, Venkatesh S, Nelson KE, Li Y, Aguerre I, Zhu W, Masown K, Rimmer KT, Diaconu CI, Onomichi KB, Leavitt VM, Levine LL, Strauss-Farber R, Vargas WS, Banwell B, Bar-Or A, Berger JR, Goodman AD, Longbrake EE, Oh J, Weinstock-Guttman B, Thakur KT, Edwards KR, Riley CS, Xia Z, De Jager PL (2021) Manifestations and impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in neuroinflammatory diseases. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 8:918–928
Baig AM (2020) Deleterious outcomes in long-hauler COVID-19: the effects of SARS-CoV-2 on the CNS in chronic COVID syndrome. ACS Chem Neurosci 11:4017–4020
Ongur D, Perlis R, Goff D (2020) Psychiatry and COVID-19. JAMA 324:1149–1150
Vindegaard N, Benros ME (2020) COVID-19 pandemic and mental health consequences: systematic review of the current evidence. Brain Behav Immun 89:531–542
Pfefferbaum B, North CS (2020) Mental health and the Covid-19 pandemic. N Engl J Med 383:510–512
Xiang YT, Yang Y, Li W, Zhang L, Zhang Q, Cheung T, Ng CH (2020) Timely mental health care for the 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak is urgently needed. Lancet Psychiatry 7:228–229
Gordon JA, Borja SE (2020) The COVID-19 pandemic: setting the mental health research agenda. Biol Psychiatry 88:130–131
Taquet M, Luciano S, Geddes JR, Harrison PJ (2021) Bidirectional associations between COVID-19 and psychiatric disorder: retrospective cohort studies of 62 354 COVID-19 cases in the USA. Lancet Psychiatry 8:130–140
de Erausquin GA, Snyder H, Carrillo M, Hosseini AA, Brugha TS, Seshadri S (2021) The chronic neuropsychiatric sequelae of COVID-19: the need for a prospective study of viral impact on brain functioning. Alzheimers Dement 17:1056–1065
Schirinzi T, Landi D, Liguori C (2021) COVID-19: dealing with a potential risk factor for chronic neurological disorders. J Neurol 268:1171–1178
Steardo L Jr, Steardo L, Verkhratsky A (2020) Psychiatric face of COVID-19. Transl Psychiatry 10:261
Shader RI (2020) COVID-19 and depression. Clin Ther 42:962–963
Smith CM, Komisar JR, Mourad A, Kincaid BR (2020) COVID-19-associated brief psychotic disorder. BMJ Case Rep 13:e236940
Druss BG (2020) Addressing the COVID-19 pandemic in populations with serious mental illness. JAMA Psychiat 77:891–892
Theoharides TC, Cholevas C, Polyzoidis K, Politis A (2021) Long-COVID syndrome-associated brain fog and chemofog: luteolin to the rescue. BioFactors 47:232–241
Graham EL, Clark JR, Orban ZS, Lim PH, Szymanski AL, Taylor C, DiBiase RM, Jia DT, Balabanov R, Ho SU, Batra A, Liotta EM, Koralnik IJ (2021) Persistent neurologic symptoms and cognitive dysfunction in non-hospitalized Covid-19 “long haulers.” Ann Clin Transl Neurol 8:1073–1085
Stefano GB, Buttiker P, Weissenberger S, Martin A, Ptacek R, Kream RM (2021) Editorial: the pathogenesis of long-term neuropsychiatric COVID-19 and the role of microglia, mitochondria, and persistent neuroinflammation: a hypothesis. Med Sci Monit 27:e933015
Bell ML, Catalfamo CJ, Farland LV, Ernst KC, Jacobs ET, Klimentidis YC, Jehn M, Pogreba-Brown K (2021) Post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 in a non-hospitalized cohort: results from the Arizona CoVHORT. PLoS ONE 16:e0254347
Hugon J, Msika EF, Queneau M, Farid K, Paquet C (2022) Long COVID: cognitive complaints (brain fog) and dysfunction of the cingulate cortex. J Neurol 269:44–46
Frontera JA, Yang D, Lewis A, Patel P, Medicherla C, Arena V, Fang T, Andino A, Snyder T, Madhavan M, Gratch D, Fuchs B, Dessy A, Canizares M, Jauregui R, Thomas B, Bauman K, Olivera A, Bhagat D, Sonson M, Park G, Stainman R, Sunwoo B, Talmasov D, Tamimi M, Zhu Y, Rosenthal J, Dygert L, Ristic M, Ishii H, Valdes E, Omari M, Gurin L, Huang J, Czeisler BM, Kahn DE, Zhou T, Lin J, Lord AS, Melmed K, Meropol S, Troxel AB, Petkova E, Wisniewski T, Balcer L, Morrison C, Yaghi S, Galetta S (2021) A prospective study of long-term outcomes among hospitalized COVID-19 patients with and without neurological complications. J Neurol Sci 426:117486
Dixon L, Varley J, Gontsarova A, Mallon D, Tona F, Muir D, Luqmani A, Jenkins IH, Nicholas R, Jones B, Everitt A (2020) COVID-19-related acute necrotizing encephalopathy with brain stem involvement in a patient with aplastic anemia. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm 7:e789
Boroujeni ME, Simani L, Bluyssen HAR, Samadikhah HR, Zamanlui BS, Hassani S, Akbari DN, Fathi M, Vakili K, Mahmoudiasl GR, Abbaszadeh HA, Hassani MM, Abdollahifar MA, Aliaghaei A (2021) Inflammatory response leads to neuronal death in human post-mortem cerebral cortex in patients with COVID-19. ACS Chem Neurosci 12:2143–2150
Shen WB, Logue J, Yang P, Baracco L, Elahi M, Reece EA, Wang B, Li L, Blanchard TG, Han Z, Frieman MB, Rissman RA, Yang P (2022) SARS-CoV-2 invades cognitive centers of the brain and induces Alzheimer’s-like neuropathology. 2022.01.31.478476
Radhakrishnan RK, Kandasamy M (2022) SARS-CoV-2-mediated neuropathogenesis, deterioration of hippocampal neurogenesis and dementia. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen 37:15333175221078418
Troubat R, Barone P, Leman S, Desmidt T, Cressant A, Atanasova B, Brizard B, El HW, Surget A, Belzung C, Camus V (2021) Neuroinflammation and depression: a review. Eur J Neurosci 53:151–171
Brites D, Fernandes A (2015) Neuroinflammation and depression: microglia activation, extracellular microvesicles and microRNA dysregulation. Front Cell Neurosci 9:476
Karnik M, Beeraka NM, Uthaiah CA, Nataraj SM, Bettadapura ADS, Aliev G, Madhunapantula SV (2021) A review on SARS-CoV-2-induced neuroinflammation, neurodevelopmental complications, and recent updates on the vaccine development. Mol Neurobiol 1–29
Liberman AC, Trias E, da Silva CL, Trindade P, Dos Santos PM, Refojo D, Hedin-Pereira C, Serfaty CA (2018) Neuroimmune and inflammatory signals in complex disorders of the central nervous system. NeuroImmunoModulation 25:246–270
Welcome MO, Mastorakis NE (2021) Neuropathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019: neuroinflammation and blood brain barrier disruption are critical pathophysiological processes that contribute to the clinical symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Inflammopharmacology 29:939–963
Lee MH, Perl DP, Nair G, Li W, Maric D, Murray H, Dodd SJ, Koretsky AP, Watts JA, Cheung V, Masliah E, Horkayne-Szakaly I, Jones R, Stram MN, Moncur J, Hefti M, Folkerth RD, Nath A (2021) Microvascular injury in the brains of patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med 384:481–483
Magro CM, Mulvey J, Kubiak J, Mikhail S, Suster D, Crowson AN, Laurence J, Nuovo G (2021) Severe COVID-19: a multifaceted viral vasculopathy syndrome. Ann Diagn Pathol 50:151645
Bodnar B, Patel K, Ho W, Luo JJ, Hu W (2021) Cellular mechanisms underlying neurological/neuropsychiatric manifestations of COVID-19. J Med Virol 93:1983–1998
Ng JH, Sun A, Je HS, Tan EK (2023) Unravelling pathophysiology of neurological and psychiatric complications of COVID-19 using brain organoids. Neuroscientist 29:30–40
Tremblay ME, Madore C, Bordeleau M, Tian L, Verkhratsky A (2020) Neuropathobiology of COVID-19: the role for glia. Front Cell Neurosci 14:592214
McMahon CL, Staples H, Gazi M, Carrion R, Hsieh J (2021) SARS-CoV-2 targets glial cells in human cortical organoids. Stem Cell Reports 16:1156–1164
Harvey WT, Carabelli AM, Jackson B, Gupta RK, Thomson EC, Harrison EM, Ludden C, Reeve R, Rambaut A, Peacock SJ, Robertson DL (2021) SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nat Rev Microbiol 19:409–424
Hickman S, Izzy S, Sen P, Morsett L, El KJ (2018) Microglia in neurodegeneration. Nat Neurosci 21:1359–1369
Ginhoux F, Greter M, Leboeuf M, Nandi S, See P, Gokhan S, Mehler MF, Conway SJ, Ng LG, Stanley ER, Samokhvalov IM, Merad M (2010) Fate mapping analysis reveals that adult microglia derive from primitive macrophages. Science 330:841–845
Gomez PE, Schulz C, Geissmann F (2013) Development and homeostasis of “resident” myeloid cells: the case of the microglia. Glia 61:112–120
Bennett ML, Song H, Ming GL (2021) Microglia modulate neurodevelopment in human neuroimmune organoids. Cell Stem Cell 28:2035–2036
Colonna M, Butovsky O (2017) Microglia function in the central nervous system during health and neurodegeneration. Annu Rev Immunol 35:441–468
Vargas G, Medeiros Geraldo LH, Gedeao SN, Viana PM, Regina Souza LF, Carvalho Alcantara GF (2020) Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and glial cells: insights and perspectives. Brain Behav Immun Health 7:100127
Murta V, Villarreal A, Ramos AJ (2020) Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 impact on the central nervous system: are astrocytes and microglia main players or merely bystanders? ASN Neuro 12:1759091420954960
Subhramanyam CS, Wang C, Hu Q, Dheen ST (2019) Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Semin Cell Dev Biol 94:112–120
Voet S, Prinz M, van Loo G (2019) Microglia in central nervous system inflammation and multiple sclerosis pathology. Trends Mol Med 25:112–23
Perry VH, Nicoll JA, Holmes C (2010) Microglia in neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol 6:193–201
Ransohoff RM (2016) How neuroinflammation contributes to neurodegeneration. Science 353:777–783
Jack CS, Arbour N, Manusow J, Montgrain V, Blain M, McCrea E, Shapiro A, Antel JP (2005) TLR signaling tailors innate immune responses in human microglia and astrocytes. J Immunol 175:4320–4330
Olajide OA, Iwuanyanwu VU, Adegbola OD, Al-Hindawi AA (2022) SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein S1 induces neuroinflammation in BV-2 microglia. Mol Neurobiol 59:445–458
Onofrio L, Caraglia M, Facchini G, Margherita V, Placido S, Buonerba C (2020) Toll-like receptors and COVID-19: a two-faced story with an exciting ending. Future Sci OA 6:FSO605
Sariol A, Perlman S (2021) SARS-CoV-2 takes its Toll. Nat Immunol 22:801–802
Singh H, Singh A, Khan AA, Gupta V (2021) Immune mediating molecules and pathogenesis of COVID-19-associated neurological disease. Microb Pathog 158:105023
Espindola OM, Gomes YCP, Brandao CO, Torres RC, Siqueira M, Soares CN, Lima MASD, Leite ACCB, Venturotti CO, Carvalho AJC, Torezani G, Araujo AQC, Silva MTT (2021) Inflammatory cytokine patterns associated with neurological diseases in coronavirus disease 2019. Ann Neurol 89:1041–1045
Oka Y, Ueda A, Nakagawa T, Kikuchi Y, Inoue D, Marumo S, Matsumoto S (2021) SARS-CoV-2-related progressive brain white matter lesion associated with an increased cerebrospinal fluid level of IL-6. Intern Med 60:3167–3170
Kaushik D, Bhandari R, Kuhad A (2021) TLR4 as a therapeutic target for respiratory and neurological complications of SARS-CoV-2. Expert Opin Ther Targets 25:491–508
Aboudounya MM, Heads RJ (2021) COVID-19 and Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4): SARS-CoV-2 may bind and activate TLR4 to increase ACE2 expression, facilitating entry and causing hyperinflammation. Mediators Inflamm 2021:8874339
Jeong GU, Lyu J, Kim KD, Chung YC, Yoon GY, Lee S, Hwang I, Shin WH, Ko J, Lee JY, Kwon YC (2022) SARS-CoV-2 infection of microglia elicits proinflammatory activation and apoptotic cell death. Microbiol Spectr 10:e0109122
Ihim SA, Abubakar SD, Zian Z, Sasaki T, Saffarioun M, Maleknia S, Azizi G (2022) Interleukin-18 cytokine in immunity, inflammation, and autoimmunity: biological role in induction, regulation, and treatment. Front Immunol 13:919973
Bauman ML, Kemper TL (2003) The neuropathology of the autism spectrum disorders: what have we learned? Novartis Found Symp 251:112–122
Bliss-Moreau E, Moadab G, Santistevan A, Amaral DG (2017) The effects of neonatal amygdala or hippocampus lesions on adult social behavior. Behav Brain Res 322:123–137
Impellizzeri D, Di PR, Cordaro M, Gugliandolo E, Casili G, Morittu VM, Britti D, Esposito E, Cuzzocrea S (2016) Adelmidrol, a palmitoylethanolamide analogue, as a new pharmacological treatment for the management of acute and chronic inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol 119:27–41
Lee JK, Kim SH, Lewis EC, Azam T, Reznikov LL, Dinarello CA (2004) Differences in signaling pathways by IL-1beta and IL-18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:8815–8820
Goswami D, Anuradha U, Angati A, Kumari N, Singh RK (2022) Pharmacological and pathological relevance of S100 proteins in neurological disorders. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527322666221128160653
Michetti F, D’Ambrosi N, Toesca A, Puglisi MA, Serrano A, Marchese E, Corvino V, Geloso MC (2019) The S100B story: from biomarker to active factor in neural injury. J Neurochem 148:168–187
Oris C, Kahouadji S, Durif J, Bouvier D, Sapin V (2023) S100B, actor and biomarker of mild traumatic brain injury. Int J Mol Sci 24:6602
Hopman H, Santing AL, Foks A, Verheul J, der Linden Mv, den Brand Lv, Jellema K (2023) Biomarker S100B in plasma a screening tool for mild traumatic brain injury in an emergency department. Brain Inj 37:47–53
Angelopoulou E, Paudel YN, Piperi C (2021) Emerging role of S100B protein implication in Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci 78:1445–1453
Zheng Z, Zheng P, Zou X (2021) Peripheral blood S100B levels in autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Autism Dev Disord 51:2569–2577
Mete E, Sabirli R, Goren T, Turkcuer I, Kurt O, Koseler A (2021) Association between S100b levels and COVID-19 pneumonia: a case control study. In Vivo 35:2923–2928
Aceti A, Margarucci LM, Scaramucci E, Orsini M, Salerno G, Di SG, Gianfranceschi G, Di LR, Valeriani F, Ria F, Simmaco M, Parnigotto PP, Vitali M, Romano SV, Michetti F (2020) Serum S100B protein as a marker of severity in Covid-19 patients. Sci Rep 10:18665
Zhou S, Zhu W, Zhang Y, Pan S, Bao J (2018) S100B promotes microglia M1 polarization and migration to aggravate cerebral ischemia. Inflamm Res 67:937–949
Xu J, Wang H, Won SJ, Basu J, Kapfhamer D, Swanson RA (2016) Microglial activation induced by the alarmin S100B is regulated by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1. Glia 64:1869–1878
Finsterer J, Scorza FA (2021) Clinical and pathophysiologic spectrum of neuro-COVID. Mol Neurobiol 58:3787–3791
Davies DA, Adlimoghaddam A, Albensi BC (2021) The effect of COVID-19 on NF-kappaB and neurological manifestations of disease. Mol Neurobiol 58:4178–4187
Norouzi M, Miar P, Norouzi S, Nikpour P (2021) Nervous system involvement in COVID-19: a review of the current knowledge. Mol Neurobiol 58:3561–3574
Dewanjee S, Vallamkondu J, Kalra RS, Puvvada N, Kandimalla R, Reddy PH (2021) Emerging COVID-19 neurological manifestations: present outlook and potential neurological challenges in COVID-19 pandemic. Mol Neurobiol 58:4694–4715
Wohleb ES (2016) Neuron-microglia interactions in mental health disorders: “For Better, and For Worse.” Front Immunol 7:544
de Goncalves AE, Simoncicova E, Carrier M, Vecchiarelli HA, Robert ME, Tremblay ME (2021) Microglia fighting for neurological and mental health: on the central nervous system frontline of COVID-19 pandemic. Front Cell Neurosci 15:647378
Rahimian R, Wakid M, O’Leary LA, Mechawar N (2021) The emerging tale of microglia in psychiatric disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 131:1–29
Monje M, Iwasaki A (2022) The neurobiology of long COVID. Neuron 110:3484–3496
McQuaid C, Brady M, Deane R (2021) SARS-CoV-2: is there neuroinvasion? Fluids Barriers CNS 18:32
Veleri S (2022) Neurotropism of SARS-CoV-2 and neurological diseases of the central nervous system in COVID-19 patients. Exp Brain Res 240:9–25
Zhang L, Zhou L, Bao L, Liu J, Zhu H, Lv Q, Liu R, Chen W, Tong W, Wei Q, Xu Y, Deng W, Gao H, Xue J, Song Z, Yu P, Han Y, Zhang Y, Sun X, Yu X, Qin C (2021) SARS-CoV-2 crosses the blood-brain barrier accompanied with basement membrane disruption without tight junctions alteration. Signal Transduct Target Ther 6:337
Buzhdygan TP, DeOre BJ, Baldwin-Leclair A, Bullock TA, McGary HM, Khan JA, Razmpour R, Hale JF, Galie PA, Potula R, Andrews AM, Ramirez SH (2020) The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein alters barrier function in 2D static and 3D microfluidic in-vitro models of the human blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol Dis 146:105131
Rhea EM, Logsdon AF, Hansen KM, Williams LM, Reed MJ, Baumann KK, Holden SJ, Raber J, Banks WA, Erickson MA (2021) The S1 protein of SARS-CoV-2 crosses the blood-brain barrier in mice. Nat Neurosci 24:368–378
Meinhardt J, Radke J, Dittmayer C, Franz J, Thomas C, Mothes R, Laue M, Schneider J, Brunink S, Greuel S, Lehmann M, Hassan O, Aschman T, Schumann E, Chua RL, Conrad C, Eils R, Stenzel W, Windgassen M, Rossler L, Goebel HH, Gelderblom HR, Martin H, Nitsche A, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ, Hakroush S, Winkler MS, Tampe B, Scheibe F, Kortvelyessy P, Reinhold D, Siegmund B, Kuhl AA, Elezkurtaj S, Horst D, Oesterhelweg L, Tsokos M, Ingold-Heppner B, Stadelmann C, Drosten C, Corman VM, Radbruch H, Heppner FL (2021) Olfactory transmucosal SARS-CoV-2 invasion as a port of central nervous system entry in individuals with COVID-19. Nat Neurosci 24:168–175
Jiao L, Yang Y, Yu W, Zhao Y, Long H, Gao J, Ding K, Ma C, Li J, Zhao S, Wang H, Li H, Yang M, Xu J, Wang J, Yang J, Kuang D, Luo F, Qian X, Xu L, Yin B, Liu W, Liu H, Lu S, Peng X (2021) The olfactory route is a potential way for SARS-CoV-2 to invade the central nervous system of rhesus monkeys. Signal Transduct Target Ther 6:169
Khaddaj-Mallat R, Aldib N, Bernard M, Paquette AS, Ferreira A, Lecordier S, Saghatelyan A, Flamand L, ElAli A (2021) SARS-CoV-2 deregulates the vascular and immune functions of brain pericytes via spike protein. Neurobiol Dis 161:105561
Theoharides TC (2022) Could SARS-CoV-2 spike protein be responsible for long-COVID syndrome? Mol Neurobiol 13:1–12
Paidas MJ, Cosio DS, Ali S, Kenyon NS, Jayakumar AR (2022) Long-term sequelae of COVID-19 in experimental mice. Mol Neurobiol 59:5970–5986
Funding
The authors declare that this work was supported by Anonymous Donation to Eirini (Irene) Tsilioni and Theoharis C. Theoharides.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Eirini (Irene) Tsilioni. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Eirini (Irene) Tsilioni and Theoharis C. Theoharides. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
Not applicable.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

Supplementary Figure 1
SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein stimulates secretion of proinflammatory mediators from human microglia in a dose-dependent manner. SV40 microglia (1.0 x 105 cells) were stimulated with recombinant SARS-CoV-2 full-length S protein (1-10 ng/mL) (supplied from GeneTex) for 24 h. Secretion of IL-1β (A) and CXCL8 (C) was determined by specific ELISAs. LPS (10 ng/mL) and NT (10 nM) were used as “positive” controls. All conditions were performed in triplicate for each dataset and repeated 3 times (n=3). Significance of comparisons is denoted by P < 0.05.(PNG 406 kb)

Supplementary Figure 2
SARS-CoV-2 S and RBD stimulate a differential secretion of pro-inflammatory mediators from human microglia. SV40 microglia (1.0 x 105 cells) were stimulated with recombinant SARS-CoV-2 full-length S protein (1-10 ng/mL) and RBD (1-10 ng/mL) (supplied from GeneTex) for 24 h. Secretion of IL-1β (A), CXCL8 (B), IL-6 (C), MMP9 (D), TNF-α (E), S100B (F) and IL-18 (G) was determined by specific ELISAs. LPS (10 ng/mL) and NT (10 nM) were used as “positive” controls. All conditions were performed in triplicate for each dataset and repeated 3 times (n=3). Significance of comparisons is denoted by P < 0.05. (PNG 423 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tsilioni, I., Theoharides, T.C. Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Its Receptor Binding Domain Stimulate Release of Different Pro-Inflammatory Mediators via Activation of Distinct Receptors on Human Microglia Cells. Mol Neurobiol 60, 6704–6714 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03493-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03493-7