Abstract
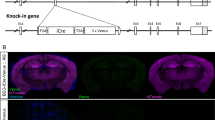
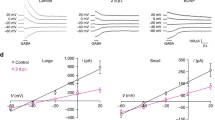
Chronic neuropathic pain often leads to cognitive impairment, but the exact mechanism remains unclear. Gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptors (GABAARs) are the major inhibitory receptors in the brain, of which the α5-containing GABAARs (GABAARs-α5) are implicated in a range of neuropsychiatric disorders with cognitive deficits. However, whether GABAARs-α5 are involved in chronic neuropathic pain-related cognitive impairment remains unknown. In this study, the rats with chronic neuropathic pain induced by right sciatic nerve ligation injury (SNI) exhibited cognitive impairment with declined spontaneous alternation in Y-maze test and discrimination index in novel object recognition test. The GABAARs-α5 expressing on parvalbumin and somatostatin interneurons increased remarkably in hippocampus, resulting in decreased mean frequency of spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Significantly, antagonizing the GABAARs-α5 by L655708 rescued weakened inhibitory synaptic transmission and cognitive impairment induced by chronic neuropathic pain. Taken together, these data suggest that the GABAARs-α5 play a crucial role in chronic neuropathic pain-induced cognitive impairment by weakening inhibitory synaptic transmission, which may provide insights into the pharmacologic treatment of chronic neuropathic pain-related cognitive impairment.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used during the present study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Murray CJ, Lopez AD (2013) Measuring the global burden of disease. N Engl J Med 369(5):448–457. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1201534
Moriarty O, Ruane N, O’Gorman D, Maharaj CH, Mitchell C, Sarma KM, Finn DP, McGuire BE (2017) Cognitive impairment in patients with chronic neuropathic or radicular pain: an interaction of pain and age. Front Behav Neurosci 11:100. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2017.00100
Bushnell MC, Ceko M, Low LA (2013) Cognitive and emotional control of pain and its disruption in chronic pain. Nat Rev Neurosci 14(7):502–511. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3516
Mao M, Zhou Z, Sun M, Wang C, Sun J (2021) The dysfunction of parvalbumin interneurons mediated by microglia contributes to cognitive impairment induced by lipopolysaccharide challenge. Neurosci Lett 762:136133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2021.136133
Engin E, Benham RS, Rudolph U (2018) An emerging circuit pharmacology of GABA(A) receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 39(8):710–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2018.04.003
Udakis M, Pedrosa V, Chamberlain SEL, Clopath C, Mellor JR (2020) Interneuron-specific plasticity at parvalbumin and somatostatin inhibitory synapses onto CA1 pyramidal neurons shapes hippocampal output. Nat Commun 11(1):4395. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18074-8
Palop JJ, Mucke L (2016) Network abnormalities and interneuron dysfunction in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 17(12):777–792. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2016.141
Dienel SJ, Lewis DA (2019) Alterations in cortical interneurons and cognitive function in schizophrenia. Neurobiol Dis. 131:104208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2018.06.020
Sakimoto Y, Oo PM, Goshima M, Kanehisa I, Tsukada Y, Mitsushima D (2021) Significance of GABA(A) receptor for cognitive function and hippocampal pathology. Int J Molec Sci 22(22). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212456.
Mohamad FH, Has ATC (2019) The α5-containing GABA(A) receptors—a brief summary. J Molec Neurosci : MN 67(2):343–351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1246-4
Saari TI, Uusi-Oukari M, Ahonen J, Olkkola KT (2011) Enhancement of GABAergic activity: neuropharmacological effects of benzodiazepines and therapeutic use in anesthesiology. Pharmacol Rev 63(1):243–267. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.110.002717
Khodaei S, Avramescu S, Wang DS, Sheng H, Chan NK, Lecker I, Fernandez-Escobar A, Lei G, Dewar MB, Whissell PD, Baker AJ, Orser BA (2020) Inhibiting α5 subunit-Containing γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors attenuates cognitive deficits after traumatic brain injury. Crit Care Med 48(4):533–544. https://doi.org/10.1097/ccm.0000000000004161
Bugay V, McCoy AM, Lodge DJ, Brenner R, Frazer A, Carreno FR (2020) Mechanisms associated with the antidepressant-like effects of L-655,708. Neuropsychopharmacology 45(13):2289–2298. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-020-0772-2
Zhao ZF, Du L, Gao T, Bao L, Luo Y, Yin YQ, Wang YA (2019) Inhibition of α5 GABAA receptors has preventive but not therapeutic effects on isoflurane-induced memory impairment in aged rats. Neural Regen Res 14(6):1029–1036. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.250621
Decosterd I, Woolf CJ (2000) Spared nerve injury: an animal model of persistent peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain 87(2):149–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3959(00)00276-1
He WM, Ying-Fu L, Wang H, Peng YP (2019) Delayed treatment of α5 GABAA receptor inverse agonist improves functional recovery by enhancing neurogenesis after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat MCAO model. Sci Rep 9(1):2287. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-38750-0
Su Y, Liu J, Yu B, Ba R, Zhao C (2019) Brpf1 Haploinsufficiency impairs dendritic arborization and spine formation, leading to cognitive deficits. Front Cell Neurosci. 13:249. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00249
Su M, Liu J, Yu B, Zhou K, Sun C, Yang M, Zhao C (2021) Loss of Calretinin in L5a impairs the formation of the barrel cortex leading to abnormal whisker-mediated behaviors. Mol Brain 14(1):67. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-021-00775-w
Oaklander AL (2008) Mechanisms of pain and itch caused by herpes zoster (shingles). J Pain 9(1 Suppl 1):S10–S18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2007.10.003
Baron R, Förster M, Binder A (2012) Subgrouping of patients with neuropathic pain according to pain-related sensory abnormalities: a first step to a stratified treatment approach. Lancet Neurol 11(11):999–1005. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(12)70189-8
Zhang GF, Zhou ZQ, Guo J, Gu HW, Su MZ, Yu BC, Zhou F, Han BY, Jia M, Ji MH, Tao YX, Zhao CJ, Yang JJ (2021) Histone deacetylase 3 in hippocampus contributes to memory impairment after chronic constriction injury of sciatic nerve in mice. Pain 162(2):382–395. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002056
Huang Y, Brosch M (2016) Neuronal activity in primate prefrontal cortex related to goal-directed behavior during auditory working memory tasks. Brain Res 1640(Pt B):314–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2016.02.010
Xia SH, Hu SW, Ge DG, Liu D, Wang D, Zhang S, Zhang Q, Yuan L, Li YQ, Yang JX, Wu P, Zhang H, Han MH, Ding HL, Cao JL (2020) Chronic pain impairs memory formation via disruption of neurogenesis mediated by mesohippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling. Biol Psychiat 88(8):597–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2020.02.013
Boccella S, Marabese I, Iannotta M, Belardo C, Neugebauer V, Mazzitelli M, Pieretti G, Maione S, Palazzo E (2019) Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 and 8 modulate the ameliorative effect of ultramicronized palmitoylethanolamide on cognitive decline associated with neuropathic pain. Int J Molec Sci 20(7). doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071757.
Manzo MA, Wang DS, Li WW, Pinguelo A, Popa MO, Khodaei S, Atack JR, Ross RA, Orser BA (2021) Inhibition of a tonic inhibitory conductance in mouse hippocampal neurones by negative allosteric modulators of α5 subunit-containing γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors: implications for treating cognitive deficits. Br J Anaesth 126(3):674–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bja.2020.11.032
Zhang W, Xiong BR, Zhang LQ, Huang X, Zhou WC, Zou Q, Manyande A, Wang J, Tian XB, Tian YK (2020) Disruption of the GABAergic system contributes to the development of perioperative neurocognitive disorders after anesthesia and surgery in aged mice. CNS Neurosci Ther 26(9):913–924. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.13388
Clarkson AN, Huang BS, Macisaac SE, Mody I, Carmichael ST (2010) Reducing excessive GABA-mediated tonic inhibition promotes functional recovery after stroke. Nature 468(7321):305–309. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09511
Yuan C, Gao A, Xu Q, Zhang B, Xue R, Dou Y, Yu C (2021) A multi-dosing regimen to enhance the spatial memory of normal rats with α5-containing GABA(A) receptor negative allosteric modulator L-655,708. Psychopharmacology 238(12):3375–3389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-021-05951-3
Bravo-Hernández M, Corleto JA, Barragán-Iglesias P, González-Ramírez R, Pineda-Farias JB, Felix R, Calcutt NA, Delgado-Lezama R, Marsala M, Granados-Soto V (2016) The α5 subunit containing GABAA receptors contribute to chronic pain. Pain 157(3):613–626. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000410
Delgado-Lezama R, Bravo-Hernández M, Franco-Enzástiga Ú, De la Luz-Cuellar YE, Alvarado-Cervantes NS, Raya-Tafolla G, Martínez-Zaldivar LA, Vargas-Parada A, Rodríguez-Palma EJ, Vidal-Cantú GC, Guzmán-Priego CG, Torres-López JE, Murbartián J, Felix R, Granados-Soto V (2021) The role of spinal cord extrasynaptic α(5) GABA(A) receptors in chronic pain. Physiol Rep 9(16):e14984. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.14984
Saab BJ, Maclean AJ, Kanisek M, Zurek AA, Martin LJ, Roder JC, Orser BA (2010) Short-term memory impairment after isoflurane in mice is prevented by the α5 γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor inverse agonist L-655,708. Anesthesiology 113(5):1061–1071. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181f56228
Collinson N, Kuenzi FM, Jarolimek W, Maubach KA, Cothliff R, Sur C, Smith A, Otu FM, Howell O, Atack JR, McKernan RM, Seabrook GR, Dawson GR, Whiting PJ, Rosahl TW (2002) Enhanced learning and memory and altered GABAergic synaptic transmission in mice lacking the alpha 5 subunit of the GABAA receptor. J Neurosci 22(13):5572–5580. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.22-13-05572.2002
Antonucci F, Alpár A, Kacza J, Caleo M, Verderio C, Giani A, Martens H, Chaudhry FA, Allegra M, Grosche J, Michalski D, Erck C, Hoffmann A, Harkany T, Matteoli M, Härtig W (2012) Cracking down on inhibition: selective removal of GABAergic interneurons from hippocampal networks. J Neurosci 32(6):1989–2001. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2720-11.2012
Kann O, Papageorgiou IE, Draguhn A (2014) Highly energized inhibitory interneurons are a central element for information processing in cortical networks. J Cerebral Blood Flow Metab 34(8):1270–1282. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2014.104
Chen D, Wang C, Li M, She X, Yuan Y, Chen H, Zhang W, Zhao C (2019) Loss of Foxg1 impairs the development of cortical SST-interneurons leading to abnormal emotional and social behaviors. Cerebral cortex (New Work, NY: 1991) 29(8):3666–82. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhz114
Zhang Z, Gadotti VM, Chen L, Souza IA, Stemkowski PL, Zamponi GW (2015) Role of prelimbic GABAergic circuits in sensory and emotional aspects of neuropathic pain. Cell Rep 12(5):752–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.07.001
Shao F, Fang J, Qiu M, Wang S, Xi D, Shao X, He X, Fang J, Du J (2021) Electroacupuncture ameliorates chronic inflammatory pain-related anxiety by activating PV interneurons in the anterior cingulate cortex. Front Neurosci 15:691931. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2021.691931
Cichon J, Blanck TJJ, Gan WB, Yang G (2017) Activation of cortical somatostatin interneurons prevents the development of neuropathic pain. Nat Neurosci 20(8):1122–1132. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4595
Gao R, Ji MH, Gao DP, Yang RH, Zhang SG, Yang JJ, Shen JC (2017) Neuroinflammation-induced downregulation of hippocampacal neuregulin 1-ErbB4 signaling in the parvalbumin interneurons might contribute to cognitive impairment in a mouse model of sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Inflammation 40(2):387–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0484-2
Prévot T, Sibille E (2021) Altered GABA-mediated information processing and cognitive dysfunctions in depression and other brain disorders. Mol Psychiatry 26(1):151–167. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-020-0727-3
Klausberger T, Somogyi P (2008) Neuronal diversity and temporal dynamics: the unity of hippocampal circuit operations. Science (New York, NY) 321(5885):53–57. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1149381
Jiang C, Wang X, Le Q, Liu P, Liu C, Wang Z, He G, Zheng P, Wang F, Ma L (2021) Morphine coordinates SST and PV interneurons in the prelimbic cortex to disinhibit pyramidal neurons and enhance reward. Mol Psychiatry 26(4):1178–1193. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-019-0480-7
Song YH, Yoon J, Lee SH (2021) The role of neuropeptide somatostatin in the brain and its application in treating neurological disorders. Exp Mol Med 53(3):328–338. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-021-00580-4
Rodgers FC, Zarnowska ED, Laha KT, Engin E, Zeller A, Keist R, Rudolph U, Pearce RA (2015) Etomidate impairs long-term potentiation in vitro by targeting α5-subunit containing GABAA receptors on nonpyramidal cells. J Neuroscience 35(26):9707–9716. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0315-15.2015
Lee E, Lee J, Kim E (2017) Excitation/inhibition imbalance in animal models of autism spectrum disorders. Biol Psychiat 81(10):838–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.05.011
Bast T, Pezze M, McGarrity S (2017) Cognitive deficits caused by prefrontal cortical and hippocampal neural disinhibition. Br J Pharmacol 174(19):3211–3225. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13850
Magnin E, Francavilla R, Amalyan S, Gervais E, David LS, Luo X, Topolnik L (2019) Input-specific synaptic location and function of the α5 GABA(A) receptor subunit in the mouse CA1 hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 39(5):788–801. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0567-18.2018
Mtchedlishvili Z, Lepsveridze E, Xu H, Kharlamov EA, Lu B, Kelly KM (2010) Increase of GABAA receptor-mediated tonic inhibition in dentate granule cells after traumatic brain injury. Neurobiol Dis 38(3):464–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2010.03.012
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number: 82071196), the Jiangsu Commission of Health (grant number: z201949) and the Basic Research Grant of Southeast University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xuechun Cai, Jie Sun, and Wei Zhu contributed to study design; Xuechun Cai, Jie Sun, and Wei Zhu contributed to manuscript editing; Lili Qiu, Chaoran Wang, Hang Yang, Zhenhui Zhou, Meng Mao, and Yunqing Zhu contributed to experimental studies; Xuechun Cai, Lili Qiu, Chaoran Wang, Yazhou Wen, and Wenlan Cai contributed to data analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Declarations
The experimental procedures were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Nanjing Medical University (Nanjing, China: Approval No.: IACUC- 2101035).
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
All authors consent to the publication of this manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, X., Qiu, L., Wang, C. et al. Hippocampal Inhibitory Synapsis Deficits Induced by α5-Containing GABAA Receptors Mediate Chronic Neuropathic Pain–Related Cognitive Impairment. Mol Neurobiol 59, 6049–6061 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-02955-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-02955-8