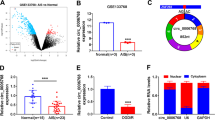
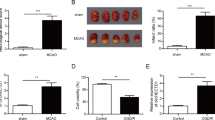
Abstract
Circ-Memo1 has been proved to be upregulated in ischemia–reperfusion induced acute injury of kidney tissues. However, the potential role of circ-Memo1 in cerebral hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) injury is still unclear.
Blood samples were collected from 25 ischemic stroke patients and 25 healthy controls. To construct the H/R model, human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMVECs) were cultured under the hypoxic condition, followed by reoxygenation. Cell viability was analyzed by MTT assay. Flow cytometry was carried out to examine cell apoptosis. The level of malondialdehyde (MDA) and the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) were measured by MDA and SOD assay kits, respectively. The levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Dual-luciferase reporter gene detection was employed to verify the binding relationships between circ-Memo1, miR-17-5p, and SOS1.
Circ-Memo1 and SOS1 expressions were increased, and miR-17-5p expression was reduced in ischemic stroke patients. Circ-Memo1 silencing promoted cell viability, inhibited the activation of ERK/NF-κB signaling pathway, reduced oxidative stress and inflammatory response, and inhibited cell apoptosis. Moreover, miR-17-5p functioned as the sponge of circ-Memo1, and SOS1 was identified as the target of miR-17-5p. The protective effect of circ-Memo1 knockdown on cell injury after H/R treatment was weakened by miR-17-5p inhibition.
Knockdown of circ-Memo1 alleviated H/R injury of HBMVEC cells by regulating the miR-17-5p/SOS1 axis, indicating that circ-Memo1 might be a potential treatment target for cerebral H/R injury.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article. The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- CircRNAs:
-
Circular RNAs long non-coding RNAs
- Circ-Memo1:
-
Circular mediator of ErbB2-driven cell motility 1
- H/R:
-
Hypoxia-reoxygenation
- IRI:
-
Ischemia-reperfusion injury
- IRS1:
-
Insulin receptor substrate 1
- HUVECs:
-
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- HBMVECs:
-
Human brain microvascular endothelial cells
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulating kinases
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-κB
- SOS1:
-
Son of Sevenless 1
- ceRNA:
-
Competing endogenous RNA
References
Behdarvandy M, Karimian M, Atlasi MA, Azami Tameh A (2020) Heat shock protein 27 as a neuroprotective biomarker and a suitable target for stem cell therapy and pharmacotherapy in ischemic stroke. Cell Biol Int 44(2):356–367. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11237
Schregel K, Behme D, Tsogkas I, Knauth M, Maier I, Karch A, Mikolajczyk R, Bähr M, Schäper J, Hinz J, Liman J, Psychogios MN (2018) Optimized management of endovascular treatment for acute ischemic stroke. Journal of visualized experiments : JoVE (131). https://doi.org/10.3791/56397
Sun MS, Jin H, Sun X, Huang S, Zhang FL, Guo ZN, Yang Y (2018) Free radical damage in ischemia-reperfusion injury: an obstacle in acute ischemic stroke after revascularization therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018:3804979. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3804979
Ma Y, Wang J, Wang Y, Yang GY (2017) The biphasic function of microglia in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol 157:247–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2016.01.005
Wang C, Wang Z, Zhang X, Zhang X, Dong L, Xing Y, Li Y, Liu Z, Chen L, Qiao H, Wang L, Zhu C (2012) Protection by silibinin against experimental ischemic stroke: up-regulated pAkt, pmTOR, HIF-1α and Bcl-2, down-regulated Bax. NF-κB expression Neuroscience letters 529(1):45–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2012.08.078
Hong KS, Ko SB, Lee JS, Yu KH, Rha JH (2015) Endovascular recanalization therapy in acute ischemic stroke: updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of stroke 17(3):268–281. https://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2015.17.3.268
Fang M, Liu S, Zhou Y, Deng Y, Yin Q, Hu L, Ouyang X, Hou Y, Chen C (2019) Circular RNA involved in the protective effect of losartan on ischemia and reperfusion induced acute kidney injury in rat model. American journal of translational research 11(2):1129–1144
Zhang P, Ming Y, Ye Q, Niu Y (2019) Comprehensive circRNA expression profile during ischemic postconditioning attenuating hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Sci Rep 9(1):264. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-36443-8
Garikipati VNS, Verma SK, Cheng Z, Liang D, Truongcao MM, Cimini M, Yue Y, Huang G, Wang C, Benedict C, Tang Y, Mallaredy V, Ibetti J, Grisanti L, Schumacher SM, Gao E, Rajan S, Wilusz JE, Goukassian D, Houser SR, Koch WJ, Kishore R (2019) Circular RNA CircFndc3b modulates cardiac repair after myocardial infarction via FUS/VEGF-A axis. Nat Commun 10(1):4317. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11777-7
Lin SP, Ye S, Long Y, Fan Y, Mao HF, Chen MT, Ma QJ (2016) Circular RNA expression alterations are involved in OGD/R-induced neuron injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 471(1):52–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.01.183
Yang B, Zang L, Cui J, Wei L (2021) Circular RNA TTC3 regulates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and neural stem cells by miR-372-3p/TLR4 axis in cerebral infarction. Stem Cell Res Ther 12(1):125. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-021-02187-y
Sorokin AV, Chen J (2013) MEMO1, a new IRS1-interacting protein, induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in mammary epithelial cells. Oncogene 32(26):3130–3138. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.327
Alamdari AF, Rahnemayan S, Rajabi H, Vahed N, Kashani HRK, Rezabakhsh A, Sanaie S (2021) Melatonin as a promising modulator of aging related neurodegenerative disorders: Role of microRNAs. Pharmacol Res 173:105839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105839
Rahbarghazi R, Keyhanmanesh R, Rezaie J, Mirershadi F, Heiran H, Saghaei Bagheri H, Saberianpour S, Rezabakhsh A, Delkhosh A, Bagheri Y, Rajabi H, Ahmadi M (2021) c-kit+ cells offer hopes in ameliorating asthmatic pathologies via regulation of miRNA-133 and miRNA-126. Iranian journal of basic medical sciences 24 (3):369–376. https://doi.org/10.22038/ijbms.2021.49008.11231
Sabet Sarvestani F, Azarpira N (2020) microRNAs alterations of myocardium and brain ischemia-reperfusion injury: insight to improve infarction. Immunological investigations:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/08820139.2020.1808672
Ma GP, Yang BZ, Zhang YS, Wang B, Wei XH, Zhang RF, Jia KH, Gao JP (2020) Protective effects of miRNA-589 on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Journal of biological regulators and homeostatic agents 34 (4):1269–1275. https://doi.org/10.23812/20-52-a
Du W, Pan Z, Chen X, Wang L, Zhang Y, Li S, Liang H, Xu C, Zhang Y, Wu Y, Shan H, Lu Y (2014) By targeting Stat3 microRNA-17-5p promotes cardiomyocyte apoptosis in response to ischemia followed by reperfusion. Cellular physiology and biochemistry : international journal of experimental cellular physiology, biochemistry, and pharmacology 34(3):955–965. https://doi.org/10.1159/000366312
Hao J, Wei Q, Mei S, Li L, Su Y, Mei C, Dong Z (2017) Induction of microRNA-17-5p by p53 protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by targeting death receptor 6. Kidney Int 91(1):106–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2016.07.017
Ren X, Jing YX, Zhou ZW, Yang QM (2020) MiR-17–5p inhibits cerebral hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by targeting PTEN through regulation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. The International journal of neuroscience:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207454.2020.1806836
Song H, Sun J, Kong W, Ji Y, Xu D, Wang J (2020) Construction of a circRNA-Related ceRNA Prognostic Regulatory Network in Breast Cancer. Onco Targets Ther 13:8347–8358. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.S266507
Chen W, Wang H, Feng J, Chen L (2020) Overexpression of circRNA circUCK2 Attenuates cell apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via miR-125b-5p/GDF11 signaling. Molecular therapy Nucleic acids 22:673–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2020.09.032
Yang X, Ji H, Yao Y, Lai X, Jiang Y, Wu D, Cai L, Zhu W, Gu X, Hu R, Li L, Xu L, Jiang M (2018) Downregulation of circ_008018 protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by targeting miR-99a. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 499(4):758–764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.218
Zhou J, Du T, Li B, Rong Y, Verkhratsky A, Peng L (2015) Crosstalk between MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signal pathways during brain ischemia/reperfusion. ASN neuro 7 (5). https://doi.org/10.1177/1759091415602463
Ali Syeda Z, Langden SSS, Munkhzul C, Lee M, Song SJ (2020) Regulatory mechanism of microRNA expression in cancer. International journal of molecular sciences 21 (5). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21051723
Li R, Li X, Wu H, Yang Z, Fei L, Zhu J (2019) Theaflavin attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by abolishing miRNA-128-3p-mediated Nrf2 inhibition and reducing oxidative stress. Mol Med Rep 20(6):4893–4904. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10755
Lan CC, Peng CK, Tang SE, Wu SY, Huang KL, Wu CP (2016) Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody suppresses ERK and NF-κB activation in ischemia-reperfusion lung injury. PLoS ONE 11(8):e0159922. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0159922
Zhang X, Chen L, Dang X, Liu J, Ito Y, Sun W (2014) Neuroprotective effects of total steroid saponins on cerebral ischemia injuries in an animal model of focal ischemia/reperfusion. Planta Med 80(8–9):637–644. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1368584
Li Q, Verma IM (2002) NF-kappaB regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2(10):725–734. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri910
Mohamed NMJJoC, Immunology C (2015) Inflammatory cytokines in neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy and their correlation with brain marker S100 protein: a case control study in Saudi Arabia. Alsulaimani et al., J Clin Cell Immunol 2015 (6:1)
Jiang M, Li J, Peng Q, Liu Y, Liu W, Luo C, Peng J, Li J, Yung KK, Mo Z (2014) Neuroprotective effects of bilobalide on cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury are associated with inhibition of pro-inflammatory mediator production and down-regulation of JNK1/2 and p38 MAPK activation. J Neuroinflammation 11:167. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-014-0167-6
De S, Dermawan JK, Stark GR (2014) EGF receptor uses SOS1 to drive constitutive activation of NFκB in cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(32):11721–11726. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1412390111
Mathivanan I, Trepp C, Brunold C, Baerlocher G, Enzmann V (2015) Retinal differentiation of human bone marrow-derived stem cells by co-culture with retinal pigment epithelium in vitro. Exp Cell Res 333(1):11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.02.001
Pierot L, Gawlitza M, Soize S (2017) Techniques for endovascular treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Revue neurologique 173(9):594–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurol.2017.09.005
Sun L, Clarke R, Bennett D, Guo Y, Walters RG, Hill M, Parish S, Millwood IY, Bian Z, Chen Y, Yu C, Lv J, Collins R, Chen J, Peto R, Li L, Chen Z (2019) Causal associations of blood lipids with risk of ischemic stroke and intracerebral hemorrhage in Chinese adults. Nat Med 25(4):569–574. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0366-x
Li X, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Zhao D, Sun C, Zhou S, Xu D, Zhao J (2020) Exosomes derived from CXCR4-overexpressing BMSC promoted activation of microvascular endothelial cells in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Plast 2020:8814239. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8814239
Nagy Z, Vastag M, Kolev K, Bori Z, Karáidi I, Skopál J (2005) Human cerebral microvessel endothelial cell culture as a model system to study the blood-brain interface in ischemic/hypoxic conditions. Cell Mol Neurobiol 25(1):201–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-004-1384-9
Jiang MM, Mai ZT, Wan SZ, Chi YM, Zhang X, Sun BH, Di QG (2018) Microarray profiles reveal that circular RNA hsa_circ_0007385 functions as an oncogene in non-small cell lung cancer tumorigenesis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 144(4):667–674. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-017-2576-2
Zhang Q, Shang M, Zhang M, Wang Y, Chen Y, Wu Y, Liu M, Song J, Liu Y (2016) Microvesicles derived from hypoxia/reoxygenation-treated human umbilical vein endothelial cells promote apoptosis and oxidative stress in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. BMC Cell Biol 17(1):25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12860-016-0100-1
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, Kjems J (2013) Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 495(7441):384–388. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11993
Ding C, Xi G, Wang G, Cui D, Zhang B, Wang H, Jiang G, Song J, Xu G, Wang J (2020) Exosomal Circ-MEMO1 promotes the progression and aerobic glycolysis of non-small cell lung cancer through targeting MiR-101-3p/KRAS Axis. Front Genet 11:962. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.00962
Sawe N, Steinberg G, Zhao H (2008) Dual roles of the MAPK/ERK1/2 cell signaling pathway after stroke. J Neurosci Res 86(8):1659–1669. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.21604
Oeztuerk-Winder F, Guinot A, Ochalek A, Ventura JJ (2012) Regulation of human lung alveolar multipotent cells by a novel p38α MAPK/miR-17-92 axis. EMBO J 31(16):3431–3441. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2012.192
Tan J, Liu D, Lv X, Wang L, Zhao C, Che Y, Xie Q, Cui X (2013) MAPK mediates inflammatory response and cell death in rat pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells in an ischemia-reperfusion model of lung transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 32(8):823–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2013.05.005
Li W, Suwanwela NC, Patumraj S (2017) Curcumin prevents reperfusion injury following ischemic stroke in rats via inhibition of NF-κB, ICAM-1, MMP-9 and caspase-3 expression. Mol Med Rep 16(4):4710–4720. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.7205
Holdt LM, Kohlmaier A, Teupser D (2018) Molecular functions and specific roles of circRNAs in the cardiovascular system. Non-coding RNA research 3(2):75–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncrna.2018.05.002
Nakagawa N, Plestant C, Yabuno-Nakagawa K, Li J, Lee J, Huang CW, Lee A, Krupa O, Adhikari A, Thompson S, Rhynes T, Arevalo V, Stein JL, Molnár Z, Badache A, Anton ES (2019) Memo1-mediated tiling of radial glial cells facilitates cerebral cortical development. Neuron 103(5):836-852.e835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2019.05.049
Van Otterloo E, Feng W, Jones KL, Hynes NE, Clouthier DE, Niswander L, Williams T (2016) MEMO1 drives cranial endochondral ossification and palatogenesis. Dev Biol 415(2):278–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.12.024
Acknowledgements
We would like to give our sincere gratitude to the reviewers for their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and study design: XR.
Data acquisition: XR and YXJ.
Data analysis: ZWZ.
Funding acquisition: XR.
Manuscript drafting: XR and JWY.
Manuscript revising: XR.
All authors have read and approved the final version of this manuscript to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
The experiment of this work was approved by the Ethics Committee of Hunan Provincial People’s Hospital.
Consent to Participate
All the subjects and their families agreed to enter the study and signed the informed consent form.
Consent for Publication
All the subjects and their families agreed to enter the study and signed the informed consent form.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, X., Jing, YX., Zhou, ZW. et al. Knockdown of circRNA-Memo1 Reduces Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury in Human Brain Endothelial Cells Through miRNA-17-5p/SOS1 Axis. Mol Neurobiol 59, 2085–2097 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-02743-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-022-02743-4