Abstract
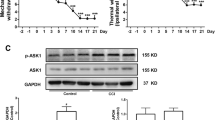
Neuropathic pain is a disease that has become one of the major public health problems and a global burden. Nox4-induced oxidative stress can lead to ferroptosis and neuropathic pain. Methyl ferulic acid (MFA) can inhibit the Nox4-induced oxidative stress. This study aimed to estimate whether methyl ferulic acid alleviates neuropathic pain by inhibiting the expression of Nox4 and its induction of ferroptosis. Adult male Sprague–Dawley rats were subjected to spared nerve injury (SNI) model to induce neuropathic pain. After the establishment of the model, methyl ferulic acid was given 14 days by gavage. Nox4 overexpression was induced by microinjection of the AAV-Nox4 vector. All groups measured paw mechanical withdrawal threshold (PMWT), paw thermal withdrawal latency (PTWL), and paw withdrawal cold duration (PWCD). The expression of Nox4, ACSL4, GPX4, and ROS was investigated by Western blot and immunofluorescence staining. The changes in iron content were detected by a tissue iron kit. The morphological changes in mitochondria were observed by transmission electron microscopy. In the SNI group, the paw mechanical withdrawal threshold, the paw withdrawal cold duration decreased, the paw thermal withdrawal latency did not change, the Nox4, ACSL4, ROS, and iron content increased, the GPX4 decreased, and the number of abnormal mitochondria increased. Methyl ferulic acid can increase PMWT and PWCD but does not affect PTWL. Methyl ferulic acid can inhibit Nox4 protein expression. Meanwhile, ferroptosis-related protein ACSL4 expression was decreased, GPX4 expression was increased, ROS, iron content and abnormal mitochondrial number were decreased. By overexpressing Nox4, the PMWT, PWCD, and ferroptosis of rats were more severe than those of the SNI group, but they could be reversed after treatment with methyl ferulic acid. In conclusion, methyl ferulic acid can alleviate neuropathic pain, which is related to Nox4-induced ferroptosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Treede RD, Jensen TS, Campbell JN, Cruccu G, Dostrovsky JO, Griffin JW, Hansson P, Hughes R et al (2008) Neuropathic pain: redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology 70(18):1630–1635. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000282763.29778.59
Bouhassira D (2019) Neuropathic pain: definition, assessment and epidemiology. Rev Neurol (Paris) 175(1–2):16–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurol.2018.09.016
Cherif F, Zouari HG, Cherif W, Hadded M, Cheour M, Damak R (2020) Depression Prevalence in neuropathic pain and its impact on the quality of life. Pain Res Manag 2020:7408508. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/7408508
Colloca L, Ludman T, Bouhassira D, Baron R, Dickenson AH, Yarnitsky D, Freeman R, Truini A et al (2017) Neuropathic pain. Nat Rev Dis Primers 3:17002. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2017.2
Alles SRA, Smith PA (2018) Etiology and pharmacology of neuropathic pain. Pharmacol Rev 70(2):315–347. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.117.014399
Guo Y, Du J, Xiao C, Xiang P, Deng Y, Hei Z, Li X (2021) Inhibition of ferroptosis-like cell death attenuates neuropathic pain reactions induced by peripheral nerve injury in rats. Eur J Pain 25(6):1227–1240. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejp.1737
Jia S, Chen G, Liang Y, Liang X, Meng C (2021) GCH1-regulated miRNAs are potential targets for microglial activation in neuropathic pain. Biosci Rep 41(9). 10.1042/bsr20210051
Tang Y, Liu C, Zhu T, Chen H, Sun Y, Zhang X, Zhao Q, Wu J et al (2022) Transcriptome profiles of IncRNA and mRNA highlight the role of ferroptosis in chronic neuropathic pain with memory impairment. Front Cell Dev Biol 10:843297. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2022.843297
Zhang X, Song T, Zhao M, Tao X, Zhang B, Sun C, Wang P, Wang K et al (2022) Sirtuin 2 alleviates chronic neuropathic pain by suppressing ferroptosis in rats. Front Pharmacol 13:827016. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.827016
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ et al (2012) Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 149(5):1060–1072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
Chen GH, Song CC, Pantopoulos K, Wei XL, Zheng H, Luo Z (2022) Mitochondrial oxidative stress mediated Fe-induced ferroptosis via the NRF2-ARE pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 180:95–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.01.012
Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME, Shimada K, Skouta R, Viswanathan VS, Cheah JH, Clemons PA et al (2014) Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell 156(1–2):317–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.010
Doll S, Proneth B, Tyurina YY, Panzilius E, Kobayashi S, Ingold I, Irmler M, Beckers J et al (2017) ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat Chem Biol 13(1):91–98. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2239
Wang H, Huo X, Han C, Ning J, Chen H, Li B, Liu J, Ma W et al (2021) Ferroptosis is involved in the development of neuropathic pain and allodynia. Mol Cell Biochem 476(8):3149–3161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-021-04138-w
Bedard K, Krause KH (2007) The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 87(1):245–313. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00044.2005
Serrander L, Cartier L, Bedard K, Banfi B, Lardy B, Plastre O, Sienkiewicz A, Fórró L et al (2007) NOX4 activity is determined by mRNA levels and reveals a unique pattern of ROS generation. Biochem J 406(1):105–114. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20061903
Park MW, Cha HW, Kim J, Kim JH, Yang H, Yoon S, Boonpraman N, Yi SS et al (2021) NOX4 promotes ferroptosis of astrocytes by oxidative stress-induced lipid peroxidation via the impairment of mitochondrial metabolism in Alzheimer’s diseases. Redox Biol 41:101947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2021.101947
Yang WH, Ding CC, Sun T, Rupprecht G, Lin CC, Hsu D, Chi JT (2019) The hippo pathway effector TAZ regulates ferroptosis in renal cell carcinoma. Cell Rep 28(10):2501-2508.e2504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.107
Miao F, Wang R, Cui G, Li X, Wang T, Li X (2019) Engagement of microRNA-155 in exaggerated oxidative stress signal and TRPA1 in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord and neuropathic pain during chemotherapeutic oxaliplatin. Neurotox Res 36(4):712–723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-019-00039-5
Cheng Q, Li C, Yang CF, Zhong YJ, Wu D, Shi L, Chen L, Li YW et al (2019) Methyl ferulic acid attenuates liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell activation through the TGF-β1/Smad and NOX4/ROS pathways. Chem Biol Interact 299:131–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2018.12.006
Cheng Q, Li YW, Yang CF, Zhong YJ, He H, Zhu FC, Li L (2018) Methyl ferulic acid attenuates ethanol-induced hepatic steatosis by regulating AMPK and FoxO1 pathways in rats and L-02 cells. Chem Biol Interact 291:180–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2018.06.028
Li C, Li L, Yang CF, Zhong YJ, Wu D, Shi L, Chen L, Li YW (2017) Hepatoprotective effects of Methyl ferulic acid on alcohol-induced liver oxidative injury in mice by inhibiting the NOX4/ROS-MAPK pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 493(1):277–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.09.030
Li L, Zhong Y, Ma Z, Yang C, Wei H, Chen L, Li C, Wu D et al (2018) Methyl ferulic acid exerts anti-apoptotic effects on L-02 cells via the ROS-mediated signaling pathway. Int J Oncol 53(1):225–236. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2018.4379
Xu ZZ, Chen QY, Deng SY, Zhang M, Tan CY, Yang W, Ma KT, Li L et al (2019) 17β-estradiol attenuates neuropathic pain caused by spared nerve injury by upregulating CIC-3 in the dorsal root ganglion of ovariectomized rats. Front Neurosci 13:1205. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.01205
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53(1):55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0270(94)90144-9
Xu X, Fu S, Shi X, Liu R (2019) Microglial BDNF, PI3K, and p-ERK in the spinal cord are suppressed by pulsed radiofrequency on dorsal root ganglion to ease SNI-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Pain Res Manag 2019:5948686. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5948686
Brenner DS, Golden JP, Vogt SK, Gereau RWt (2015) A simple and inexpensive method for determining cold sensitivity and adaptation in mice. J Vis Exp(97). https://doi.org/10.3791/52640
Xiang H, Liu Z, Wang F, Xu H, Roberts C, Fischer G, Stucky C, Caron D et al (2017) Primary sensory neuron-specific interference of TRPV1 signaling by AAV-encoded TRPV1 peptide aptamer attenuates neuropathic pain. Mol Pain 13:1744806917717040. https://doi.org/10.1177/1744806917717040
Shinu P, Morsy MA, Nair AB, Mouslem AKA, Venugopala KN, Goyal M, Bansal M, Jacob S et al. (2022) Novel Therapies for the treatment of neuropathic pain: potential and pitfalls. J Clin Med 11(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113002
Roch G, Batallé G, Bai X, Pouso-Vázquez E, Rodríguez L, Pol O (2022) The beneficial effects of heme oxygenase 1 and hydrogen sulfide activation in the management of neuropathic pain, anxiety- and depressive-like effects of paclitaxel in mice. Antioxidants (Basel) 11(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11010122
Zhao X, Liu L, Wang Y, Wang G, Zhao Y, Zhang Y (2019) Electroacupuncture enhances antioxidative signal pathway and attenuates neuropathic pain induced by chemotherapeutic paclitaxel. Physiol Res 68(3):501–510. https://doi.org/10.33549/physiolres.934084
Yang C, Li L, Ma Z, Zhong Y, Pang W, Xiong M, Fang S, Li Y (2018) Hepatoprotective effect of methyl ferulic acid against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in rats. Exp Ther Med 15(3):2228–2238. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.5678
Decosterd I, Woolf CJ (2000) Spared nerve injury: an animal model of persistent peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain 87(2):149–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3959(00)00276-1
Xu Z, Xie W, Feng Y, Wang Y, Li X, Liu J, Xiong Y, He Y et al (2022) Positive interaction between GPER and β-alanine in the dorsal root ganglion uncovers potential mechanisms: mediating continuous neuronal sensitization and neuroinflammation responses in neuropathic pain. J Neuroinflammation 19(1):164. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-022-02524-9
Fu CN, Wei H, Gao WS, Song SS, Yue SW, Qu YJ (2021) Obesity increases neuropathic pain via the AMPK-ERK-NOX4 pathway in rats. Aging (Albany NY) 13(14):18606–18619. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.203305
Li D, Song C, Zhang J, Zhao X (2022) ROS and iron homeostasis dependent ferroptosis play a vital role in 5-Fluorouracil induced cardiotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. Toxicology 468:153113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2022.153113
Liu Y, Li L, Yang Z, Wen D, Hu Z (2022) Circular RNA circACAP2 suppresses ferroptosis of cervical cancer during malignant progression by miR-193a-5p/GPX4. J Oncol 2022:5228874. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5228874
Poursaitidis I, Wang X, Crighton T, Labuschagne C, Mason D, Cramer SL, Triplett K, Roy R et al (2017) Oncogene-selective sensitivity to synchronous cell death following modulation of the amino acid nutrient cystine. Cell Rep 18(11):2547–2556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.02.054
Dong G, Huang X, Chen R, Wu L, Jiang S, Chen S (2022) Increased PD-L1 restricts liver injury in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022:5954437. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5954437
Acknowledgements
We thank American Journal Experts (www.aje.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82160235) and the Scientific Research Project of Shihezi University (No. ZZZC202068A).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J-W Y, R-X W, and Z-G D contributed to the study design and revised the manuscript. T-L L, W-Q Q, and L J conducted the experiment and collected and analyzed the data. K-T M, J-Q S, J-T Y, and Y-J Z provided assistance in performing the experiments. T-L L and R-X W wrote the manuscript. All authors gave final approval of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All protocols complied with the Animal Research Committee by Shihezi University (Protocol A2021-074–01).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T., Wang, R., Qi, W. et al. Methyl Ferulic Acid Alleviates Neuropathic Pain by Inhibiting Nox4-induced Ferroptosis in Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurons in Rats. Mol Neurobiol 60, 3175–3189 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03270-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-023-03270-6