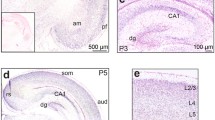
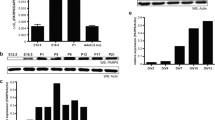
Abstract
Proper dendrite development is essential for establishing neural circuitry, and Rho GTPases play key regulatory roles in this process. From mouse brain lysates, we identified Brefeldin A-inhibited guanine exchange factor 2 (BIG2) as a novel Rho GTPase regulatory protein involved in dendrite growth and maintenance. BIG2 was highly expressed during early development, and knockdown of the ARFGEF2 gene encoding BIG2 significantly reduced total dendrite length and the number of branches. Expression of the constitutively active ADP-ribosylation factor 1 ARF1 Q71L rescued the defective dendrite morphogenesis of ARFGEF2-null neurons, indicating that BIG2 controls dendrite growth and maintenance by activating ARF1. Moreover, BIG2 co-localizes with the Golgi apparatus and is required for Golgi deployment into major dendrites in cultured hippocampal neurons. Simultaneous overexpression of BIG2 and ARF1 activated RhoA, and treatment with the RhoA activator lysophosphatidic acid in neurons lacking BIG2 or ARF1 increased the number of cells with dendritic Golgi, suggesting that BIG2 and ARF1 activate RhoA to promote dendritic Golgi polarization. mDia1 was identified as a downstream effector of BIG2-ARF1-RhoA axis, mediating Golgi polarization and dendritic morphogenesis. Furthermore, in utero electroporation of ARFGEF2 shRNA into the embryonic mouse brain confirmed an in vivo role of BIG2 for Golgi deployment into the apical dendrite. Taken together, our results suggest that BIG2-ARF1-RhoA-mDia1 signaling regulates dendritic Golgi polarization and dendrite growth and maintenance in hippocampal neurons.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arimura N, Kaibuchi K (2007) Neuronal polarity: from extracellular signals to intracellular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci 8(3):194–205. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2056
Dehmelt L, Smart FM, Ozer RS, Halpain S (2003) The role of microtubule-associated protein 2c in the reorganization of microtubules and lamellipodia during neurite initiation. J Neurosci 23(29):9479–9490
Govek EE, Newey SE, Van Aelst L (2005) The role of the Rho GTPases in neuronal development. Genes Dev 19(1):1–49. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1256405
Luo L (2000) Rho GTPases in neuronal morphogenesis. Nat Rev Neurosci 1(3):173–180. https://doi.org/10.1038/35044547
Polishchuk RS, Mironov AA (2004) Structural aspects of Golgi function. Cell Mol Life Sci 61(2):146–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-003-3353-8
Linstedt AD (2004) Positioning the Golgi apparatus. Cell 118(3):271–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.07.015
Matsuki T, Matthews RT, Cooper JA, van der Brug MP, Cookson MR, Hardy JA, Olson EC, Howell BW (2010) Reelin and stk25 have opposing roles in neuronal polarization and dendritic Golgi deployment. Cell 143(5):826–836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.10.029
Meseke M, Rosenberger G, Forster E (2013) Reelin and the Cdc42/Rac1 guanine nucleotide exchange factor alphaPIX/Arhgef6 promote dendritic Golgi translocation in hippocampal neurons. Eur J Neurosci 37(9):1404–1412. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.12153
Nichols AJ, Olson EC (2010) Reelin promotes neuronal orientation and dendritogenesis during preplate splitting. Cereb Cortex 20(9):2213–2223. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhp303
O'Dell RS, Ustine CJ, Cameron DA, Lawless SM, Williams RM, Zipfel WR, Olson EC (2012) Layer 6 cortical neurons require Reelin-Dab1 signaling for cellular orientation, Golgi deployment, and directed neurite growth into the marginal zone. Neural Dev 7:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/1749-8104-7-25
Chen C, Wirth A, Ponimaskin E (2012) Cdc42: an important regulator of neuronal morphology. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44(3):447–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2011.11.022
Leemhuis J, Bouche E, Frotscher M, Henle F, Hein L, Herz J, Meyer DK, Pichler M et al (2010) Reelin signals through apolipoprotein E receptor 2 and Cdc42 to increase growth cone motility and filopodia formation. J Neurosci 30(44):14759–14772. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4036-10.2010
Dubois T, Paleotti O, Mironov AA, Fraisier V, Stradal TE, De Matteis MA, Franco M, Chavrier P (2005) Golgi-localized GAP for Cdc42 functions downstream of ARF1 to control Arp2/3 complex and F-actin dynamics. Nat Cell Biol 7(4):353–364. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1244
Quassollo G, Wojnacki J, Salas DA, Gastaldi L, Marzolo MP, Conde C, Bisbal M, Couve A et al (2015) A RhoA signaling pathway regulates dendritic Golgi outpost formation. Curr Biol 25(8):971–982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2015.01.075
Islam A, Shen X, Hiroi T, Moss J, Vaughan M, Levine SJ (2007) The brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein, BIG2, regulates the constitutive release of TNFR1 exosome-like vesicles. J Biol Chem 282(13):9591–9599. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M607122200
Ishizaki R, Shin HW, Mitsuhashi H, Nakayama K (2008) Redundant roles of BIG2 and BIG1, guanine-nucleotide exchange factors for ADP-ribosylation factors in membrane traffic between the trans-Golgi network and endosomes. Mol Biol Cell 19(6):2650–2660. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E07-10-1067
Manolea F, Claude A, Chun J, Rosas J, Melancon P (2008) Distinct functions for Arf guanine nucleotide exchange factors at the Golgi complex: GBF1 and BIGs are required for assembly and maintenance of the Golgi stack and trans-Golgi network, respectively. Mol Biol Cell 19(2):523–535. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E07-04-0394
Mansour SJ, Skaug J, Zhao XH, Giordano J, Scherer SW, Melancon P (1999) p200 ARF-GEP1: a Golgi-localized guanine nucleotide exchange protein whose Sec7 domain is targeted by the drug brefeldin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96(14):7968–7973
Shen X, Xu KF, Fan Q, Pacheco-Rodriguez G, Moss J, Vaughan M (2006) Association of brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein 2 (BIG2) with recycling endosomes during transferrin uptake. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(8):2635–2640. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0510599103
Shin HW, Nakayama K (2004) Guanine nucleotide-exchange factors for arf GTPases: their diverse functions in membrane traffic. J Biochem 136(6):761–767. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvh185
Yamaji R, Adamik R, Takeda K, Togawa A, Pacheco-Rodriguez G, Ferrans VJ, Moss J, Vaughan M (2000) Identification and localization of two brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange proteins for ADP-ribosylation factors in a macromolecular complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(6):2567–2572
Zhang J, Neal J, Lian G, Hu J, Lu J, Sheen V (2013) Filamin A regulates neuronal migration through brefeldin A-inhibited guanine exchange factor 2-dependent Arf1 activation. J Neurosci 33(40):15735–15746. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1939-13.2013
Zhang J, Neal J, Lian G, Shi B, Ferland RJ, Sheen V (2012) Brefeldin A-inhibited guanine exchange factor 2 regulates filamin A phosphorylation and neuronal migration. J Neurosci 32(36):12619–12629. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1063-12.2012
Fox JW, Lamperti ED, Eksioglu YZ, Hong SE, Feng Y, Graham DA, Scheffer IE, Dobyns WB et al (1998) Mutations in filamin 1 prevent migration of cerebral cortical neurons in human periventricular heterotopia. Neuron 21(6):1315–1325
Sheen VL, Jansen A, Chen MH, Parrini E, Morgan T, Ravenscroft R, Ganesh V, Underwood T et al (2005) Filamin A mutations cause periventricular heterotopia with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Neurology 64(2):254–262. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.WNL.0000149512.79621.DF
Li MZ, Elledge SJ (2012) SLIC: a method for sequence- and ligation-independent cloning. Methods Mol Biol 852:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-564-0_5
Tabata H, Nakajima K (2001) Efficient in utero gene transfer system to the developing mouse brain using electroporation: visualization of neuronal migration in the developing cortex. Neuroscience 103(4):865–872
Sheen VL, Topcu M, Berkovic S, Yalnizoglu D, Blatt I, Bodell A, Hill RS, Ganesh VS et al (2003) Autosomal recessive form of periventricular heterotopia. Neurology 60(7):1108–1112
Gillingham AK, Munro S (2007) The small G proteins of the Arf family and their regulators. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 23:579–611. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.23.090506.123209
Popoff V, Langer JD, Reckmann I, Hellwig A, Kahn RA, Brugger B, Wieland FT (2011) Several ADP-ribosylation factor (Arf) isoforms support COPI vesicle formation. J Biol Chem 286(41):35634–35642. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.261800
Horton AC, Racz B, Monson EE, Lin AL, Weinberg RJ, Ehlers MD (2005) Polarized secretory trafficking directs cargo for asymmetric dendrite growth and morphogenesis. Neuron 48(5):757–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2005.11.005
Sheen VL, Ganesh VS, Topcu M, Sebire G, Bodell A, Hill RS, Grant PE, Shugart YY et al (2004) Mutations in ARFGEF2 implicate vesicle trafficking in neural progenitor proliferation and migration in the human cerebral cortex. Nat Genet 36(1):69–76. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1276
Shin HW, Morinaga N, Noda M, Nakayama K (2004) BIG2, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for ADP-ribosylation factors: its localization to recycling endosomes and implication in the endosome integrity. Mol Biol Cell 15(12):5283–5294. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E04-05-0388
Donaldson JG, Honda A, Weigert R (2005) Multiple activities for Arf1 at the Golgi complex. Biochim Biophys Acta 1744(3):364–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2005.03.001
Charych EI, Yu W, Miralles CP, Serwanski DR, Li X, Rubio M, De Blas AL (2004) The brefeldin A-inhibited GDP/GTP exchange factor 2, a protein involved in vesicular trafficking, interacts with the beta subunits of the GABA receptors. J Neurochem 90(1):173–189. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02481.x
Ren XD, Kiosses WB, Schwartz MA (1999) Regulation of the small GTP-binding protein Rho by cell adhesion and the cytoskeleton. EMBO J 18(3):578–585. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/18.3.578
Callow MG, Zozulya S, Gishizky ML, Jallal B, Smeal T (2005) PAK4 mediates morphological changes through the regulation of GEF-H1. J Cell Sci 118(Pt 9):1861–1872. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.02313
Pathak R, Dermardirossian C (2013) GEF-H1: orchestrating the interplay between cytoskeleton and vesicle trafficking. Small GTPases 4(3):174–179. https://doi.org/10.4161/sgtp.24616
Nalbant P, Chang YC, Birkenfeld J, Chang ZF, Bokoch GM (2009) Guanine nucleotide exchange factor-H1 regulates cell migration via localized activation of RhoA at the leading edge. Mol Biol Cell 20(18):4070–4082. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E09-01-0041
Kang MG, Guo Y, Huganir RL (2009) AMPA receptor and GEF-H1/Lfc complex regulates dendritic spine development through RhoA signaling cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(9):3549–3554. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0812861106
Zilberman Y, Alieva NO, Miserey-Lenkei S, Lichtenstein A, Kam Z, Sabanay H, Bershadsky A (2011) Involvement of the Rho-mDia1 pathway in the regulation of Golgi complex architecture and dynamics. Mol Biol Cell 22(16):2900–2911. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E11-01-0007
Horton AC, Ehlers MD (2003) Neuronal polarity and trafficking. Neuron 40(2):277–295
Frotscher M (1998) Cajal-Retzius cells, Reelin, and the formation of layers. Curr Opin Neurobiol 8(5):570–575
Ori-McKenney KM, Jan LY, Jan YN (2012) Golgi outposts shape dendrite morphology by functioning as sites of acentrosomal microtubule nucleation in neurons. Neuron 76(5):921–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2012.10.008
Horton AC, Ehlers MD (2004) Secretory trafficking in neuronal dendrites. Nat Cell Biol 6(7):585–591. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb0704-585
Bando Y, Irie K, Shimomura T, Umeshima H, Kushida Y, Kengaku M, Fujiyoshi Y, Hirano T et al (2016) Control of spontaneous Ca2+ transients is critical for neuronal maturation in the developing neocortex. Cereb Cortex 26(1):106–117. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhu180
Guerrier S, Coutinho-Budd J, Sassa T, Gresset A, Jordan NV, Chen K, Jin WL, Frost A et al (2009) The F-BAR domain of srGAP2 induces membrane protrusions required for neuronal migration and morphogenesis. Cell 138(5):990–1004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.06.047
Gupta A, Sanada K, Miyamoto DT, Rovelstad S, Nadarajah B, Pearlman AL, Brunstrom J, Tsai LH (2003) Layering defect in p35 deficiency is linked to improper neuronal-glial interaction in radial migration. Nat Neurosci 6(12):1284–1291. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1151
Ohshima T, Hirasawa M, Tabata H, Mutoh T, Adachi T, Suzuki H, Saruta K, Iwasato T et al (2007) Cdk5 is required for multipolar-to-bipolar transition during radial neuronal migration and proper dendrite development of pyramidal neurons in the cerebral cortex. Development 134(12):2273–2282. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.02854
Hoshiba Y, Toda T, Ebisu H, Wakimoto M, Yanagi S, Kawasaki H (2016) Sox11 balances dendritic morphogenesis with neuronal migration in the developing cerebral cortex. J Neurosci 36(21):5775–5784. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3250-15.2016
O'Dell RS, Cameron DA, Zipfel WR, Olson EC (2015) Reelin prevents apical neurite retraction during terminal translocation and dendrite initiation. J Neurosci 35(30):10659–10674. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1629-15.2015
Bottanelli F, Kilian N, Ernst AM, Rivera-Molina F, Schroeder LK, Kromann EB, Lessard MD, Erdmann RS et al (2017) A novel physiological role for ARF1 in the formation of bidirectional tubules from the Golgi. Mol Biol Cell 28(12):1676–1687. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E16-12-0863
Watanabe N, Madaule P, Reid T, Ishizaki T, Watanabe G, Kakizuka A, Saito Y, Nakao K et al (1997) p140mDia, a mammalian homolog of drosophila diaphanous, is a target protein for Rho small GTPase and is a ligand for profilin. EMBO J 16(11):3044–3056. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/16.11.3044
Ishizaki T, Morishima Y, Okamoto M, Furuyashiki T, Kato T, Narumiya S (2001) Coordination of microtubules and the actin cytoskeleton by the Rho effector mDia1. Nat Cell Biol 3(1):8–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/35050598
Riento K, Ridley AJ (2003) Rocks: multifunctional kinases in cell behaviour. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4(6):446–456. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1128
Chesarone MA, DuPage AG, Goode BL (2010) Unleashing formins to remodel the actin and microtubule cytoskeletons. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11(1):62–74. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2816
Wehland J, Henkart M, Klausner R, Sandoval IV (1983) Role of microtubules in the distribution of the Golgi apparatus: effect of taxol and microinjected anti-alpha-tubulin antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 80(14):4286–4290
Thyberg J, Moskalewski S (1999) Role of microtubules in the organization of the Golgi complex. Exp Cell Res 246(2):263–279. https://doi.org/10.1006/excr.1998.4326
Miller PM, Folkmann AW, Maia AR, Efimova N, Efimov A, Kaverina I (2009) Golgi-derived CLASP-dependent microtubules control Golgi organization and polarized trafficking in motile cells. Nat Cell Biol 11(9):1069–1080. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1920
Lewkowicz E, Herit F, Le Clainche C, Bourdoncle P, Perez F, Niedergang F (2008) The microtubule-binding protein CLIP-170 coordinates mDia1 and actin reorganization during CR3-mediated phagocytosis. J Cell Biol 183(7):1287–1298. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200807023
Rosales-Nieves AE, Johndrow JE, Keller LC, Magie CR, Pinto-Santini DM, Parkhurst SM (2006) Coordination of microtubule and microfilament dynamics by drosophila Rho1, spire and cappuccino. Nat Cell Biol 8(4):367–376. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1385
Martin SG, McDonald WH, Yates JR 3rd, Chang F (2005) Tea4p links microtubule plus ends with the formin for3p in the establishment of cell polarity. Dev Cell 8(4):479–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2005.02.008
Coles CH, Bradke F (2015) Coordinating neuronal actin-microtubule dynamics. Curr Biol 25(15):R677–R691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2015.06.020
Salmon WC, Adams MC, Waterman-Storer CM (2002) Dual-wavelength fluorescent speckle microscopy reveals coupling of microtubule and actin movements in migrating cells. J Cell Biol 158(1):31–37. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200203022
Henty-Ridilla JL, Rankova A, Eskin JA, Kenny K, Goode BL (2016) Accelerated actin filament polymerization from microtubule plus ends. Science 352(6288):1004–1009. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf1709
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Keith Burridge at University of North Carolina for GST-tagged RhoA, Rac1, and Cdc42 mutant DNAs, Dr. Myeong-Gu Kang at Institute of Basic Science for GEF-H1 shRNA, and Dr. Naoki Watanabe at Kyoto University for mDia1 plasmids. This study was supported by Chungnam National University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Chungnam National University, Korea and carried out in accordance with guidelines for laboratory animal care.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Online Resource 1
(PPTX 1.75 mb)
Online Resource 2
(PPTX 112 kb)
Online Resource 3
(PPTX 94.3 kb)
Online Resource 4
(PPTX 252 kb)
Online Resource 5
(PPTX 232 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, EH., Kim, JY., Kim, JH. et al. BIG2-ARF1-RhoA-mDia1 Signaling Regulates Dendritic Golgi Polarization in Hippocampal Neurons. Mol Neurobiol 55, 7701–7716 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-0954-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-0954-7