Abstract
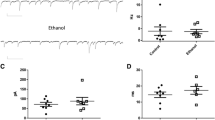
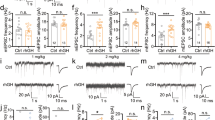
Early life alteration in the activity of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors is associated with long-lasting developmental effects on the brain and behavior. GABAA receptors act as excitatory rather than inhibitory in neonates. Excessive activation of GABAA receptors during the early postnatal period may affect cognitive functions later in life. In this study, we sought to determine whether neonatal activation of GABAA receptors with muscimol can alter the electrophysiology profile of hippocampal CA1 neurons and spatial learning and memory in adult rats. Male and female Wistar rat pups received a subcutaneous injection of either saline or muscimol (500 µg/kg) on postnatal days (PND) 7, 9, and 11 and then underwent different electrophysiology and behavioral experiments in adulthood. Early life treatment with muscimol did not alter the basic synaptic transmission but significantly reduced the paired-pulse facilitation (PPF) in the CA1 area. Neonatal application of muscimol led to a pronounced decrease in long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD) in CA1 neurons along with a declined theta-burst responses in both sexes. We obtained some evidence that neonatal GABAA activation leads to reduced brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Our electrophysiology data was supported with spatial reference and working memory deficits in rats. This study provides the first detailed description of altered electrophysiology in hippocampal CA1 neurons in adult rats undergone GABAA activation early in life.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Wang GJ, Chung HJ, Schnuer J et al (1998) Dihydrokainate-sensitive neuronal glutamate transport is required for protection of rat cortical neurons in culture against synaptically released glutamate. Eur J Neurosci 10:2523–2531
Rivera C, Voipio J, Payne JA et al (1999) The K+/Cl- co-transporter KCC2 renders GABA hyperpolarizing during neuronal maturation. Nature 397:251–255
Schulte JT, Wierenga CJ, Bruining H (2018) Chloride transporters and GABA polarity in developmental, neurological and psychiatric conditions. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 90:260–271
Pisella LI, Gaiarsa J-L, Diabira D et al (2019) Impaired regulation of KCC2 phosphorylation leads to neuronal network dysfunction and neurodevelopmental pathology. Sci Signal 15:603
Tyzio R, Holmes GL, Ben-Ari Y, Khazipov R (2007) Timing of the developmental switch in GABAA mediated signaling from excitation to inhibition in CA3 rat hippocampus using gramicidin perforated patch and extracellular recordings. Epilepsia 48:96–105
Represa A, Ben-Ari Y (2005) Trophic actions of GABA on neuronal development. Trends Neurosci 28:278–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2005.03.010
Sun B, Halabisky B, Zhou Y et al (2009) Imbalance between GABAergic and glutamatergic transmission impairs adult neurogenesis in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Stem Cell 5:624–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2009.10.003
Peerboom C, Wierenga CJ (2021) The postnatal GABA shift: a developmental perspective. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 124:179–192
Garaschuk O, Hanse E, Konnerth A (1998) Developmental profile and synaptic origin of early network oscillations in the CA1 region of rat neonatal hippocampus. J Physiol 507:219–236
Wang DD, Kriegstein AR (2008) GABA regulates excitatory synapse formation in the neocortex via NMDA receptor activation. J Neurosci 28:5547–5558
Lim AL, Taylor DA, Malone DT (2012) Consequences of early life MK-801 administration: long-term behavioural effects and relevance to schizophrenia research. Behav Brain Res 227:276–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2011.10.052
Platel JC, Stamboulian S, Nguyen I, Bordey A (2010) Neurotransmitter signaling in postnatal neurogenesis: the first leg. Brain Res Rev 63:60–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresrev.2010.02.004
Zhao YL, Xiang Q, Shi QY et al (2011) GABAergic excitotoxicity injury of the immature hippocampal pyramidal neurons exposure to isoflurane. Anesth & Analg 113:1152–1160
Sanders RD, Hassell J, Davidson AJ et al (2013) Impact of anaesthetics and surgery on neurodevelopment: an update. Br J Anaesth 110:i53–i72
Vutskits L, Xie Z (2016) Lasting impact of general anaesthesia on the brain: mechanisms and relevance. Nat Rev Neurosci 17:705–717
Satomoto M, Sun Z, Adachi YU, Makita K (2018) Neonatal sevoflurane exposure induces adulthood fear-induced learning disability and decreases glutamatergic neurons in the basolateral amygdala. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 30:59–64
Chung W, Park S, Hong J et al (2015) Sevoflurane exposure during the neonatal period induces long-term memory impairment but not autism-like behaviors. Pediatr Anesth 25:1033–1045
Tsien JZ, Huerta PT, Tonegawa S (1996) The essential role of hippocampal CA1 NMDA receptor–dependent synaptic plasticity in spatial memory. Cell 87:1327–1338
Sugar J, Moser M-B (2019) Episodic memory: neuronal codes for what, where, and when. Hippocampus 29:1190–1205
Overstreet-Wadiche LS, Bensen AL, Westbrook GL (2006) Delayed development of adult-generated granule cells in dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 26:2326–2334
Servick K (2014) Researchers struggle to gauge risks of childhood anesthesia. Science 346:1161–1162
Salari A-A, Bakhtiari A, Homberg JR (2015) Activation of GABA-A receptors during postnatal brain development increases anxiety-and depression-related behaviors in a time-and dose-dependent manner in adult mice. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 25:1260–1274
Ajayi AF, Akhigbe RE (2020) Staging of the estrous cycle and induction of estrus in experimental rodents: an update. Fertil Res Pract 6:1–15
George P, Charles W (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Qingchuan Zhuge Transl People’s Med Publ House, Beijing, p 32
Aksoy Aksel A, Manahan-Vaughan D (2013) The temporoammonic input to the hippocampal CA1 region displays distinctly different synaptic plasticity compared to the Schaffer collateral input in vivo: significance for synaptic information processing. Front Synaptic Neurosci 5:5
Babri S, Amani M, Mohaddes G et al (2012) Effect of aggregated beta-amyloid (1–42) on synaptic plasticity of hippocampal dentate gyrus granule cells in vivo. Bioimpacts 2:189–194. https://doi.org/10.5681/bi.2012.022
Amani M, Lauterborn JC, Le AA et al (2021) Rapid Aging in the Perforant Path Projections to the Rodent Dentate Gyrus. J Neurosci 41:2301–2312
Zeier Z, Kumar A, Bodhinathan K et al (2009) Fragile X mental retardation protein replacement restores hippocampal synaptic function in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome. Gene Ther 16:1122–1129
Larson J, Wong D, Lynch G (1986) Patterned stimulation at the theta frequency is optimal for the induction of hippocampal long-term potentiation. Brain Res 368:347–350
Le AA, Quintanilla J, Amani M, et al (2021) Persistent sexually dimorphic effects of adolescent THC exposure on hippocampal synaptic plasticity and episodic memory in rodents. Neurobiol Dis 162:105565
Babri S, Amani M, Mohaddes G et al (2012) Protective effects of troxerutin on β-amyloid (1–42)-induced impairments of spatial learning and memory in rats. Neurophysiology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-012-9309-6
Pasini S, Corona C, Liu J et al (2015) Specific downregulation of hippocampal ATF4 reveals a necessary role in synaptic plasticity and memory. Cell Rep 11:183–191
Hamidi N, Nozad A, Milan HS et al (2019) Effect of ceftriaxone on paired-pulse response and long-term potentiation of hippocampal dentate gyrus neurons in rats with Alzheimer-like disease. Life Sci 238:116969
Hamidi N, Nozad A, Sheikhkanloui Milan H, Amani M (2019) Okadaic acid attenuates short-term and long-term synaptic plasticity of hippocampal dentate gyrus neurons in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 158:24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2019.01.007
Mohammad A, Ali N, Reza B, Ali K (2010) Effect of ascorbic acid supplementation on nitric oxide metabolites and systolic blood pressure in rats exposed to lead. Indian J Pharmacol 42:78
Citri A, Malenka RC (2008) Synaptic plasticity: multiple forms, functions, and mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:18–41
Murata Y, Colonnese MT (2020) GABAergic interneurons excite neonatal hippocampus in vivo. Sci Adv 6:eaba1430
Galanopoulou AS (2008) Sexually dimorphic expression of KCC2 and GABA function. Epilepsy Res 80:99–113
Nuñez JL, McCarthy MM (2007) Evidence for an extended duration of GABA-mediated excitation in the developing male versus female hippocampus. Dev Neurobiol 67:1879–1890
Owens DF, Kriegstein AR (2002) Is there more to GABA than synaptic inhibition? Nat Rev Neurosci 3:715–727
Li T, Huang Z, Wang X et al (2019) Role of the GABAA receptors in the long-term cognitive impairments caused by neonatal sevoflurane exposure. Rev Neurosci 30:869–879
Sun L (2010) Early childhood general anaesthesia exposure and neurocognitive development. Br J Anaesth 105:i61–i68
Lee JH, Zhang J, Wei L, Yu SP (2015) Neurodevelopmental implications of the general anesthesia in neonate and infants. Exp Neurol 272:50–60
Gottschalk W, Pozzo-Miller LD, Figurov A, Lu B (1998) Presynaptic modulation of synaptic transmission and plasticity by brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the developing hippocampus. J Neurosci 18:6830–6839
Chen Y, Chad JE, Wheal HV (1996) Synaptic release rather than failure in the conditioning pulse results in paired-pulse facilitation during minimal synaptic stimulation in the rat hippocampal CA1 neurones. Neurosci Lett 218:204–208
Fioravante D, Regehr WG (2011) Short-term forms of presynaptic plasticity. Curr Opin Neurobiol 21:269–274
Jackman SL, Regehr WG (2017) The mechanisms and functions of synaptic facilitation. Neuron 94:447–464
Nathan T, Jensen MS, Lambert JDC (1990) GABAB receptors play a major role in paired-pulse facilitation in area CA1 of the rat hippocampus. Brain Res 531:55–65
Kubová H, Bendová Z, Moravcová S et al (2020) Neonatal clonazepam administration induced long-lasting changeS in GABAA and GABAB receptors. Int J Mol Sci 21:3184
Tyler WJ, Zhang X, Hartman K et al (2006) BDNF increases release probability and the size of a rapidly recycling vesicle pool within rat hippocampal excitatory synapses. J Physiol 574:787–803
Tyler WJ, Pozzo-Miller LD (2001) BDNF enhances quantal neurotransmitter release and increases the number of docked vesicles at the active zones of hippocampal excitatory synapses. J Neurosci 21:4249–4258
Kubová H, Bendová Z, Moravcová S et al (2018) Neonatal clonazepam administration induces long-lasting changes in glutamate receptors. Front Mol Neurosci 11:382
Sumi T, Harada K (2020) Mechanism underlying hippocampal long-term potentiation and depression based on competition between endocytosis and exocytosis of AMPA receptors. Sci Rep 10:1–14
Lee H-K, Takamiya K, Han J-S et al (2003) Phosphorylation of the AMPA receptor GluR1 subunit is required for synaptic plasticity and retention of spatial memory. Cell 112:631–643
Barria A, Malinow R (2005) NMDA receptor subunit composition controls synaptic plasticity by regulating binding to CaMKII. Neuron 48:289–301
Massey PV, Johnson BE, Moult PR et al (2004) Differential roles of NR2A and NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in cortical long-term potentiation and long-term depression. J Neurosci 24:7821–7828
Halt AR, Dallapiazza RF, Zhou Y et al (2012) CaMKII binding to GluN2B is critical during memory consolidation. EMBO J 31:1203–1216
Rex CS, Lin C-Y, Kramár EA et al (2007) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes long-term potentiation-related cytoskeletal changes in adult hippocampus. J Neurosci 27:3017–3029
Thiels E, Kanterewicz BI, Norman ED et al (2002) Long-term depression in the adult hippocampus in vivo involves activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and phosphorylation of Elk-1. J Neurosci 22:2054–2062
Chao MV (2003) Neurotrophins and their receptors: a convergence point for many signalling pathways. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:299–309
Ju L, Jia M, Sun J et al (2016) Hypermethylation of hippocampal synaptic plasticity-related genes is involved in neonatal sevoflurane exposure-induced cognitive impairments in rats. Neurotox Res 29:243–255
Baarendse PJJ, Van Grootheest G, Jansen RF et al (2008) Differential involvement of the dorsal hippocampus in passive avoidance in C57bl/6J and DBA/2J mice. Hippocampus 18:11–19
Ögren SO, Stiedl O (2010) Passive avoidance. Encycl Psychopharmacol 2:960–967
Hyman JM, Zilli EA, Paley AM, Hasselmo ME (2010) Working memory performance correlates with prefrontal-hippocampal theta interactions but not with prefrontal neuron firing rates. Front Integr Neurosci 4:2
Liu T, Bai W, Xia M, Tian X (2018) Directional hippocampal-prefrontal interactions during working memory. Behav Brain Res 338:1–8
O’Neill P-K, Gordon JA, Sigurdsson T (2013) Theta oscillations in the medial prefrontal cortex are modulated by spatial working memory and synchronize with the hippocampus through its ventral subregion. J Neurosci 33:14211–14224
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Department of Physiology and Pharmacology for their technical support.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from the Vice-Chancellor of Research of Ardabil University of Medical Sciences (GN-064).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mohammad Amani designed the study, supervised the experiments, performed the electrophysiology and data analyses, and wrote the manuscript. Forouzan Mohammadian and Nastaran Golitabari performed the behavioral experiments. Ali-Akbar Salari contributed to biochemistry and reviewed the manuscript. All authors contributed to and have approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All experimental procedures were conducted according to the guidelines for animal experimentation of the Ardabil University of Medical Sciences and animal experiments were approved by the local ethics committee (under grant GN-064).
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
All authors whose names appear on the submission agreed to the version to be published.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amani, M., Mohammadian, F., Golitabari, N. et al. Postnatal GABAA Receptor Activation Alters Synaptic Plasticity and Cognition in Adult Wistar Rats. Mol Neurobiol 59, 3585–3599 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-02805-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-02805-7